What is Global Incinerator Heat Exchanger Market?
The Global Incinerator Heat Exchanger Market refers to the worldwide industry focused on the production, distribution, and utilization of heat exchangers specifically designed for incinerators. Incinerators are devices used to burn waste materials at high temperatures, converting them into ash, flue gas, and heat. Heat exchangers in this context are crucial components that capture and transfer the heat generated during the incineration process to other systems or processes, thereby improving energy efficiency and reducing environmental impact. These heat exchangers are used in various sectors, including industrial, medical, and municipal applications, to recover and utilize the heat that would otherwise be wasted. The market for these specialized heat exchangers is driven by the growing need for efficient waste management solutions, stringent environmental regulations, and the increasing focus on sustainable energy practices. As industries and municipalities seek to optimize their waste-to-energy processes, the demand for advanced incinerator heat exchangers continues to rise, making this market a vital part of the global effort to manage waste and energy resources more effectively.
Diesel, LPG, Natural Gas, Bio Fuel, Others in the Global Incinerator Heat Exchanger Market:
In the Global Incinerator Heat Exchanger Market, various fuel types are utilized to power incinerators, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Diesel is a commonly used fuel due to its high energy density and availability. It is particularly favored in industrial settings where robust and reliable energy sources are required. Diesel-powered incinerators are known for their efficiency and ability to handle large volumes of waste, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, the environmental impact of diesel, including emissions of pollutants and greenhouse gases, is a significant concern, prompting a shift towards cleaner alternatives. LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) is another fuel type used in incinerators. It is a cleaner-burning fuel compared to diesel, producing fewer emissions and pollutants. LPG is often used in smaller-scale incinerators or in settings where environmental regulations are stringent. Its portability and ease of storage make it a convenient choice for various applications, including medical waste incineration and small municipal waste management systems. The use of LPG in incinerators is growing as industries and municipalities seek to reduce their carbon footprint and comply with environmental standards. Natural gas is increasingly being adopted as a fuel for incinerators due to its lower environmental impact compared to diesel and LPG. It burns cleaner, producing fewer pollutants and greenhouse gases. Natural gas-powered incinerators are commonly used in urban areas and large-scale municipal waste management systems where access to natural gas infrastructure is available. The efficiency and environmental benefits of natural gas make it an attractive option for modern incineration facilities aiming to balance performance with sustainability. Biofuel represents a renewable and sustainable fuel option for incinerators. Derived from organic materials such as plant and animal waste, biofuels offer a way to utilize waste products while reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Biofuel-powered incinerators are particularly appealing in regions with abundant agricultural or organic waste. They contribute to a circular economy by turning waste into energy, thus minimizing environmental impact. The use of biofuels in incinerators is gaining traction as part of broader efforts to promote renewable energy sources and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Other fuel types used in incinerators include waste-derived fuels and alternative energy sources. Waste-derived fuels, such as refuse-derived fuel (RDF) and solid recovered fuel (SRF), are produced from non-recyclable waste materials. These fuels provide a way to divert waste from landfills and generate energy simultaneously. Alternative energy sources, such as electricity from renewable sources, are also being explored for powering incinerators. These innovative approaches aim to enhance the sustainability and efficiency of waste-to-energy processes. In summary, the Global Incinerator Heat Exchanger Market encompasses a diverse range of fuel types, each with its advantages and challenges. Diesel remains a reliable choice for heavy-duty applications, while LPG and natural gas offer cleaner alternatives with lower environmental impact. Biofuels and waste-derived fuels represent sustainable options that contribute to a circular economy. As the market evolves, the adoption of cleaner and more efficient fuel types is expected to drive advancements in incineration technology and promote sustainable waste management practices.
Industrial, Medical, Municipal, Others in the Global Incinerator Heat Exchanger Market:
The Global Incinerator Heat Exchanger Market finds extensive usage across various sectors, including industrial, medical, municipal, and others. In industrial settings, incinerator heat exchangers play a crucial role in managing waste generated from manufacturing processes. Industries such as chemical, pharmaceutical, and food processing produce significant amounts of waste that require efficient disposal methods. Incinerators equipped with heat exchangers help these industries convert waste into energy, which can then be reused within the facility or supplied to external systems. This not only reduces the environmental impact of industrial waste but also enhances energy efficiency and cost savings. In the medical sector, incinerator heat exchangers are essential for the safe disposal of medical waste. Hospitals, clinics, and laboratories generate various types of hazardous waste, including infectious materials, pharmaceuticals, and sharps. Incineration is a preferred method for disposing of such waste due to its ability to completely destroy pathogens and reduce waste volume. Heat exchangers in medical incinerators capture the heat generated during the incineration process and repurpose it for heating or other energy needs within the facility. This not only ensures the safe disposal of medical waste but also contributes to the overall energy efficiency of healthcare facilities. Municipal applications of incinerator heat exchangers are widespread, particularly in urban areas where waste management is a significant challenge. Municipal solid waste (MSW) includes household waste, commercial waste, and other non-hazardous materials. Incinerators equipped with heat exchangers help municipalities manage this waste by converting it into energy, which can be used for district heating, electricity generation, or other purposes. This approach not only reduces the volume of waste sent to landfills but also provides a sustainable energy source for urban communities. The integration of heat exchangers in municipal incinerators is a key component of modern waste-to-energy systems, promoting environmental sustainability and resource efficiency. Beyond industrial, medical, and municipal applications, incinerator heat exchangers are also used in various other sectors. For example, in the agricultural sector, incinerators can be used to dispose of animal carcasses and other organic waste, with heat exchangers capturing the energy produced during the process. In the maritime industry, shipboard incinerators equipped with heat exchangers help manage waste generated on vessels, converting it into energy that can be used for onboard systems. Additionally, incinerator heat exchangers are utilized in military and remote installations where waste management and energy efficiency are critical. Overall, the usage of incinerator heat exchangers in these diverse sectors highlights their importance in promoting sustainable waste management and energy efficiency. By capturing and repurposing the heat generated during incineration, these systems help reduce environmental impact, enhance resource utilization, and support the transition to a circular economy. As industries, municipalities, and other sectors continue to seek innovative solutions for waste management and energy efficiency, the demand for advanced incinerator heat exchangers is expected to grow, driving further advancements in this critical market.
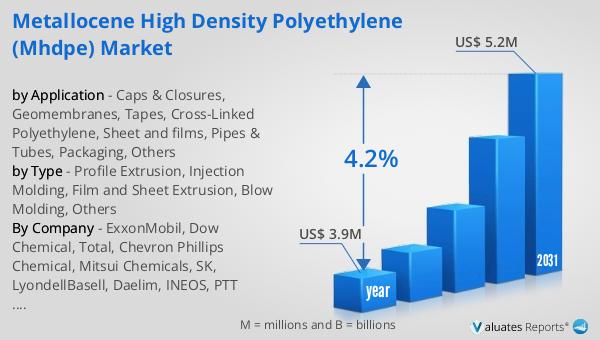
Global Incinerator Heat Exchanger Market Outlook:
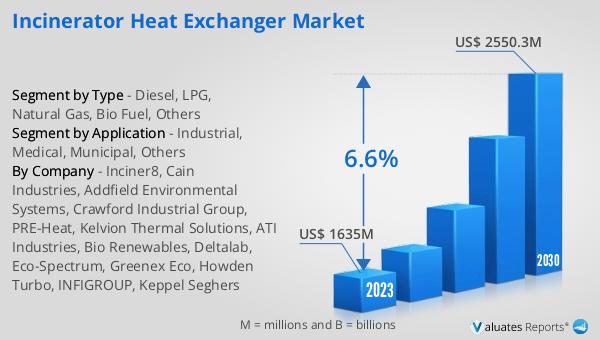
The global Incinerator Heat Exchanger market was valued at US$ 1635 million in 2023 and is anticipated to reach US$ 2550.3 million by 2030, witnessing a CAGR of 6.6% during the forecast period 2024-2030. This market outlook indicates a robust growth trajectory driven by increasing demand for efficient waste management solutions and sustainable energy practices. The significant market valuation in 2023 reflects the widespread adoption of incinerator heat exchangers across various sectors, including industrial, medical, and municipal applications. As industries and municipalities strive to optimize their waste-to-energy processes, the market for these specialized heat exchangers is poised for substantial expansion. The projected growth to US$ 2550.3 million by 2030 underscores the critical role of incinerator heat exchangers in enhancing energy efficiency and reducing environmental impact. With a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.6%, the market is set to experience steady advancements, driven by technological innovations and increasing regulatory pressures for sustainable waste management. This positive market outlook highlights the ongoing efforts to improve waste-to-energy systems and the growing recognition of incinerator heat exchangers as essential components in achieving these goals.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Incinerator Heat Exchanger Market |
| Accounted market size in 2023 | US$ 1635 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2030 | US$ 2550.3 million |
| CAGR | 6.6% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecasted years | 2024 - 2030 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Production by Region |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Inciner8, Cain Industries, Addfield Environmental Systems, Crawford Industrial Group, PRE-Heat, Kelvion Thermal Solutions, ATI Industries, Bio Renewables, Deltalab, Eco-Spectrum, Greenex Eco, Howden Turbo, INFIGROUP, Keppel Seghers |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |