What is Global Quantum Magnetometers Market?
The Global Quantum Magnetometers Market is an emerging field that focuses on the development and application of highly sensitive instruments used to measure magnetic fields. These devices leverage the principles of quantum mechanics to achieve unprecedented levels of precision and sensitivity, making them invaluable in various scientific and industrial applications. Quantum magnetometers are capable of detecting minute changes in magnetic fields, which can be crucial for tasks ranging from geological exploration to medical diagnostics. The market for these advanced instruments is driven by the increasing demand for high-precision measurement tools in sectors such as defense, healthcare, and environmental monitoring. As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of quantum magnetometers are expected to expand, offering even greater accuracy and reliability. This growth is further fueled by ongoing research and development efforts aimed at enhancing the performance and reducing the cost of these devices, making them more accessible to a broader range of industries. Overall, the Global Quantum Magnetometers Market represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector with significant potential for innovation and growth.
Optically-pumped Magnetometers, Solid-state Quantum Magnetometers in the Global Quantum Magnetometers Market:
Optically-pumped magnetometers and solid-state quantum magnetometers are two prominent types of devices within the Global Quantum Magnetometers Market, each offering unique advantages and applications. Optically-pumped magnetometers operate by using light to polarize atoms, typically alkali metals like rubidium or cesium, within a vapor cell. This polarization process aligns the atomic spins, which are then influenced by external magnetic fields. The resulting changes in the atomic spin states are detected using laser light, allowing for precise measurement of the magnetic field. These magnetometers are known for their high sensitivity and are often used in applications where detecting extremely weak magnetic fields is crucial, such as in medical imaging techniques like magnetoencephalography (MEG) and in geophysical surveys. On the other hand, solid-state quantum magnetometers utilize the properties of solid materials, such as nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers in diamond, to measure magnetic fields. These magnetometers exploit the quantum properties of defects in the crystal lattice of the material, which can be manipulated and read out using laser and microwave techniques. Solid-state quantum magnetometers are particularly valued for their robustness and ability to operate in a wide range of environmental conditions, making them suitable for applications in harsh environments, such as space exploration and military operations. Both types of magnetometers are integral to the Global Quantum Magnetometers Market, offering complementary capabilities that cater to diverse needs across various industries. As research and development efforts continue to advance, these technologies are expected to become even more sophisticated, providing enhanced performance and opening up new possibilities for their application. The ongoing innovation in this field is likely to drive further growth in the market, as industries increasingly recognize the value of quantum magnetometers in achieving high-precision measurements and improving the accuracy of their operations.
Medical, Scientific Research, Navigation, Geological Exploration, Defense and Military, Electrical Power and Industrial Diagnostics, Aerospace, Environmental Monitoring, Others in the Global Quantum Magnetometers Market:
The Global Quantum Magnetometers Market finds applications across a wide range of fields, each benefiting from the unique capabilities of these advanced measurement devices. In the medical sector, quantum magnetometers are used in techniques like magnetoencephalography (MEG), which allows for the non-invasive mapping of brain activity by detecting the magnetic fields generated by neural currents. This application is crucial for diagnosing and understanding neurological disorders, offering a level of precision that traditional methods cannot match. In scientific research, quantum magnetometers are employed to study fundamental physical phenomena, providing insights into areas such as quantum mechanics and condensed matter physics. Their ability to detect minute magnetic fields makes them invaluable tools for researchers exploring the frontiers of science. Navigation systems also benefit from the precision of quantum magnetometers, particularly in applications where traditional GPS systems may be unreliable, such as underwater or in space. These magnetometers can provide accurate heading information, enhancing the reliability of navigation in challenging environments. Geological exploration is another area where quantum magnetometers are making a significant impact. By detecting variations in the Earth's magnetic field, these devices can help identify mineral deposits and other geological features, aiding in resource exploration and extraction. In the defense and military sector, quantum magnetometers are used for applications such as submarine detection and mine countermeasures, where their ability to detect subtle magnetic anomalies can be critical. The electrical power and industrial diagnostics sectors also benefit from the precision of quantum magnetometers, which can be used to monitor the integrity of power lines and detect faults in industrial equipment. In aerospace, these devices are used for tasks such as spacecraft navigation and the detection of magnetic fields in space, contributing to the safety and efficiency of space missions. Environmental monitoring is another important application, where quantum magnetometers can be used to study the Earth's magnetic field and its interactions with the environment, providing valuable data for climate research and natural disaster prediction. Overall, the versatility and precision of quantum magnetometers make them indispensable tools across a wide range of industries, driving demand and innovation in the Global Quantum Magnetometers Market.
Global Quantum Magnetometers Market Outlook:
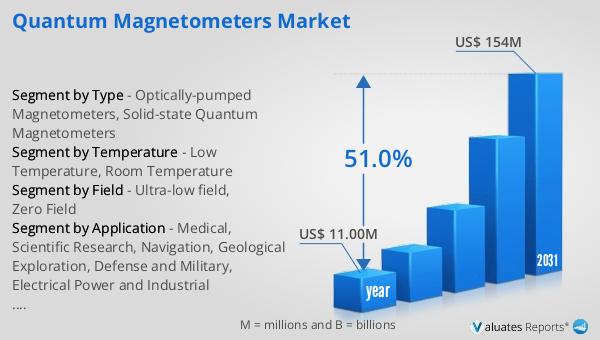
The global market for quantum magnetometers is experiencing significant growth, with its value estimated at $11 million in 2024. This market is projected to expand substantially, reaching a revised size of $154 million by 2031. This impressive growth trajectory is driven by a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 51.0% during the forecast period. The rapid expansion of this market can be attributed to the increasing demand for high-precision measurement tools across various industries, including healthcare, defense, and environmental monitoring. As industries continue to recognize the value of quantum magnetometers in achieving accurate and reliable measurements, the market is expected to witness sustained growth. The advancements in technology and ongoing research and development efforts are also contributing to the market's expansion, as they enhance the performance and reduce the cost of these devices, making them more accessible to a broader range of applications. The growing awareness of the benefits of quantum magnetometers, coupled with their expanding range of applications, is likely to drive further growth in the market, solidifying its position as a key player in the field of precision measurement.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Quantum Magnetometers Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 11.00 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 154 million |
| CAGR | 51.0% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Temperature |
|
| Segment by Field |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Production by Region |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Qnami, GEM Systems, SBQuantum, Q-CTRL, CIQTEK, Bosch, Q.ANT, Deteqt, Anhui Guosheng Quantum Technology |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |