What is Global Urban Wind Turbine Market?
The global urban wind turbine market is a rapidly evolving sector focused on harnessing wind energy within urban environments. Urban wind turbines are designed to be installed in cities and towns, where space is limited, and the need for renewable energy sources is high. These turbines are smaller and more compact compared to their rural counterparts, making them suitable for rooftops, small plots of land, and other urban settings. The market is driven by the increasing demand for clean energy, government incentives, and technological advancements that make urban wind turbines more efficient and cost-effective. As cities continue to grow and the push for sustainable energy solutions intensifies, the global urban wind turbine market is expected to expand significantly. This growth is also fueled by the rising awareness of environmental issues and the need to reduce carbon footprints in densely populated areas. Urban wind turbines offer a viable solution for generating renewable energy locally, reducing reliance on fossil fuels, and contributing to a greener, more sustainable future.
Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine, Vertical Axis Wind Turbine in the Global Urban Wind Turbine Market:
Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWTs) and Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs) are the two primary types of wind turbines used in the global urban wind turbine market. HAWTs are the more traditional and widely recognized type, featuring blades that rotate around a horizontal axis. These turbines are typically more efficient at converting wind energy into electricity due to their ability to capture wind from a single direction. However, they require more space and are often more challenging to install in urban environments where wind direction can be inconsistent. On the other hand, VAWTs have blades that rotate around a vertical axis, making them more suitable for urban settings. They can capture wind from any direction, which is advantageous in cities where wind patterns are unpredictable. VAWTs are generally easier to install on rooftops and other confined spaces, making them a popular choice for urban applications. Despite their lower efficiency compared to HAWTs, VAWTs are gaining traction due to their versatility and adaptability in urban landscapes. Both types of turbines have their unique advantages and challenges, and the choice between them often depends on specific site conditions and energy requirements. As technology continues to advance, both HAWTs and VAWTs are becoming more efficient and cost-effective, further driving the growth of the global urban wind turbine market.
On-Grid, Off-Grid in the Global Urban Wind Turbine Market:
The usage of global urban wind turbines can be broadly categorized into on-grid and off-grid applications. On-grid systems are connected to the local electricity grid, allowing excess energy generated by the wind turbines to be fed back into the grid. This not only provides a reliable source of renewable energy for urban areas but also offers financial benefits through net metering or feed-in tariffs. On-grid urban wind turbines can help reduce the overall demand for fossil fuels, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and provide a stable energy supply to urban dwellers. These systems are particularly beneficial in densely populated areas where the demand for electricity is high, and the integration of renewable energy sources is crucial for sustainable development. Off-grid systems, on the other hand, operate independently of the local electricity grid. These systems are ideal for remote or underserved urban areas where access to the grid is limited or unreliable. Off-grid urban wind turbines can provide a consistent and sustainable energy source for homes, businesses, and community facilities, reducing the reliance on diesel generators or other non-renewable energy sources. They are also valuable in emergency situations, providing backup power during grid outages. Both on-grid and off-grid urban wind turbine systems play a vital role in promoting energy independence, enhancing energy security, and supporting the transition to a more sustainable and resilient urban energy infrastructure.
Global Urban Wind Turbine Market Outlook:
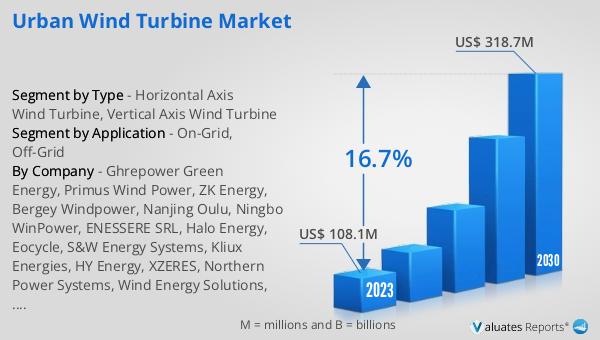
The global urban wind turbine market was valued at $108.1 million in 2023 and is projected to reach $318.7 million by 2030, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.7% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2030. This significant growth underscores the increasing adoption of wind energy solutions in urban environments as cities strive to become more sustainable and reduce their carbon footprints. The rising awareness of environmental issues, coupled with government incentives and technological advancements, is driving the demand for urban wind turbines. These turbines offer a practical solution for generating renewable energy locally, reducing reliance on fossil fuels, and contributing to a greener future. As the market continues to expand, it is expected to play a crucial role in the global transition to renewable energy, providing clean and sustainable power to urban areas worldwide.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Urban Wind Turbine Market |
| Accounted market size in 2023 | US$ 108.1 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2030 | US$ 318.7 million |
| CAGR | 16.7% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecasted years | 2024 - 2030 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Production by Region |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Ghrepower Green Energy, Primus Wind Power, ZK Energy, Bergey Windpower, Nanjing Oulu, Ningbo WinPower, ENESSERE SRL, Halo Energy, Eocycle, S&W Energy Systems, Kliux Energies, HY Energy, XZERES, Northern Power Systems, Wind Energy Solutions, Kingspan, Polaris, Endurance Wind Power, Fortis Wind Energy, Britwind |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
