What is Global Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Market?
The Global Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Market is a critical component of the energy sector, focusing on the handling, processing, and disposal of nuclear materials. This market encompasses a wide range of activities, from the production and supply of nuclear fuel to the management of radioactive waste generated by nuclear power plants and other nuclear-related activities. The primary goal is to ensure the safe and efficient use of nuclear energy while minimizing the environmental impact of nuclear waste. This involves sophisticated technologies and processes to handle both the front-end and back-end of the nuclear fuel cycle. The market is driven by the increasing demand for clean energy, as nuclear power is considered a low-carbon energy source. However, it also faces challenges such as regulatory hurdles, public perception, and the high costs associated with waste management and disposal. As countries strive to balance energy needs with environmental concerns, the Global Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Market plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of sustainable energy.
Near Surface Proposal, Deep Geological Proposal in the Global Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Market:
In the realm of nuclear waste management, two primary strategies are employed: Near Surface Disposal and Deep Geological Disposal. Near Surface Disposal involves placing waste in facilities that are constructed close to the earth's surface. This method is typically used for low-level radioactive waste, which includes materials like contaminated clothing, tools, and other items that have been exposed to radiation but do not pose a significant long-term hazard. These facilities are designed to contain and isolate the waste for a period that is sufficient to allow the radioactivity to decay to safe levels. The advantage of Near Surface Disposal is its relatively low cost and ease of access for monitoring and maintenance. However, it is not suitable for high-level waste, which remains hazardous for much longer periods. On the other hand, Deep Geological Disposal is considered the most viable solution for high-level radioactive waste, such as spent nuclear fuel and waste from nuclear reactors. This method involves burying the waste deep underground in stable geological formations, often several hundred meters below the surface. The idea is to isolate the waste from the biosphere for thousands of years, allowing the radioactivity to diminish to safe levels. Deep Geological Disposal facilities are designed to withstand natural disasters, geological changes, and human intrusion, ensuring the long-term safety of the environment and public health. The construction and maintenance of these facilities are complex and costly, requiring extensive research and planning to identify suitable sites and develop robust containment systems. Both disposal methods are integral to the Global Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Market, addressing different types of waste and ensuring that nuclear energy remains a viable and sustainable option for the future. The choice between Near Surface and Deep Geological Disposal depends on the nature of the waste, regulatory requirements, and public acceptance. As the demand for nuclear energy grows, so does the need for effective waste management solutions that can address the challenges of safety, environmental protection, and cost. The development and implementation of these disposal methods are crucial for the continued expansion of the nuclear energy sector and the reduction of its environmental footprint.
Industrial, Public Utilities in the Global Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Market:
The Global Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Market plays a significant role in various sectors, particularly in industrial applications and public utilities. In the industrial sector, nuclear energy is used for a wide range of applications, from power generation to medical and scientific research. Industries rely on nuclear power for its ability to provide a stable and reliable source of energy, which is essential for operations that require continuous power supply. The management of nuclear fuel and waste is crucial in this context, as it ensures the safe and efficient use of nuclear materials, minimizing the risk of accidents and environmental contamination. Industrial facilities must adhere to strict regulations and standards for the handling and disposal of nuclear waste, which involves sophisticated technologies and processes to ensure safety and compliance. Public utilities, on the other hand, are major consumers of nuclear energy, using it to generate electricity for residential, commercial, and industrial use. Nuclear power plants are a key component of the energy mix for many countries, providing a significant portion of the electricity supply. The management of nuclear fuel and waste is a critical aspect of the operation of these plants, as it involves the handling of spent fuel and other radioactive materials. Public utilities must implement robust waste management strategies to ensure the safe disposal of nuclear waste, protecting the environment and public health. This includes the use of advanced technologies for the storage, transportation, and disposal of waste, as well as ongoing monitoring and maintenance to prevent leaks and contamination. The Global Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Market is essential for the continued growth and sustainability of both industrial applications and public utilities. As the demand for clean and reliable energy increases, so does the need for effective waste management solutions that can address the challenges of safety, environmental protection, and cost. The development and implementation of these solutions are crucial for the continued expansion of the nuclear energy sector and the reduction of its environmental footprint. By ensuring the safe and efficient management of nuclear fuel and waste, the market supports the sustainable use of nuclear energy, contributing to the global efforts to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change.
Global Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Market Outlook:
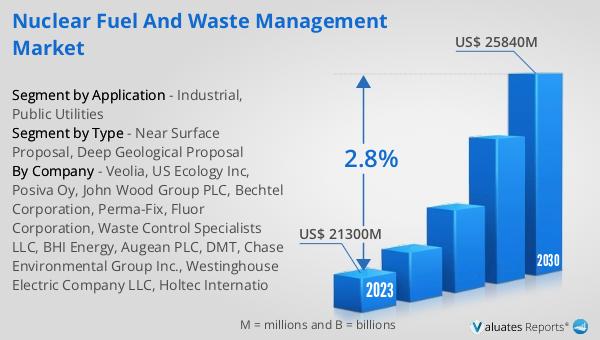
The worldwide market for Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management was estimated to be worth $22,450 million in 2024. It is anticipated to grow to a revised size of $27,160 million by 2031, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.8% during the forecast period. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for clean and sustainable energy sources, as nuclear power is considered a low-carbon alternative to fossil fuels. The market's expansion is also supported by advancements in technology and the development of new waste management solutions that enhance the safety and efficiency of nuclear operations. However, the market faces challenges such as regulatory hurdles, public perception, and the high costs associated with waste management and disposal. Despite these challenges, the Global Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Market is poised for growth, as countries around the world continue to invest in nuclear energy as part of their efforts to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. The market's outlook is positive, with opportunities for innovation and development in the areas of waste disposal, recycling, and storage. As the market evolves, it will play a crucial role in shaping the future of sustainable energy and the global transition to a low-carbon economy.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 22450 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 27160 million |
| CAGR | 2.8% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| by Type |
|
| by Application |
|
| Production by Region |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Veolia, US Ecology Inc, Posiva Oy, John Wood Group PLC, Bechtel Corporation, Perma-Fix, Fluor Corporation, Waste Control Specialists LLC, BHI Energy, Augean PLC, DMT, Chase Environmental Group Inc., Westinghouse Electric Company LLC, Holtec Internatio |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |