What is Global Hyperspectral Imaging for Food And Agriculture Market?
Global hyperspectral imaging for the food and agriculture market is an innovative technology that uses advanced imaging techniques to capture and analyze a wide spectrum of light beyond what the human eye can see. This technology is particularly useful in the food and agriculture sectors because it allows for the detailed analysis of crops, soil, and food products. By capturing images at different wavelengths, hyperspectral imaging can identify the chemical composition, moisture content, and even the ripeness of fruits and vegetables. This level of detail helps farmers and food producers make informed decisions about crop management, harvesting, and quality control. The technology is also used to detect contaminants and ensure food safety, making it an invaluable tool in maintaining high standards in food production. As the demand for sustainable and efficient agricultural practices grows, the adoption of hyperspectral imaging is expected to increase, providing significant benefits in terms of productivity and quality assurance. This technology not only enhances the efficiency of agricultural operations but also contributes to the overall sustainability of food production systems by reducing waste and optimizing resource use.
Visible/Near Infrared (VNIR), Short Wave Infrared (SWIR), Medium Wave Infrared (MWIR), Long Wave Infrared (LWIR), Others in the Global Hyperspectral Imaging for Food And Agriculture Market:
Visible/Near Infrared (VNIR), Short Wave Infrared (SWIR), Medium Wave Infrared (MWIR), and Long Wave Infrared (LWIR) are different spectral ranges used in hyperspectral imaging, each offering unique benefits for the food and agriculture market. VNIR, which covers the spectral range from approximately 400 to 1000 nanometers, is particularly useful for detecting surface features and assessing the health of plants. It can identify chlorophyll content and other pigments, which are indicators of plant health and stress levels. This information is crucial for precision agriculture, where farmers aim to optimize the use of resources like water and fertilizers. SWIR, ranging from about 1000 to 2500 nanometers, penetrates deeper into the material and is effective in identifying moisture content and chemical composition. This makes it valuable for assessing the quality and ripeness of fruits and vegetables, as well as detecting foreign objects or contaminants in food products. MWIR, covering the range from 2500 to 5000 nanometers, is less commonly used in agriculture but can provide insights into thermal properties and water content, which are important for understanding plant transpiration and soil moisture levels. LWIR, which spans from 8000 to 14000 nanometers, is primarily used for thermal imaging and can detect temperature variations in crops and soil. This information is vital for managing irrigation and preventing heat stress in plants. Each of these spectral ranges offers distinct advantages, and when combined, they provide a comprehensive view of the agricultural landscape, enabling more precise and informed decision-making. The integration of these technologies into agricultural practices not only enhances productivity but also supports sustainable farming by reducing resource wastage and improving crop yields. As the technology continues to evolve, the potential applications of hyperspectral imaging in the food and agriculture sectors are expected to expand, offering new opportunities for innovation and efficiency.
Food Industry, Agriculture in the Global Hyperspectral Imaging for Food And Agriculture Market:
The usage of global hyperspectral imaging in the food industry and agriculture is transforming these sectors by providing detailed insights that were previously unattainable. In the food industry, hyperspectral imaging is used to ensure quality control and safety. It can detect contaminants, foreign objects, and even subtle changes in food composition that might indicate spoilage or degradation. This technology allows for non-destructive testing, meaning that food products can be analyzed without being damaged, preserving their market value. Additionally, hyperspectral imaging can be used to sort and grade food products based on quality, size, and ripeness, ensuring that only the best products reach consumers. In agriculture, hyperspectral imaging is a powerful tool for precision farming. It provides detailed information about crop health, soil conditions, and environmental factors, enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions. For instance, it can identify areas of a field that require more or less water, fertilizer, or pesticides, optimizing resource use and reducing environmental impact. This technology also helps in monitoring crop growth and predicting yields, allowing farmers to plan their operations more effectively. Furthermore, hyperspectral imaging can aid in the early detection of plant diseases and pest infestations, enabling timely interventions that can save crops and reduce losses. By providing a comprehensive view of the agricultural landscape, hyperspectral imaging supports sustainable farming practices and enhances food security. As the technology becomes more accessible and affordable, its adoption is expected to increase, driving innovation and efficiency in the food and agriculture sectors.
Global Hyperspectral Imaging for Food And Agriculture Market Outlook:
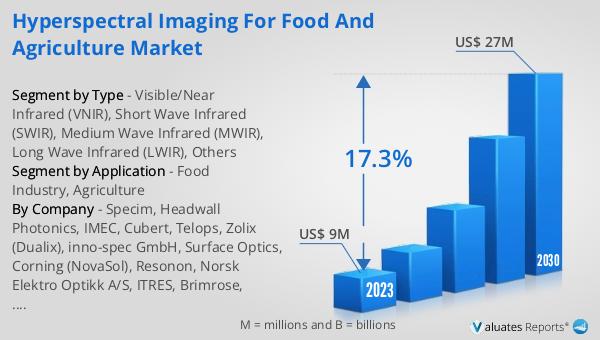
The global market for hyperspectral imaging in food and agriculture was valued at $21.88 million in 2024 and is anticipated to grow significantly, reaching an estimated $40.48 million by 2031. This growth represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.3% over the forecast period. This upward trend is driven by the increasing demand for advanced imaging technologies that can enhance productivity and quality in the food and agriculture sectors. As the world population continues to grow, there is a pressing need for sustainable and efficient agricultural practices that can meet the rising demand for food. Hyperspectral imaging offers a solution by providing detailed insights into crop health, soil conditions, and food quality, enabling more informed decision-making. The technology's ability to detect contaminants and ensure food safety is also a significant factor contributing to its growing adoption. As more industries recognize the benefits of hyperspectral imaging, its market presence is expected to expand, offering new opportunities for innovation and efficiency. This growth not only reflects the increasing importance of advanced imaging technologies in agriculture and food production but also highlights the potential for hyperspectral imaging to drive positive change in these sectors.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Hyperspectral Imaging for Food And Agriculture Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 21.88 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 40.48 million |
| CAGR | 9.3% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Dimensions |
|
| Segment by Technology |
|
| Segment by Platform |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Production by Region |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Specim, Headwall Photonics, IMEC, Norsk Elektro Optikk A/S, Cubert, Corning (NovaSol), Telops, Zolix (Dualix), Surface Optics, Wayho Technology, Resonon, ITRES, Brimrose, BaySpec, Spectra vista, TruTag, HHIT, Optosky |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
