What is Global 300 mm Wafer Electrostatic Chucks (ESC) Market?
The Global 300 mm Wafer Electrostatic Chucks (ESC) Market is a specialized segment within the semiconductor industry, focusing on the production and utilization of electrostatic chucks designed for 300 mm wafers. These chucks are critical components in semiconductor manufacturing, as they securely hold silicon wafers in place during various processing stages, such as etching, deposition, and lithography. The demand for 300 mm wafer ESCs is driven by the increasing production of semiconductors, which are essential for a wide range of electronic devices, from smartphones to advanced computing systems. As technology advances, the need for more efficient and precise manufacturing processes grows, making ESCs indispensable in achieving high yields and maintaining the quality of semiconductor products. The market is characterized by continuous innovation, with manufacturers striving to enhance the performance and reliability of ESCs to meet the evolving needs of the semiconductor industry. This market is also influenced by the broader trends in the electronics sector, including the push for miniaturization and the development of new materials and technologies. Overall, the Global 300 mm Wafer ESC Market plays a crucial role in supporting the semiconductor industry's growth and technological advancement.
Coulomb Type Electrostatic Chuck, Johnsen-Rahbek (JR) Type Electrostatic Chuck in the Global 300 mm Wafer Electrostatic Chucks (ESC) Market:
Coulomb Type Electrostatic Chucks and Johnsen-Rahbek (JR) Type Electrostatic Chucks are two primary types of electrostatic chucks used in the Global 300 mm Wafer Electrostatic Chucks (ESC) Market. The Coulomb Type Electrostatic Chuck operates on the principle of Coulomb's law, which describes the force between two charged objects. In this type of chuck, an electric field is generated between the chuck and the wafer, creating an attractive force that holds the wafer in place. This method is highly effective for handling wafers during various semiconductor manufacturing processes, as it provides a strong and stable hold without the need for mechanical clamping. The Coulomb Type ESC is particularly advantageous in processes that require high precision and minimal contamination, as it reduces the risk of physical damage to the wafer surface. On the other hand, the Johnsen-Rahbek (JR) Type Electrostatic Chuck operates on a different principle, utilizing the Johnsen-Rahbek effect. This effect involves the generation of an electrostatic force through the interaction of a dielectric material with an electric field. The JR Type ESC is known for its ability to provide a more uniform and consistent hold across the wafer surface, making it ideal for applications that demand high uniformity and precision. One of the key advantages of the JR Type ESC is its ability to maintain a stable hold even in the presence of temperature fluctuations, which is crucial in semiconductor manufacturing processes that involve high temperatures. Additionally, the JR Type ESC is often preferred in applications where the wafer needs to be held securely during rapid movements or changes in orientation. Both types of electrostatic chucks have their unique advantages and are chosen based on the specific requirements of the semiconductor manufacturing process. The choice between Coulomb Type and JR Type ESCs depends on factors such as the type of process, the level of precision required, and the operating conditions. As the semiconductor industry continues to evolve, manufacturers are constantly working to improve the performance and reliability of both types of electrostatic chucks, ensuring they meet the demands of modern semiconductor manufacturing. The development of new materials and technologies is also playing a significant role in enhancing the capabilities of these chucks, enabling them to handle increasingly complex and demanding manufacturing processes. Overall, both Coulomb Type and JR Type Electrostatic Chucks are essential components in the Global 300 mm Wafer ESC Market, each offering unique benefits that contribute to the efficiency and effectiveness of semiconductor manufacturing.
Fab, Semiconductor Equipment Factory in the Global 300 mm Wafer Electrostatic Chucks (ESC) Market:
The usage of Global 300 mm Wafer Electrostatic Chucks (ESC) Market in fabs and semiconductor equipment factories is integral to the production of semiconductors. In a fab, which is a semiconductor fabrication plant, ESCs are used extensively throughout the manufacturing process. These chucks are crucial for holding the wafers securely during various stages of production, such as etching, deposition, and lithography. The precision and stability provided by ESCs are essential for ensuring the accuracy and quality of the semiconductor devices being produced. In fabs, the use of 300 mm wafer ESCs allows for the efficient handling of larger wafers, which is critical for increasing production capacity and reducing costs. The ability to process larger wafers means that more chips can be produced from a single wafer, leading to higher yields and improved profitability for semiconductor manufacturers. In semiconductor equipment factories, ESCs are used in the design and development of the equipment used in fabs. These factories rely on ESCs to test and validate the performance of their equipment, ensuring that it meets the stringent requirements of the semiconductor industry. The use of ESCs in equipment factories is essential for developing new technologies and processes that enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of semiconductor manufacturing. The integration of ESCs into semiconductor equipment also plays a crucial role in improving the overall performance and reliability of the manufacturing process. By providing a stable and secure hold on the wafers, ESCs help to minimize the risk of defects and improve the quality of the final product. This is particularly important in the production of advanced semiconductor devices, where even minor defects can have a significant impact on performance. The use of ESCs in fabs and equipment factories also supports the industry's push for greater automation and precision in manufacturing. As the demand for semiconductors continues to grow, manufacturers are increasingly looking for ways to streamline their production processes and improve efficiency. ESCs play a key role in achieving these goals by enabling the precise and reliable handling of wafers throughout the manufacturing process. Overall, the usage of Global 300 mm Wafer Electrostatic Chucks in fabs and semiconductor equipment factories is essential for supporting the growth and advancement of the semiconductor industry. These chucks provide the precision, stability, and reliability needed to produce high-quality semiconductor devices, while also enabling manufacturers to increase production capacity and reduce costs. As the industry continues to evolve, the role of ESCs in fabs and equipment factories will remain critical to the success of semiconductor manufacturing.
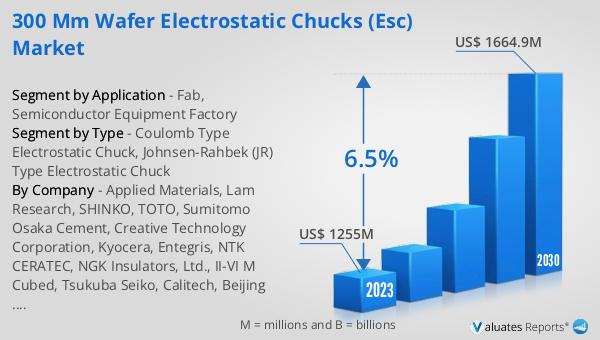
Global 300 mm Wafer Electrostatic Chucks (ESC) Market Outlook:
The global market for 300 mm Wafer Electrostatic Chucks (ESC) was valued at $1,208 million in 2024 and is anticipated to expand to a revised size of $1,865 million by 2031, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% over the forecast period. Applied Materials emerged as the market leader, capturing a significant 43.84% share of the revenue market. Following closely, Lam Research secured a 31.58% revenue share, while SHINKO held a 10.21% share. This market outlook highlights the competitive landscape and the dominance of key players in the industry. The growth trajectory of the market is driven by the increasing demand for semiconductors, which are essential components in a wide range of electronic devices. As technology continues to advance, the need for efficient and precise manufacturing processes becomes more critical, further fueling the demand for 300 mm wafer ESCs. The market's expansion is also supported by ongoing innovations and improvements in ESC technology, which enhance the performance and reliability of these critical components. As the semiconductor industry continues to grow, the Global 300 mm Wafer ESC Market is poised to play a vital role in supporting the production of high-quality semiconductor devices.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | 300 mm Wafer Electrostatic Chucks (ESC) Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 1208 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 1865 million |
| CAGR | 6.5% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| by Type |
|
| by Application |
|
| Production by Region |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Applied Materials, Lam Research, SHINKO, TOTO, Sumitomo Osaka Cement, Creative Technology Corporation, Kyocera, Entegris, NTK CERATEC, NGK Insulators, Ltd., II-VI M Cubed, Tsukuba Seiko, Calitech, Beijing U-PRECISION TECH CO., LTD. |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |