What is Global Beta-lactam and Beta-lactamase Inhibitors Market?
The Global Beta-lactam and Beta-lactamase Inhibitors Market is a significant segment of the pharmaceutical industry, focusing on antibiotics that are crucial in treating bacterial infections. These antibiotics, including penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, and monobactams, work by interfering with the bacteria's cell wall synthesis, ultimately leading to the destruction of the bacteria. Beta-lactamase inhibitors are compounds that enhance the efficacy of beta-lactam antibiotics by preventing bacterial enzymes from breaking down the antibiotic molecules. This market is driven by the increasing prevalence of bacterial infections, the rise in antibiotic resistance, and the need for effective treatment options. The market is characterized by a diverse range of products and formulations, catering to different types of infections and patient needs. The demand for these antibiotics is expected to grow as healthcare systems worldwide continue to combat infectious diseases. The market is also influenced by regulatory policies, research and development activities, and the introduction of new and improved antibiotic formulations. Overall, the Global Beta-lactam and Beta-lactamase Inhibitors Market plays a vital role in the healthcare sector, providing essential tools for managing bacterial infections and improving patient outcomes.
Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Carbapenems, Monobactams, Combinations in the Global Beta-lactam and Beta-lactamase Inhibitors Market:
Penicillins are one of the oldest and most widely used classes of antibiotics in the Global Beta-lactam and Beta-lactamase Inhibitors Market. They are effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria and are commonly used to treat infections such as strep throat, pneumonia, and syphilis. Penicillins work by inhibiting the synthesis of bacterial cell walls, leading to cell lysis and death. Despite their effectiveness, the emergence of penicillin-resistant bacteria has necessitated the development of beta-lactamase inhibitors to restore their efficacy. Cephalosporins, another major class of beta-lactam antibiotics, are structurally similar to penicillins but have a broader spectrum of activity. They are categorized into generations, with each subsequent generation having increased activity against gram-negative bacteria and resistance to beta-lactamase enzymes. Cephalosporins are used to treat a variety of infections, including urinary tract infections, skin infections, and meningitis. Carbapenems are a class of beta-lactam antibiotics known for their broad-spectrum activity and resistance to most beta-lactamases. They are often used as a last resort for treating severe or multidrug-resistant bacterial infections. Monobactams, such as aztreonam, are unique among beta-lactams as they are effective primarily against gram-negative bacteria and are resistant to certain beta-lactamases. They are used in patients who are allergic to penicillins or cephalosporins. Combinations of beta-lactam antibiotics with beta-lactamase inhibitors, such as amoxicillin-clavulanate and piperacillin-tazobactam, have been developed to overcome resistance and extend the spectrum of activity. These combinations are particularly useful in treating infections caused by beta-lactamase-producing bacteria. The Global Beta-lactam and Beta-lactamase Inhibitors Market is continually evolving, with ongoing research and development efforts aimed at discovering new antibiotics and improving existing ones to address the challenges of antibiotic resistance and emerging infectious diseases.
Oral, Intravenous in the Global Beta-lactam and Beta-lactamase Inhibitors Market:
The usage of Global Beta-lactam and Beta-lactamase Inhibitors Market products can be broadly categorized into oral and intravenous applications, each serving distinct clinical needs. Oral beta-lactam antibiotics are typically prescribed for mild to moderate infections that can be managed outside of a hospital setting. These include conditions such as sinusitis, bronchitis, and uncomplicated urinary tract infections. Oral formulations offer the convenience of outpatient treatment, allowing patients to take their medication at home. This route of administration is particularly beneficial for pediatric and elderly patients who may have difficulty with intravenous treatments. However, the effectiveness of oral antibiotics can be limited by factors such as poor absorption in the gastrointestinal tract and the presence of resistant bacteria. Intravenous beta-lactam antibiotics, on the other hand, are used for more severe infections that require rapid and high concentrations of the drug in the bloodstream. These include life-threatening conditions such as sepsis, bacterial meningitis, and hospital-acquired pneumonia. Intravenous administration ensures that the antibiotic reaches the site of infection quickly and in sufficient quantities to exert its therapeutic effect. This route is also preferred in patients who are unable to take oral medications due to vomiting, unconsciousness, or severe illness. The choice between oral and intravenous administration depends on various factors, including the severity of the infection, the patient's overall health, and the susceptibility of the bacteria to the antibiotic. In some cases, treatment may begin with intravenous antibiotics in a hospital setting, followed by a switch to oral antibiotics as the patient's condition improves. This approach, known as step-down therapy, helps to reduce hospital stays and healthcare costs while ensuring effective treatment. The Global Beta-lactam and Beta-lactamase Inhibitors Market continues to innovate in both oral and intravenous formulations, with ongoing research focused on improving drug delivery, enhancing absorption, and overcoming resistance mechanisms.
Global Beta-lactam and Beta-lactamase Inhibitors Market Outlook:
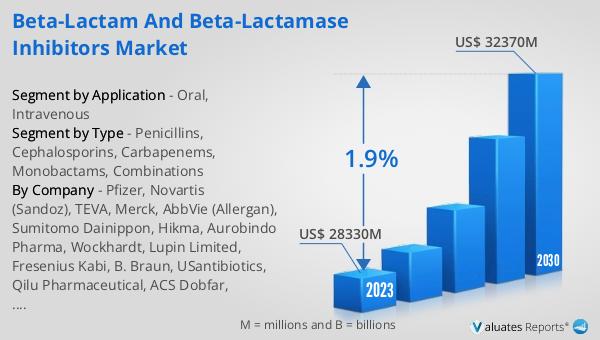
In 2024, the global market for Beta-lactam and Beta-lactamase Inhibitors was valued at approximately $28,210 million, with projections indicating growth to a revised size of $32,210 million by 2031, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 1.9% over the forecast period. The market is dominated by the top five manufacturers, who collectively hold a market share exceeding 10%. The Asia-Pacific region emerges as the largest market for these antibiotics, accounting for over 30% of the global share, followed closely by Europe and North America, which hold shares of 30% and 20%, respectively. Within the product categories, cephalosporins represent the largest segment, capturing over 38% of the market share. In terms of application, intravenous administration is the most prevalent, constituting about 50% of the market. This data underscores the critical role of Beta-lactam and Beta-lactamase Inhibitors in the global healthcare landscape, highlighting the ongoing demand for effective antibiotic treatments in various regions and clinical settings. The market's steady growth is driven by factors such as the rising incidence of bacterial infections, the need for advanced treatment options, and the continuous efforts of manufacturers to innovate and expand their product offerings.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Beta-lactam and Beta-lactamase Inhibitors Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 28210 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 32210 million |
| CAGR | 1.9% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Pfizer, Novartis (Sandoz), TEVA, Merck & Co., AbbVie (Allergan), Sumitomo Dainippon, Hikma, Aurobindo Pharma, Wockhardt, Lupin Limited, Fresenius Kabi, B. Braun, USantibiotics, Qilu Pharmaceutical, ACS Dobfar, Nichi-Iko (Sagent), Antibiotice |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |