What is Grid Battery Storage Systems - Global Market?
Grid battery storage systems are an essential component of modern energy infrastructure, designed to store electricity for later use. These systems play a crucial role in balancing supply and demand, ensuring a stable and reliable power supply. They are particularly important as the world shifts towards renewable energy sources like solar and wind, which are intermittent by nature. By storing excess energy generated during peak production times, grid battery storage systems can release this energy when production is low or demand is high. This capability helps to smooth out fluctuations in energy supply, reducing the need for fossil fuel-based backup power and enhancing grid stability. Additionally, these systems can provide ancillary services such as frequency regulation and voltage support, further contributing to grid reliability. As the global energy landscape evolves, the demand for efficient and scalable grid battery storage solutions is expected to grow, driven by technological advancements and supportive policy frameworks.
Lithium-Ion Batteries, Sodium–Sulfur Batteries, Lead-Acid Batteries, Others in the Grid Battery Storage Systems - Global Market:
Lithium-ion batteries are the most widely used type of battery in grid storage systems due to their high energy density, efficiency, and long cycle life. They are favored for their ability to quickly charge and discharge, making them ideal for applications that require rapid response times. Lithium-ion batteries are also relatively lightweight and compact, which allows for more flexible installation options. However, they can be expensive to produce, and there are concerns about the availability of raw materials like lithium and cobalt, which are essential for their manufacture. Despite these challenges, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving the cost-effectiveness and sustainability of lithium-ion technology. Sodium-sulfur batteries, on the other hand, are known for their high energy capacity and long discharge duration, making them suitable for large-scale energy storage applications. These batteries operate at high temperatures and are typically used in utility-scale projects where space and thermal management are less of a concern. Sodium-sulfur batteries are less expensive than lithium-ion batteries and do not rely on scarce materials, but they require careful handling due to their corrosive nature and the high temperatures at which they operate. Lead-acid batteries are one of the oldest types of rechargeable batteries and are known for their reliability and low cost. They are commonly used in applications where cost is a primary concern and where the weight and size of the battery are not critical factors. However, lead-acid batteries have a relatively low energy density and shorter cycle life compared to other battery types, which limits their use in modern grid storage systems. Efforts to improve lead-acid technology are ongoing, with a focus on enhancing their energy density and cycle life. Other types of batteries used in grid storage systems include flow batteries, which store energy in liquid electrolytes contained in external tanks. Flow batteries offer the advantage of being able to independently scale power and energy capacity, making them highly adaptable to different storage needs. They are also known for their long cycle life and ability to provide a steady output over extended periods. However, flow batteries can be complex and costly to implement, which has limited their widespread adoption. As the grid battery storage market continues to evolve, a diverse range of battery technologies will likely coexist, each serving specific applications and requirements.
Residential, Utility & Commercial in the Grid Battery Storage Systems - Global Market:
Grid battery storage systems are utilized across various sectors, including residential, utility, and commercial applications, each with unique requirements and benefits. In residential settings, these systems are often used in conjunction with rooftop solar panels to store excess energy generated during the day for use at night or during cloudy periods. This not only helps homeowners reduce their reliance on the grid but also provides a backup power source during outages. Residential battery storage systems can also enable homeowners to participate in demand response programs, where they can sell stored energy back to the grid during peak demand periods, potentially earning financial incentives. In the utility sector, grid battery storage systems are deployed at a larger scale to enhance grid stability and integrate renewable energy sources. Utilities use these systems to store energy generated from solar farms or wind turbines, releasing it when production is low or demand is high. This helps to reduce the need for fossil fuel-based peaker plants, which are typically used to meet peak demand but are less efficient and more polluting. Utility-scale battery storage systems can also provide ancillary services such as frequency regulation and voltage support, which are essential for maintaining grid reliability. In commercial applications, businesses use grid battery storage systems to manage their energy consumption more effectively and reduce costs. By storing energy during off-peak hours when electricity rates are lower, businesses can draw on this stored energy during peak periods, reducing their overall energy costs. Commercial battery storage systems can also provide backup power during outages, ensuring business continuity. Additionally, businesses can participate in demand response programs, similar to residential users, by selling excess stored energy back to the grid. As the cost of battery storage technology continues to decline and the benefits become more widely recognized, the adoption of grid battery storage systems across these sectors is expected to increase, contributing to a more resilient and sustainable energy future.
Grid Battery Storage Systems - Global Market Outlook:
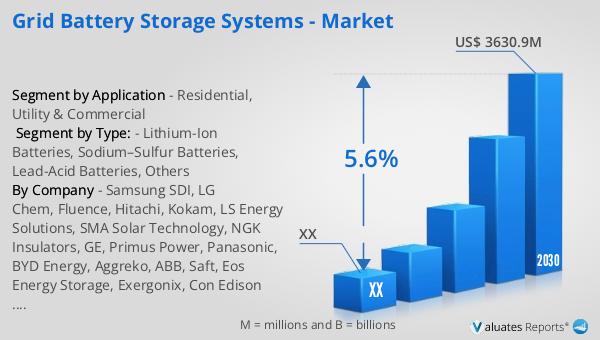
The global market for grid battery storage systems was valued at approximately $2,596.3 million in 2023, with projections indicating a growth to around $3,630.9 million by 2030. This growth represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.6% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2030. The market is primarily driven by the increasing demand for reliable and efficient energy storage solutions, as well as the growing integration of renewable energy sources into the power grid. China, Europe, and the United States are at the forefront of this market, collectively accounting for 86% of the global market share. These regions have been leading the development and deployment of grid battery storage systems, supported by favorable government policies, technological advancements, and significant investments in renewable energy infrastructure. As these regions continue to expand their renewable energy capacity, the demand for grid battery storage systems is expected to rise, further driving market growth. The focus on reducing carbon emissions and enhancing energy security is also contributing to the increasing adoption of these systems worldwide. As the market evolves, it is anticipated that new technologies and business models will emerge, further shaping the landscape of the global grid battery storage market.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Grid Battery Storage Systems - Market |
| Forecasted market size in 2030 | US$ 3630.9 million |
| CAGR | 5.6% |
| Forecasted years | 2024 - 2030 |
| Segment by Type: |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| By Company | Samsung SDI, LG Chem, Fluence, Hitachi, Kokam, LS Energy Solutions, SMA Solar Technology, NGK Insulators, GE, Primus Power, Panasonic, BYD Energy, Aggreko, ABB, Saft, Eos Energy Storage, Exergonix, Con Edison Solutions, East Penn Manufacturing, Enerdel |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
