What is Global Non-Insulin Peptide Drug Market?
The Global Non-Insulin Peptide Drug Market is a rapidly evolving sector within the pharmaceutical industry, focusing on peptide-based medications that do not involve insulin. These drugs are designed to treat a variety of conditions, primarily those related to metabolic disorders, such as diabetes, and other diseases where peptide hormones play a crucial role. Unlike traditional insulin therapies, non-insulin peptide drugs offer alternative mechanisms of action, targeting specific pathways to regulate bodily functions. This market is driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, advancements in peptide drug development, and a growing demand for more effective and targeted therapies. The market encompasses a wide range of products, including GLP-1 receptor agonists, somatostatin analogs, PTH analogs, and calcitonin analogs, each serving different therapeutic purposes. As research and development in this field continue to advance, the Global Non-Insulin Peptide Drug Market is expected to expand, offering new opportunities for innovation and improved patient outcomes. The market's growth is also supported by the rising awareness of peptide therapies' benefits, such as their specificity, efficacy, and reduced side effects compared to traditional treatments. Overall, this market represents a significant area of interest for pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers alike.
GLP-1, Somatostatin Analogs (octreotide, lanreotide, etc.), PTH Analogs, Calcitonin & Analogs, Other in the Global Non-Insulin Peptide Drug Market:
GLP-1, or glucagon-like peptide-1, is a key player in the Global Non-Insulin Peptide Drug Market. It is a type of incretin hormone that stimulates insulin secretion in response to meals, thereby helping to regulate blood sugar levels. GLP-1 receptor agonists, such as exenatide and liraglutide, are used to treat type 2 diabetes by enhancing the body's natural insulin response and slowing gastric emptying, which helps control appetite and weight. These drugs have gained popularity due to their dual benefits of glycemic control and weight management, making them a preferred choice for many patients and healthcare providers. Somatostatin analogs, including octreotide and lanreotide, are another important category within this market. These drugs mimic the action of somatostatin, a hormone that inhibits the release of several other hormones, including growth hormone and insulin. They are primarily used to treat acromegaly, a condition characterized by excessive growth hormone production, and neuroendocrine tumors. By controlling hormone levels, somatostatin analogs help manage symptoms and slow disease progression. PTH analogs, or parathyroid hormone analogs, are used to treat conditions related to calcium imbalances, such as hypoparathyroidism and osteoporosis. These drugs work by mimicking the action of parathyroid hormone, which regulates calcium and phosphate levels in the body. PTH analogs help improve bone density and reduce fracture risk, offering significant benefits for patients with bone-related disorders. Calcitonin and its analogs are another group of non-insulin peptide drugs that play a crucial role in managing bone health. Calcitonin is a hormone that helps regulate calcium levels by inhibiting bone resorption, making it useful in treating conditions like osteoporosis and Paget's disease. Calcitonin analogs provide an alternative treatment option for patients who cannot tolerate other osteoporosis medications. In addition to these well-known categories, the Global Non-Insulin Peptide Drug Market also includes other peptide-based therapies targeting various diseases. These may include drugs for cardiovascular conditions, gastrointestinal disorders, and certain types of cancer. As research in peptide therapeutics continues to advance, new analogs and formulations are being developed to address unmet medical needs and improve patient outcomes. The versatility and specificity of peptide drugs make them an attractive option for treating a wide range of conditions, and their role in modern medicine is expected to grow as more is understood about their mechanisms of action and potential applications. Overall, the Global Non-Insulin Peptide Drug Market is characterized by a diverse array of products, each offering unique benefits and addressing different therapeutic areas. The continued development and adoption of these drugs are driven by the need for more effective and targeted treatments, as well as the growing recognition of the advantages of peptide-based therapies. As the market expands, it presents numerous opportunities for innovation and collaboration among pharmaceutical companies, researchers, and healthcare providers, ultimately leading to improved patient care and outcomes.
