What is Global Bioplastics for Food Package Market?
Global bioplastics for the food package market represent a transformative shift in how we approach packaging materials, particularly in the food industry. Bioplastics are derived from renewable biomass sources, such as vegetable fats, oils, corn starch, or microbiota, unlike conventional plastics, which are petroleum-based. This market is gaining traction due to increasing environmental concerns and the push for sustainable alternatives. Bioplastics offer the advantage of being biodegradable or compostable, reducing the environmental footprint of packaging waste. In the food packaging sector, bioplastics are used to create both rigid and flexible packaging solutions, ensuring food safety while minimizing environmental impact. The market is driven by consumer demand for eco-friendly products, regulatory pressures to reduce plastic waste, and technological advancements that improve the performance and cost-effectiveness of bioplastics. As awareness grows and technology advances, the global bioplastics for food package market is poised for significant growth, offering a sustainable solution to the pressing issue of plastic pollution. This shift not only benefits the environment but also aligns with the values of increasingly eco-conscious consumers, making it a critical area of focus for businesses in the food packaging industry.
Polylactic Acid (PLA), Biobased-PE, Biobased-PET, Other in the Global Bioplastics for Food Package Market:
Polylactic Acid (PLA), Biobased-PE, Biobased-PET, and other bioplastics are pivotal components of the global bioplastics for food package market, each offering unique properties and benefits. Polylactic Acid (PLA) is one of the most widely used bioplastics, derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane. PLA is favored for its compostability and is often used in applications such as food containers, cups, and bottles. It is transparent and has similar properties to conventional plastics like PET, making it a versatile choice for various packaging needs. However, PLA's performance can be limited by its lower thermal resistance, which restricts its use in high-temperature applications. Biobased-PE, or polyethylene, is another significant player in the bioplastics market. It is produced from bioethanol derived from sugarcane or other biomass sources. Biobased-PE retains the properties of traditional polyethylene, such as flexibility and durability, but with a reduced carbon footprint. This makes it suitable for a wide range of packaging applications, including films, bags, and bottles. Its recyclability further enhances its appeal as a sustainable packaging solution. Biobased-PET, or polyethylene terephthalate, is similar to its fossil-based counterpart but is partially derived from renewable resources. It is commonly used in beverage bottles and food containers due to its strength, clarity, and barrier properties. Biobased-PET offers the advantage of being recyclable within existing PET recycling streams, facilitating a circular economy approach. Other bioplastics, such as polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) and starch blends, also contribute to the diversity of the bioplastics market. PHA is produced by microbial fermentation and is fully biodegradable, making it suitable for applications where complete degradation is desired. Starch blends, often combined with other biopolymers, offer cost-effective solutions for specific packaging needs. These materials are typically used in applications like disposable cutlery, trays, and films. The choice of bioplastic depends on various factors, including the desired properties, cost considerations, and environmental impact. As technology advances, the performance and cost-effectiveness of these materials continue to improve, broadening their application scope in the food packaging industry. The global bioplastics for food package market is characterized by ongoing innovation and collaboration among stakeholders, including material producers, packaging manufacturers, and end-users. This collaborative approach is essential to overcoming challenges such as cost competitiveness and performance limitations, ensuring that bioplastics can effectively replace conventional plastics in food packaging applications. As the market evolves, the focus remains on developing materials that meet the functional requirements of food packaging while minimizing environmental impact. This balance is crucial to achieving sustainable growth in the bioplastics market and addressing the global challenge of plastic pollution.
