What is Global Nuclear Power Heat Exchanger Market?
The Global Nuclear Power Heat Exchanger Market is a specialized segment within the broader energy sector, focusing on the development, production, and distribution of heat exchangers used in nuclear power plants. These devices are crucial for transferring heat from the nuclear reactor to the power generation system, ensuring efficient energy production. As nuclear power remains a significant source of low-carbon energy, the demand for advanced and reliable heat exchangers is on the rise. The market encompasses various types of heat exchangers, each designed to meet the specific requirements of different reactor technologies. Innovations in materials and design are driving improvements in efficiency and safety, making these components vital for the sustainable operation of nuclear facilities. The market is influenced by factors such as technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, and the global push towards cleaner energy sources. As countries strive to meet their energy needs while reducing carbon emissions, the Global Nuclear Power Heat Exchanger Market is poised for growth, offering opportunities for manufacturers and stakeholders to contribute to a more sustainable energy future. This market plays a pivotal role in the nuclear energy sector, supporting the transition to a more sustainable and low-carbon energy landscape.
Pressurized Water Reactor Heat Exchanger, Boiling Water Reactor Heat Exchanger, High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactor Heat Exchanger, Heavy Water Reactor Heat Exchanger in the Global Nuclear Power Heat Exchanger Market:
In the realm of nuclear power, heat exchangers are indispensable components, each tailored to the specific needs of various reactor types. The Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) Heat Exchanger is one of the most common types, used extensively in nuclear power plants worldwide. In a PWR, water is heated by nuclear fission in the reactor core and kept under high pressure to prevent it from boiling. The heat exchanger then transfers this heat to a secondary loop, where steam is generated to drive turbines for electricity production. This design ensures that radioactive water remains contained within the primary loop, enhancing safety. On the other hand, the Boiling Water Reactor (BWR) Heat Exchanger operates differently. In a BWR, water in the reactor core is allowed to boil, and the resulting steam directly drives the turbines. The heat exchanger in this system is crucial for condensing the steam back into water, which is then recirculated into the reactor core. This direct cycle design simplifies the system but requires robust heat exchangers to handle the radioactive steam. The High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactor (HTGR) Heat Exchanger represents a more advanced technology. HTGRs use helium gas as a coolant, which is heated to high temperatures in the reactor core. The heat exchanger then transfers this heat to a secondary loop, often using a gas turbine for electricity generation. This design allows for higher thermal efficiencies and can support cogeneration applications, such as hydrogen production. Lastly, the Heavy Water Reactor (HWR) Heat Exchanger is used in reactors that utilize heavy water (deuterium oxide) as both a coolant and a neutron moderator. The heat exchanger in an HWR transfers heat from the heavy water to a secondary loop, where steam is generated for power production. This type of reactor is known for its ability to use natural uranium as fuel, reducing the need for enrichment. Each of these heat exchanger types plays a critical role in the safe and efficient operation of nuclear reactors, highlighting the importance of continued innovation and development in this field.
Nuclear Power Plants, Nuclear Fuel Reprocessing Plants, Nuclear Waste Management, Others in the Global Nuclear Power Heat Exchanger Market:
The Global Nuclear Power Heat Exchanger Market finds its applications across various sectors within the nuclear industry, each with distinct requirements and challenges. In Nuclear Power Plants, heat exchangers are integral to the reactor's cooling system, ensuring that the reactor core remains at a safe temperature while efficiently transferring heat for electricity generation. These devices must withstand extreme conditions, including high temperatures and pressures, as well as exposure to radiation. The reliability and efficiency of heat exchangers directly impact the plant's operational safety and economic viability. In Nuclear Fuel Reprocessing Plants, heat exchangers play a crucial role in the chemical processes used to separate usable fuel from waste products. These facilities require heat exchangers that can handle corrosive materials and maintain precise temperature control to ensure the efficiency and safety of the reprocessing operations. In the realm of Nuclear Waste Management, heat exchangers are used in systems designed to stabilize and store radioactive waste. These systems often involve the solidification of liquid waste, a process that requires precise temperature management to ensure the safe encapsulation of radioactive materials. Heat exchangers in this context must be highly reliable and capable of operating in harsh environments. Beyond these primary applications, the Global Nuclear Power Heat Exchanger Market also serves other areas, such as research reactors and naval propulsion systems. In research reactors, heat exchangers are used to manage the thermal output of experimental setups, often requiring custom designs to meet specific research needs. In naval applications, particularly in nuclear-powered submarines and aircraft carriers, compact and efficient heat exchangers are essential for maintaining the operational readiness of these vessels. Across all these areas, the demand for advanced heat exchanger technology is driven by the need for improved safety, efficiency, and environmental performance, underscoring the critical role these components play in the broader nuclear industry.
Global Nuclear Power Heat Exchanger Market Outlook:
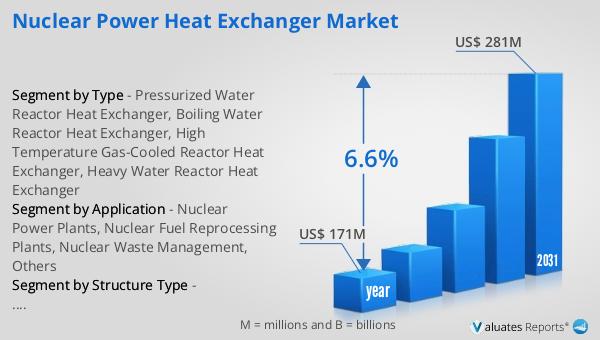
The outlook for the Global Nuclear Power Heat Exchanger Market is promising, with significant growth anticipated over the coming years. In 2024, the market was valued at approximately US$ 171 million. By 2031, it is expected to expand to a revised size of US$ 281 million, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.6% during the forecast period. This growth trajectory underscores the increasing demand for efficient and reliable heat exchangers in the nuclear sector, driven by the global shift towards cleaner energy sources and the need for sustainable power generation solutions. As countries continue to invest in nuclear energy as a means to reduce carbon emissions and meet growing energy demands, the market for nuclear power heat exchangers is set to benefit from these trends. The anticipated growth also highlights the importance of technological advancements and innovation in heat exchanger design and materials, which are crucial for enhancing the performance and safety of nuclear power systems. This positive market outlook presents opportunities for manufacturers and stakeholders to capitalize on the expanding demand for nuclear power heat exchangers, contributing to the development of a more sustainable and resilient energy infrastructure.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Nuclear Power Heat Exchanger Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 171 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 281 million |
| CAGR | 6.6% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Structure Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Production by Region |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Holtec International, Larsen & Toubro (L&T), BWX Technologies, Nexson Group, STF Loterios, Alfa Laval AB, Aerofin Heat Transfer Products, Turnbull & Scott Ltd, Aerofin, NEM Energy Group, Ellis & Watts |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
