What is Global Wind Turbine Nacelle Inspection Robot Market?
The Global Wind Turbine Nacelle Inspection Robot Market is a specialized segment within the broader wind energy industry, focusing on the development and deployment of robotic systems designed to inspect the nacelles of wind turbines. Nacelles are the housings on top of wind turbines that contain critical components such as the gearbox, generator, and control electronics. Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are crucial for ensuring the efficient operation and longevity of wind turbines. Traditionally, these inspections have been conducted manually, which can be time-consuming, costly, and potentially hazardous for human workers. The introduction of inspection robots has revolutionized this process by offering a safer, more efficient, and cost-effective solution. These robots are equipped with advanced sensors and imaging technologies that allow them to perform detailed inspections, identify potential issues, and even carry out minor repairs. As the demand for renewable energy continues to grow, the market for wind turbine nacelle inspection robots is expected to expand, driven by the need for improved maintenance practices and the increasing complexity of wind turbine technology.
Fully-automatic, Semi-automatic in the Global Wind Turbine Nacelle Inspection Robot Market:
In the Global Wind Turbine Nacelle Inspection Robot Market, the distinction between fully-automatic and semi-automatic systems is significant, as it defines the level of human intervention required during the inspection process. Fully-automatic inspection robots are designed to operate independently, with minimal to no human input once they are deployed. These robots are equipped with sophisticated algorithms and artificial intelligence capabilities that enable them to navigate the nacelle, conduct inspections, and analyze data autonomously. They can identify issues such as wear and tear, corrosion, or misalignment of components, and report these findings back to a central system for further analysis. The primary advantage of fully-automatic systems is their ability to perform inspections quickly and efficiently, reducing downtime and labor costs. However, the development and deployment of these systems can be costly, and they require a high level of technical expertise to operate and maintain. On the other hand, semi-automatic inspection robots require some level of human intervention during the inspection process. These systems are typically operated remotely by a technician who guides the robot through the inspection process. While they may not be as efficient as fully-automatic systems, semi-automatic robots offer greater flexibility and control, allowing operators to focus on specific areas of concern and make real-time adjustments as needed. This can be particularly beneficial in complex or challenging environments where fully-automatic systems may struggle to perform effectively. Additionally, semi-automatic systems are generally less expensive to develop and deploy, making them an attractive option for smaller operators or those with limited budgets. Both fully-automatic and semi-automatic systems have their own unique advantages and challenges, and the choice between the two often depends on the specific needs and resources of the operator. For instance, fully-automatic systems may be more suitable for large-scale wind farms with a high number of turbines, where the efficiency and speed of inspections are critical. In contrast, semi-automatic systems may be better suited for smaller operations or those with more complex inspection requirements. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see further developments in both fully-automatic and semi-automatic systems, with improvements in areas such as artificial intelligence, sensor technology, and data analysis capabilities. These advancements will likely lead to more efficient and effective inspection processes, ultimately contributing to the overall growth and success of the Global Wind Turbine Nacelle Inspection Robot Market.
Onshore Wind Turbines, Offshore Wind Turbines in the Global Wind Turbine Nacelle Inspection Robot Market:
The usage of Global Wind Turbine Nacelle Inspection Robots in onshore and offshore wind turbines presents unique opportunities and challenges. Onshore wind turbines, which are located on land, typically have easier access for maintenance and inspection activities compared to their offshore counterparts. The deployment of inspection robots in onshore wind farms can significantly enhance the efficiency and safety of maintenance operations. These robots can quickly and accurately inspect nacelles, identifying potential issues before they lead to costly failures. This proactive approach to maintenance can help extend the lifespan of onshore wind turbines and improve their overall performance. Additionally, the use of inspection robots can reduce the need for human workers to perform potentially dangerous tasks, such as climbing tall turbine towers, thereby enhancing safety and reducing labor costs. Offshore wind turbines, on the other hand, are located in bodies of water, often far from shore, which presents additional challenges for maintenance and inspection activities. The harsh marine environment can accelerate wear and tear on turbine components, making regular inspections even more critical. However, the remote location and challenging conditions can make it difficult and costly to perform these inspections manually. This is where inspection robots can play a crucial role. By deploying robots that can operate autonomously or semi-autonomously, operators can conduct regular inspections without the need for costly and time-consuming human intervention. These robots can navigate the nacelle, perform detailed inspections, and transmit data back to shore for analysis, allowing operators to identify and address potential issues before they lead to significant downtime or damage. The use of inspection robots in offshore wind farms can also help reduce the environmental impact of maintenance activities. By minimizing the need for human intervention, operators can reduce the number of trips required to and from the wind farm, thereby reducing fuel consumption and emissions. Additionally, the use of robots can help minimize the risk of accidents or spills that could harm the marine environment. Overall, the deployment of Global Wind Turbine Nacelle Inspection Robots in both onshore and offshore wind farms offers significant benefits in terms of efficiency, safety, and environmental impact. As the demand for renewable energy continues to grow, the use of these robots is likely to become increasingly common, helping to ensure the reliable and sustainable operation of wind turbines around the world.
Global Wind Turbine Nacelle Inspection Robot Market Outlook:
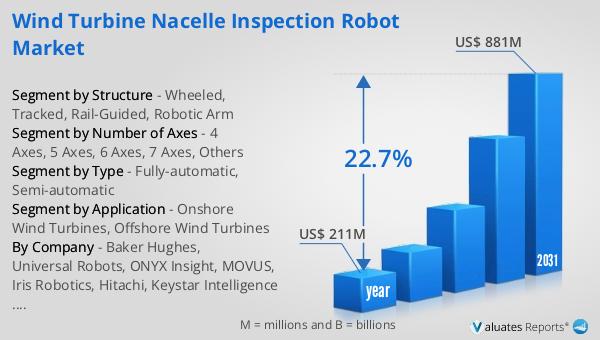
The global market for Wind Turbine Nacelle Inspection Robots is experiencing significant growth, reflecting the increasing demand for efficient and reliable maintenance solutions in the wind energy sector. In 2024, the market was valued at approximately $211 million, indicating a strong foundation for future expansion. By 2031, it is projected that the market will reach a revised size of $881 million, driven by a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.7% during the forecast period. This impressive growth rate underscores the critical role that inspection robots are playing in the maintenance and operation of wind turbines. As wind energy continues to gain traction as a key component of the global energy mix, the need for advanced inspection technologies is becoming increasingly apparent. Inspection robots offer a range of benefits, including improved safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, making them an attractive option for operators looking to optimize their maintenance practices. The projected growth of the market reflects the increasing recognition of these benefits and the growing adoption of inspection robots across the industry. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see further innovations in this space, driving continued growth and development in the Global Wind Turbine Nacelle Inspection Robot Market.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Wind Turbine Nacelle Inspection Robot Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 211 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 881 million |
| CAGR | 22.7% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Structure |
|
| Segment by Number of Axes |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Production by Region |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Baker Hughes, Universal Robots, ONYX Insight, MOVUS, Iris Robotics, Hitachi, Keystar Intelligence Robot, Gosion Robot, Tianchuang Electronic, Launch Digital, Runbei Electric Power, Three Gorges Intelligent Control, Pulong Technology, Wallis Intelligent Technology, Huily Technology, BingooRobot, SROD Robotics |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
