What is Global Low-Carbon Aviation Fuel Market?
The Global Low-Carbon Aviation Fuel Market is an emerging sector focused on reducing the carbon footprint of the aviation industry. This market revolves around the development and utilization of alternative fuels that emit significantly less carbon dioxide compared to traditional fossil fuels. The aviation industry is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, and with increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures, there is a growing demand for sustainable aviation solutions. Low-carbon aviation fuels are derived from renewable resources such as plant-based materials and waste products, making them a more environmentally friendly option. These fuels not only help in reducing emissions but also enhance energy security by diversifying the fuel supply. The market is driven by technological advancements, government incentives, and the aviation industry's commitment to achieving carbon-neutral growth. As the world moves towards a more sustainable future, the Global Low-Carbon Aviation Fuel Market is expected to play a crucial role in transforming the aviation sector into a more eco-friendly industry.
Plants-based, Waste-based in the Global Low-Carbon Aviation Fuel Market:
In the Global Low-Carbon Aviation Fuel Market, plant-based and waste-based fuels are two primary categories that are gaining traction. Plant-based fuels, also known as biofuels, are derived from organic materials such as crops, algae, and other plant matter. These fuels are produced through processes like fermentation and transesterification, which convert the organic material into usable fuel. One of the main advantages of plant-based fuels is their renewability, as they can be replenished through agricultural practices. Additionally, they have the potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, as the carbon dioxide absorbed by the plants during their growth offsets the emissions produced during fuel combustion. However, the production of plant-based fuels can be resource-intensive, requiring large amounts of land, water, and energy. This has led to concerns about their impact on food security and land use. On the other hand, waste-based fuels are produced from various waste materials, including municipal solid waste, agricultural residues, and industrial by-products. These fuels are often referred to as second-generation biofuels, as they do not compete with food crops for resources. Waste-based fuels offer a sustainable solution by utilizing materials that would otherwise contribute to landfill waste and environmental pollution. The production process for waste-based fuels typically involves advanced technologies such as gasification and pyrolysis, which convert waste materials into synthetic fuels. These fuels have a lower carbon footprint compared to traditional fossil fuels and can be used in existing aircraft engines without significant modifications. However, the collection and processing of waste materials can be challenging, requiring efficient logistics and infrastructure. Both plant-based and waste-based fuels have their own set of advantages and challenges. Plant-based fuels are more established in the market, with several commercial flights already using biofuels as part of their fuel mix. However, the scalability of plant-based fuels is limited by the availability of feedstock and the competition for agricultural resources. Waste-based fuels, while still in the early stages of development, offer a promising alternative with their potential to utilize abundant waste materials. The success of waste-based fuels depends on advancements in technology and the establishment of efficient supply chains. The Global Low-Carbon Aviation Fuel Market is witnessing increased collaboration between governments, research institutions, and private companies to overcome these challenges and promote the adoption of sustainable fuels. Governments are providing incentives and funding for research and development, while airlines are entering into partnerships with fuel producers to secure a steady supply of low-carbon fuels. The market is also seeing innovations in fuel production technologies, such as the use of genetically modified organisms to enhance the efficiency of biofuel production. As the market continues to evolve, the focus is on achieving a balance between environmental sustainability, economic viability, and energy security. In conclusion, plant-based and waste-based fuels are integral components of the Global Low-Carbon Aviation Fuel Market. While plant-based fuels offer a renewable and established option, waste-based fuels present a sustainable solution with the potential to utilize abundant waste materials. Both types of fuels face challenges related to scalability, resource availability, and technological advancements. However, with continued research, collaboration, and innovation, the market is poised to make significant strides towards reducing the aviation industry's carbon footprint and achieving a more sustainable future.
