What is Global Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Satellite Market?
The Global Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Satellite Market is a rapidly evolving sector that focuses on the development and deployment of satellites equipped with SAR technology. SAR is a form of radar used to create two-dimensional images or three-dimensional reconstructions of objects, such as landscapes. Unlike traditional optical imaging, SAR can penetrate clouds, rain, and darkness, making it an invaluable tool for continuous earth observation. This technology is crucial for a variety of applications, including environmental monitoring, disaster management, and military reconnaissance. The market for SAR satellites is expanding due to the increasing demand for high-resolution imagery and data analytics across various industries. As more countries and private companies invest in space technology, the competition and innovation within the SAR satellite market are expected to intensify. This growth is further fueled by advancements in satellite technology, which are making SAR systems more affordable and accessible. The global market is characterized by a mix of established aerospace companies and emerging startups, all vying to capture a share of this lucrative market. As the need for real-time, reliable data continues to grow, the Global Synthetic Aperture Radar Satellite Market is poised for significant expansion.
High Orbit, Low Orbit in the Global Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Satellite Market:
The Global Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Satellite Market is intricately linked to the concepts of high orbit and low orbit, which refer to the altitudes at which satellites operate. High orbit, often referred to as geostationary orbit, is located approximately 35,786 kilometers above the Earth's equator. Satellites in this orbit move at the same rotational speed as the Earth, allowing them to remain fixed over a particular point. This makes high orbit ideal for communication satellites, weather monitoring, and certain types of earth observation, including some SAR applications. However, the high altitude can result in lower resolution images due to the greater distance from the Earth's surface. On the other hand, low Earth orbit (LEO) is situated between 160 to 2,000 kilometers above the Earth. Satellites in LEO travel at much higher speeds and can circle the Earth in about 90 to 120 minutes. This orbit is particularly advantageous for SAR satellites as it allows for higher resolution imaging due to the proximity to the Earth's surface. LEO is also beneficial for applications requiring frequent revisits to the same location, such as environmental monitoring, disaster response, and military reconnaissance. The choice between high and low orbit depends on the specific requirements of the SAR mission, including the desired resolution, coverage area, and revisit frequency. As the demand for SAR data grows, satellite operators are increasingly deploying constellations of small satellites in LEO to provide comprehensive and timely coverage. These constellations can offer near-real-time data, which is crucial for applications like disaster management and military operations. The trend towards smaller, more cost-effective satellites in LEO is also driving innovation in the SAR satellite market, as companies seek to balance performance with affordability. In contrast, high orbit SAR satellites, while less common, are still valuable for applications requiring continuous coverage of large areas, such as ocean monitoring and climate studies. The interplay between high and low orbit in the SAR satellite market highlights the diverse needs of end-users and the technological advancements that are shaping the future of earth observation. As the market continues to evolve, the strategic deployment of SAR satellites across different orbits will be key to meeting the growing demand for high-quality, reliable data.
Commercial Use, Military Use in the Global Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Satellite Market:
The Global Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Satellite Market plays a crucial role in both commercial and military applications, offering unique capabilities that are unmatched by other remote sensing technologies. In the commercial sector, SAR satellites are increasingly used for environmental monitoring, agriculture, and infrastructure management. The ability of SAR to penetrate clouds and operate in all weather conditions makes it ideal for monitoring deforestation, tracking changes in land use, and assessing the health of crops. In agriculture, SAR data can be used to optimize irrigation, monitor crop growth, and predict yields, helping farmers make informed decisions and improve productivity. Infrastructure management is another area where SAR satellites are making a significant impact. By providing detailed images of urban areas, SAR can help detect structural changes, monitor construction progress, and assess the stability of critical infrastructure such as bridges and dams. This information is invaluable for urban planners, engineers, and policymakers who need accurate data to ensure the safety and sustainability of cities. In the military domain, SAR satellites are an essential tool for reconnaissance, surveillance, and intelligence gathering. The ability to capture high-resolution images regardless of weather conditions or time of day makes SAR an invaluable asset for military operations. SAR satellites can be used to monitor troop movements, detect hidden installations, and assess damage after an attack. The real-time data provided by SAR is crucial for decision-making and strategic planning, giving military forces a significant advantage in the field. Additionally, SAR technology is used in border security and maritime surveillance, helping to detect illegal activities such as smuggling and piracy. The versatility and reliability of SAR satellites make them a critical component of modern defense systems. As the demand for accurate, timely data continues to grow, the Global Synthetic Aperture Radar Satellite Market is poised to expand, driven by the diverse needs of commercial and military users. The ongoing advancements in satellite technology, coupled with the increasing affordability of SAR systems, are expected to further enhance the capabilities and applications of SAR satellites in the coming years.
Global Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Satellite Market Outlook:
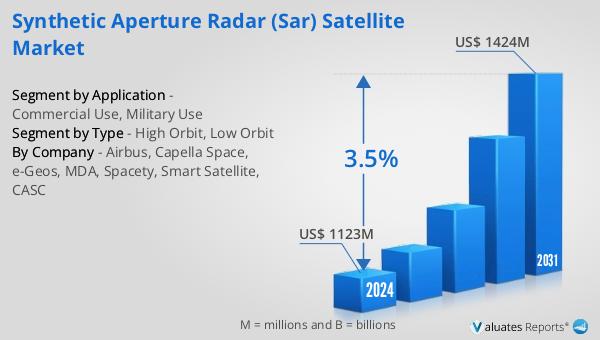
The outlook for the Global Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Satellite Market indicates a promising growth trajectory. The market is anticipated to expand from a valuation of US$ 1123 million in 2024 to US$ 1424 million by 2031. This growth is expected to occur at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.5% from 2025 to 2031. The expansion of this market is largely driven by the critical product segments and the diverse range of end-use applications that SAR technology supports. As industries increasingly rely on high-resolution imagery and data analytics, the demand for SAR satellites is set to rise. The ability of SAR to provide reliable data under all weather conditions and during both day and night is a significant factor contributing to its growing adoption. This technology is not only enhancing capabilities in traditional sectors like military and environmental monitoring but is also opening new opportunities in commercial areas such as agriculture and infrastructure management. The competitive landscape of the SAR satellite market is characterized by a mix of established aerospace companies and innovative startups, all striving to capture a share of this expanding market. As technological advancements continue to make SAR systems more affordable and accessible, the market is expected to witness increased investment and innovation. The strategic deployment of SAR satellites across different orbits will be crucial in meeting the diverse needs of end-users and sustaining the market's growth momentum.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Satellite Market |
| Accounted market size in 2024 | US$ 1123 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 1424 million |
| CAGR | 3.5% |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Sales by Region |
|
| By Company | Airbus, Capella Space, e-Geos, MDA, Spacety, Smart Satellite, CASC |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