Food Soft Package, Food Hard Package in the Global Bioplastics for Food Package Market:
The usage of global bioplastics for food package market in food soft and hard packaging is a testament to the versatility and adaptability of these materials. In the realm of food soft packaging, bioplastics are increasingly being used to create flexible packaging solutions such as films, bags, and pouches. These materials are essential for preserving the freshness and quality of food products, providing a barrier against moisture, oxygen, and other environmental factors. Bioplastics like PLA and biobased-PE are commonly used in soft packaging applications due to their flexibility, transparency, and ability to be heat-sealed. These properties make them ideal for packaging a wide range of food products, from fresh produce to snacks and ready-to-eat meals. The compostability of certain bioplastics also adds an environmental benefit, as they can break down in industrial composting facilities, reducing the burden on landfills. In the domain of food hard packaging, bioplastics are used to create rigid containers, trays, and bottles. These applications require materials that offer strength, durability, and resistance to impact. Biobased-PET is a popular choice for hard packaging due to its excellent barrier properties and recyclability. It is commonly used for beverage bottles, yogurt containers, and other products that require a sturdy and reliable packaging solution. PLA is also used in hard packaging applications, particularly for products that do not require high-temperature resistance. The use of bioplastics in hard packaging not only reduces the reliance on fossil-based plastics but also aligns with consumer preferences for sustainable packaging options. The integration of bioplastics in both soft and hard food packaging is driven by several factors, including consumer demand for eco-friendly products, regulatory pressures to reduce plastic waste, and advancements in material science. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, they are increasingly seeking out products that align with their values, including those packaged in sustainable materials. This shift in consumer behavior is prompting food manufacturers and retailers to adopt bioplastics as a way to differentiate their products and appeal to eco-conscious consumers. Regulatory initiatives aimed at reducing plastic waste are also playing a crucial role in driving the adoption of bioplastics in food packaging. Governments around the world are implementing policies and regulations that encourage the use of sustainable materials and promote the development of a circular economy. These initiatives are creating a favorable environment for the growth of the bioplastics market, as businesses seek to comply with regulations and reduce their environmental impact. The ongoing advancements in material science are also contributing to the increased use of bioplastics in food packaging. Researchers and manufacturers are continuously working to improve the performance and cost-effectiveness of bioplastics, making them more competitive with traditional plastics. These advancements are expanding the range of applications for bioplastics, enabling them to meet the diverse needs of the food packaging industry. As the global bioplastics for food package market continues to evolve, the focus remains on developing materials that offer the necessary functionality while minimizing environmental impact. This balance is essential to achieving sustainable growth in the market and addressing the global challenge of plastic pollution.
Global Bioplastics for Food Package Market Outlook:
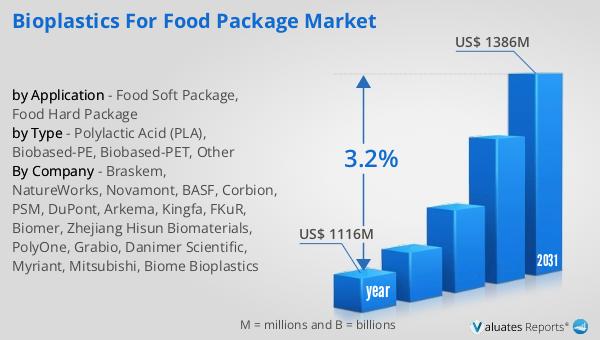
The global market for bioplastics in food packaging is experiencing a notable transformation. In 2024, the market was valued at approximately $1,116 million. By 2031, it is anticipated to grow to a revised size of around $1,386 million. This growth trajectory represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.2% over the forecast period. This steady increase underscores the rising demand for sustainable packaging solutions in the food industry. The shift towards bioplastics is driven by several factors, including increasing environmental awareness, regulatory pressures to reduce plastic waste, and advancements in bioplastic technology. As consumers become more eco-conscious, there is a growing preference for products that align with sustainable practices, including packaging. This trend is prompting businesses to adopt bioplastics as a way to meet consumer expectations and differentiate their products in a competitive market. Additionally, regulatory initiatives aimed at reducing plastic waste are creating a favorable environment for the growth of the bioplastics market. Governments around the world are implementing policies that encourage the use of sustainable materials and promote the development of a circular economy. These initiatives are driving the adoption of bioplastics in food packaging, as businesses seek to comply with regulations and reduce their environmental impact. The ongoing advancements in bioplastic technology are also contributing to the market's growth. Researchers and manufacturers are continuously working to improve the performance and cost-effectiveness of bioplastics, making them more competitive with traditional plastics. These advancements are expanding the range of applications for bioplastics, enabling them to meet the diverse needs of the food packaging industry. As the global market for bioplastics in food packaging continues to evolve, the focus remains on developing materials that offer the necessary functionality while minimizing environmental impact. This balance is essential to achieving sustainable growth in the market and addressing the global challenge of plastic pollution.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Bioplastics for Food Package Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 1116 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 1386 million |
| CAGR | 3.2% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| by Type |
|
| by Application |
|
| Production by Region |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Braskem, NatureWorks, Novamont, BASF, Corbion, PSM, DuPont, Arkema, Kingfa, FKuR, Biomer, Zhejiang Hisun Biomaterials, PolyOne, Grabio, Danimer Scientific, Myriant, Mitsubishi, Biome Bioplastics |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