Civil Aircraft, Military Aircraft in the Global Low-Carbon Aviation Fuel Market:
The usage of Global Low-Carbon Aviation Fuel Market in civil and military aircraft is a significant step towards reducing the aviation industry's environmental impact. In civil aviation, low-carbon fuels are being increasingly adopted by commercial airlines to meet regulatory requirements and consumer demand for sustainable travel options. Airlines are incorporating these fuels into their operations to reduce their carbon emissions and improve their environmental credentials. The use of low-carbon fuels in civil aircraft not only helps in achieving emission reduction targets but also enhances the airline's brand image as a responsible and environmentally conscious company. Moreover, the adoption of sustainable fuels can lead to cost savings in the long run, as airlines can benefit from government incentives and avoid potential carbon taxes. In military aviation, the use of low-carbon fuels is driven by the need for energy security and operational efficiency. Military aircraft are significant consumers of aviation fuel, and the adoption of sustainable fuels can help reduce the military's reliance on fossil fuels and enhance its energy independence. Low-carbon fuels offer a strategic advantage by providing a more stable and diversified fuel supply, reducing the risk of supply disruptions. Additionally, the use of sustainable fuels aligns with the military's commitment to reducing its environmental footprint and promoting sustainability. The adoption of low-carbon fuels in military aircraft also supports the development of advanced technologies and fuels that can be used in both military and civilian applications. The transition to low-carbon fuels in both civil and military aviation is not without challenges. The availability and cost of sustainable fuels remain significant barriers to widespread adoption. The production of low-carbon fuels is still in its early stages, and the supply chain infrastructure is not yet fully developed. Additionally, the performance and safety of these fuels need to be thoroughly tested and validated to ensure they meet the stringent requirements of the aviation industry. Despite these challenges, the aviation industry is making significant progress in adopting low-carbon fuels, with several airlines and military organizations conducting successful test flights and pilot programs. In conclusion, the usage of Global Low-Carbon Aviation Fuel Market in civil and military aircraft is a crucial step towards achieving a more sustainable aviation industry. The adoption of low-carbon fuels in civil aviation helps airlines meet regulatory requirements, improve their environmental credentials, and achieve cost savings. In military aviation, sustainable fuels enhance energy security, reduce reliance on fossil fuels, and support the development of advanced technologies. While challenges remain, the aviation industry is making significant strides in adopting low-carbon fuels, driven by regulatory pressures, consumer demand, and the commitment to sustainability. As the market continues to evolve, the focus is on overcoming these challenges and achieving a more sustainable future for the aviation industry.
Global Low-Carbon Aviation Fuel Market Outlook:
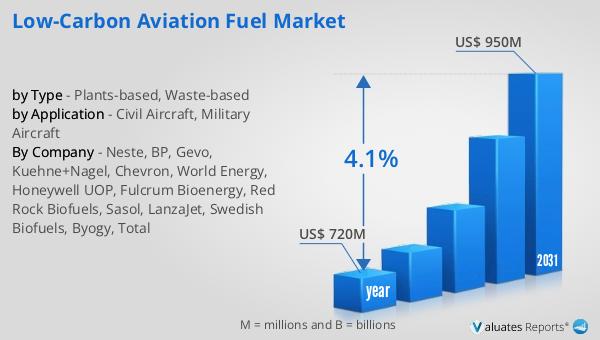
The global market for Low-Carbon Aviation Fuel was valued at approximately $720 million in 2024, and it is anticipated to grow to an estimated $950 million by 2031. This growth represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.1% over the forecast period. The increasing demand for sustainable aviation solutions, driven by environmental concerns and regulatory pressures, is a key factor contributing to this market growth. As the aviation industry seeks to reduce its carbon footprint and achieve carbon-neutral growth, the adoption of low-carbon fuels is becoming increasingly important. The market is also benefiting from technological advancements, government incentives, and collaborations between airlines and fuel producers. These factors are helping to drive the development and commercialization of low-carbon fuels, making them a viable alternative to traditional fossil fuels. As the market continues to expand, it is expected to play a crucial role in transforming the aviation industry into a more sustainable and environmentally friendly sector.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Low-Carbon Aviation Fuel Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 720 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 950 million |
| CAGR | 4.1% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| by Type |
|
| by Application |
|
| Production by Region |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Neste, BP, Gevo, Kuehne+Nagel, Chevron, World Energy, Honeywell UOP, Fulcrum Bioenergy, Red Rock Biofuels, Sasol, LanzaJet, Swedish Biofuels, Byogy, Total |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
