What is Global Low-Carbon Aviation Fuel Market?
The Global Low-Carbon Aviation Fuel Market is an emerging sector focused on reducing the carbon footprint of the aviation industry. As the world grapples with climate change, the aviation sector, known for its significant carbon emissions, is under pressure to adopt more sustainable practices. Low-carbon aviation fuels, often referred to as sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs), are designed to replace conventional jet fuels with alternatives that produce fewer greenhouse gases. These fuels are derived from renewable resources such as plant materials, waste oils, and other organic matter, making them a more environmentally friendly option. The market for these fuels is driven by increasing regulatory pressures, technological advancements, and a growing awareness of environmental issues among consumers and industry stakeholders. As airlines and governments worldwide commit to reducing emissions, the demand for low-carbon aviation fuels is expected to rise, fostering innovation and investment in this critical area. The transition to these fuels not only promises to mitigate the environmental impact of air travel but also offers economic opportunities through the development of new technologies and supply chains.
Plants-based, Waste-based in the Global Low-Carbon Aviation Fuel Market:
In the Global Low-Carbon Aviation Fuel Market, plant-based and waste-based fuels represent two primary categories of sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs) that are gaining traction. Plant-based fuels are derived from biomass, which includes crops like corn, sugarcane, and oilseeds. These crops undergo processes such as fermentation and hydroprocessing to produce biofuels that can be used in aviation. The advantage of plant-based fuels lies in their renewability and potential to significantly reduce carbon emissions compared to traditional fossil fuels. However, the production of these fuels raises concerns about land use and food security, as large-scale cultivation of biofuel crops can compete with food production and lead to deforestation. On the other hand, waste-based fuels are produced from various waste materials, including used cooking oils, agricultural residues, and municipal solid waste. These fuels offer a sustainable solution by utilizing waste that would otherwise contribute to environmental pollution. Waste-based fuels are considered more sustainable than plant-based options because they do not compete with food resources and can help reduce landfill waste. The production process for waste-based fuels often involves advanced technologies like pyrolysis and gasification, which convert waste into usable fuel. Both plant-based and waste-based fuels are crucial in the transition to low-carbon aviation, each with its own set of benefits and challenges. The development and adoption of these fuels are supported by government policies and incentives aimed at reducing carbon emissions in the aviation sector. As technology advances and production costs decrease, the availability and use of plant-based and waste-based fuels are expected to grow, contributing to a more sustainable aviation industry. The integration of these fuels into the aviation sector requires collaboration among stakeholders, including fuel producers, airlines, and regulatory bodies, to ensure that the fuels meet safety and performance standards. Overall, plant-based and waste-based fuels represent promising pathways to achieving a low-carbon future for aviation, balancing environmental benefits with economic and social considerations.
Civil Aircraft, Military Aircraft in the Global Low-Carbon Aviation Fuel Market:
The usage of Global Low-Carbon Aviation Fuel Market in civil and military aircraft is pivotal in reducing the aviation industry's carbon footprint. In civil aviation, which includes commercial airlines and private jets, the adoption of low-carbon fuels is driven by both regulatory requirements and consumer demand for more sustainable travel options. Airlines are increasingly incorporating sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs) into their operations to meet emissions reduction targets and enhance their environmental credentials. The use of SAFs in civil aircraft can significantly reduce lifecycle carbon emissions, helping airlines to achieve carbon neutrality goals. Additionally, the integration of low-carbon fuels can provide airlines with a competitive advantage, as passengers become more environmentally conscious and prefer airlines that prioritize sustainability. In military aviation, the use of low-carbon fuels is motivated by the need to enhance energy security and reduce dependency on fossil fuels. Military aircraft, which include fighter jets, transport planes, and helicopters, are significant consumers of aviation fuel. By adopting SAFs, military organizations can reduce their carbon emissions and improve operational efficiency. The use of low-carbon fuels in military aircraft also aligns with broader government initiatives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote energy independence. Furthermore, the development and use of SAFs in military aviation can drive technological advancements and innovation, benefiting the broader aviation industry. The transition to low-carbon fuels in both civil and military aviation requires collaboration among various stakeholders, including fuel producers, aircraft manufacturers, and regulatory bodies, to ensure that the fuels meet safety and performance standards. Overall, the adoption of low-carbon aviation fuels in civil and military aircraft is a critical step towards achieving a more sustainable aviation industry, balancing environmental benefits with operational and economic considerations.
Global Low-Carbon Aviation Fuel Market Outlook:
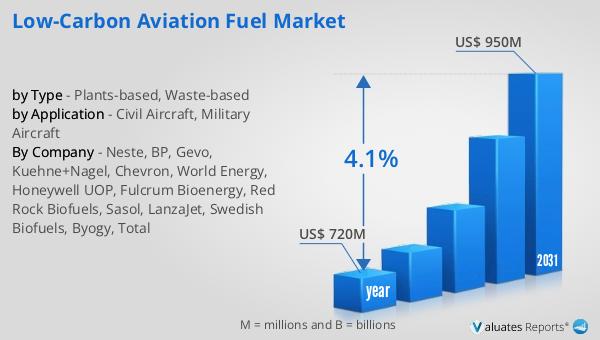
The global market for low-carbon aviation fuel was valued at approximately $720 million in 2024, with projections indicating that it will grow to around $950 million by 2031. This growth represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.1% over the forecast period. The increasing demand for sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs) is driven by a combination of regulatory pressures, technological advancements, and a growing awareness of environmental issues among consumers and industry stakeholders. As airlines and governments worldwide commit to reducing emissions, the demand for low-carbon aviation fuels is expected to rise, fostering innovation and investment in this critical area. The transition to these fuels not only promises to mitigate the environmental impact of air travel but also offers economic opportunities through the development of new technologies and supply chains. The market's growth is further supported by government policies and incentives aimed at reducing carbon emissions in the aviation sector. As technology advances and production costs decrease, the availability and use of low-carbon aviation fuels are expected to grow, contributing to a more sustainable aviation industry. The integration of these fuels into the aviation sector requires collaboration among stakeholders, including fuel producers, airlines, and regulatory bodies, to ensure that the fuels meet safety and performance standards. Overall, the adoption of low-carbon aviation fuels is a critical step towards achieving a more sustainable aviation industry, balancing environmental benefits with operational and economic considerations.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Low-Carbon Aviation Fuel Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 720 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 950 million |
| CAGR | 4.1% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| by Type |
|
| by Application |
|
| Production by Region |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Neste, BP, Gevo, Kuehne+Nagel, Chevron, World Energy, Honeywell UOP, Fulcrum Bioenergy, Red Rock Biofuels, Sasol, LanzaJet, Swedish Biofuels, Byogy, Total |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