Hospital, Retail Pharmacy, Other in the Global Non-Insulin Peptide Drug Market:
The usage of Global Non-Insulin Peptide Drugs spans various healthcare settings, including hospitals, retail pharmacies, and other medical facilities. In hospitals, these drugs are often used for acute management of conditions that require immediate intervention, such as severe cases of diabetes or hormone-related disorders. Hospital settings provide the necessary infrastructure for administering these drugs, especially those that require intravenous or subcutaneous delivery. Healthcare professionals in hospitals are well-equipped to monitor patients closely, adjust dosages as needed, and manage any potential side effects, ensuring optimal therapeutic outcomes. Additionally, hospitals often serve as centers for clinical trials and research, contributing to the development and refinement of new peptide-based therapies. In retail pharmacies, non-insulin peptide drugs are dispensed to patients for ongoing management of chronic conditions. Pharmacists play a crucial role in educating patients about their medications, ensuring adherence to prescribed regimens, and providing guidance on potential side effects and interactions with other drugs. Retail pharmacies offer convenient access to these medications, allowing patients to maintain their treatment plans and manage their conditions effectively. The availability of non-insulin peptide drugs in retail settings also supports patient autonomy, enabling individuals to take an active role in their healthcare and make informed decisions about their treatment options. Other healthcare settings, such as specialized clinics and outpatient centers, also utilize non-insulin peptide drugs for various therapeutic purposes. These facilities often focus on specific conditions, such as endocrine disorders or metabolic diseases, and provide targeted care for patients requiring specialized treatment. In these settings, healthcare providers can offer personalized treatment plans, monitor patient progress closely, and make necessary adjustments to therapy based on individual needs. The use of non-insulin peptide drugs in these environments highlights the importance of tailored care and the role of specialized expertise in managing complex medical conditions. Overall, the Global Non-Insulin Peptide Drug Market plays a vital role in modern healthcare, offering diverse treatment options across different settings. The availability and use of these drugs in hospitals, retail pharmacies, and other medical facilities underscore their significance in managing a wide range of conditions and improving patient outcomes. As the market continues to evolve, the integration of non-insulin peptide drugs into various healthcare settings will likely expand, driven by ongoing research, innovation, and the growing demand for effective and targeted therapies. This expansion will further enhance the ability of healthcare providers to deliver high-quality care and meet the diverse needs of patients worldwide.
Global Non-Insulin Peptide Drug Market Outlook:
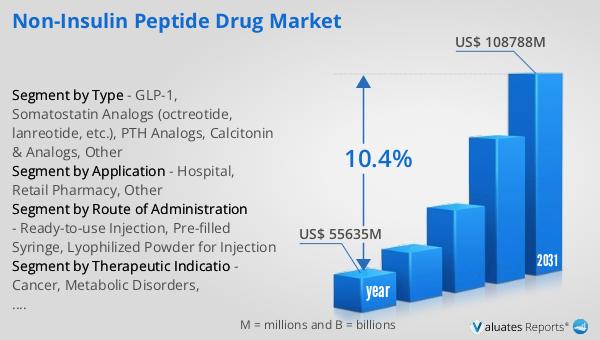
In 2024, the global market for Non-Insulin Peptide Drugs was valued at approximately $55,635 million. Looking ahead, this market is anticipated to grow significantly, reaching an estimated value of $108,788 million by 2031. This growth trajectory represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.4% over the forecast period. The substantial increase in market size reflects the rising demand for non-insulin peptide drugs, driven by factors such as the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, advancements in peptide drug development, and the growing recognition of the benefits of peptide-based therapies. As more healthcare providers and patients become aware of the advantages of these drugs, including their specificity, efficacy, and reduced side effects, the market is expected to continue its upward trend. The projected growth also highlights the potential for innovation and expansion within the Global Non-Insulin Peptide Drug Market, offering new opportunities for pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers to improve patient care and outcomes. As the market evolves, it will likely see the introduction of new products and formulations, further enhancing the range of treatment options available to patients worldwide. This positive outlook underscores the importance of continued research and development in the field of peptide therapeutics, as well as the need for collaboration among industry stakeholders to address unmet medical needs and drive future growth.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Non-Insulin Peptide Drug Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 55635 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 108788 million |
| CAGR | 10.4% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Route of Administration |
|
| Segment by Therapeutic Indicatio |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| By Company | Sanofi, Teva, Novo Nordisk, Takeda, Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Novartis, AbbVie, Ipsen, Ferring, Merck, The Medicines, J & J |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
