What is Global Geothermal Steam Turbine Market?
The Global Geothermal Steam Turbine Market is a specialized segment within the broader energy sector, focusing on the use of geothermal energy to generate electricity. Geothermal steam turbines are essential components in geothermal power plants, where they convert steam from geothermal reservoirs into mechanical energy, which is then transformed into electrical energy. This market is driven by the increasing demand for sustainable and renewable energy sources, as geothermal energy is both environmentally friendly and reliable. Unlike solar or wind energy, geothermal energy is not dependent on weather conditions, making it a stable and continuous source of power. The market encompasses various types of turbines, including those designed for different power capacities and operational conditions. As countries strive to reduce carbon emissions and transition to cleaner energy sources, the global geothermal steam turbine market is expected to grow, supported by technological advancements and government incentives. The market's growth is also influenced by the availability of geothermal resources, technological innovations, and the cost-effectiveness of geothermal energy compared to other renewable sources. Overall, the Global Geothermal Steam Turbine Market plays a crucial role in the global shift towards sustainable energy solutions.
Above 300 MW, Below 300 MW in the Global Geothermal Steam Turbine Market:
In the Global Geothermal Steam Turbine Market, turbines are categorized based on their power capacity, with two primary segments: Above 300 MW and Below 300 MW. Turbines with a capacity Above 300 MW are typically used in large-scale geothermal power plants. These turbines are designed to handle significant amounts of steam and are often employed in regions with abundant geothermal resources. The high capacity of these turbines allows for the generation of substantial amounts of electricity, making them suitable for meeting the energy demands of large urban areas or industrial zones. The efficiency and reliability of these turbines are critical, as they must operate continuously to provide a stable power supply. On the other hand, turbines with a capacity Below 300 MW are more versatile and can be used in a variety of settings, including smaller power plants and remote locations. These turbines are often employed in areas where geothermal resources are less abundant or where the energy demand is lower. They offer flexibility in installation and operation, making them ideal for decentralized power generation. The choice between Above 300 MW and Below 300 MW turbines depends on several factors, including the availability of geothermal resources, the energy needs of the area, and the economic considerations of the project. Both segments play a vital role in the global geothermal steam turbine market, contributing to the diversification and resilience of the energy supply. The development and deployment of these turbines are supported by ongoing research and innovation, which aim to enhance their efficiency, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impacts. As the demand for renewable energy continues to rise, the Global Geothermal Steam Turbine Market is expected to expand, driven by the need for sustainable and reliable power generation solutions. The market's growth is further supported by government policies and incentives that promote the use of clean energy technologies. In conclusion, the segmentation of the Global Geothermal Steam Turbine Market into Above 300 MW and Below 300 MW categories reflects the diverse applications and capabilities of geothermal steam turbines, highlighting their importance in the transition to a more sustainable energy future.
Small Power Plant, Large Power Plant in the Global Geothermal Steam Turbine Market:
The Global Geothermal Steam Turbine Market finds its application in both small and large power plants, each serving distinct purposes and catering to different energy needs. Small power plants, typically utilizing turbines with a capacity Below 300 MW, are often deployed in remote or rural areas where the energy demand is lower. These plants provide a reliable and continuous power supply, which is crucial for communities that may not have access to the main power grid. The use of geothermal steam turbines in small power plants offers several advantages, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions, lower operational costs, and minimal environmental impact. These plants can be quickly set up and are often used to support local industries, agriculture, and residential areas, contributing to regional development and energy independence. In contrast, large power plants, equipped with turbines Above 300 MW, are designed to meet the energy demands of densely populated urban areas or industrial regions. These plants require significant geothermal resources and are often located in areas with high geothermal activity. The large-scale generation capacity of these plants allows them to supply electricity to a vast number of consumers, supporting economic growth and industrial activities. The efficiency and reliability of geothermal steam turbines in large power plants are critical, as they must operate continuously to ensure a stable power supply. The integration of advanced technologies and innovative designs in these turbines enhances their performance, reduces maintenance costs, and extends their operational lifespan. Both small and large power plants play a crucial role in the Global Geothermal Steam Turbine Market, contributing to the diversification and resilience of the energy supply. The deployment of geothermal steam turbines in these plants supports the global transition to renewable energy sources, helping to reduce carbon emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change. As the demand for clean and sustainable energy continues to grow, the Global Geothermal Steam Turbine Market is expected to expand, driven by technological advancements, government incentives, and the increasing awareness of the environmental benefits of geothermal energy. In summary, the application of geothermal steam turbines in small and large power plants highlights their versatility and importance in the global energy landscape, supporting the shift towards a more sustainable and resilient energy future.
Global Geothermal Steam Turbine Market Outlook:
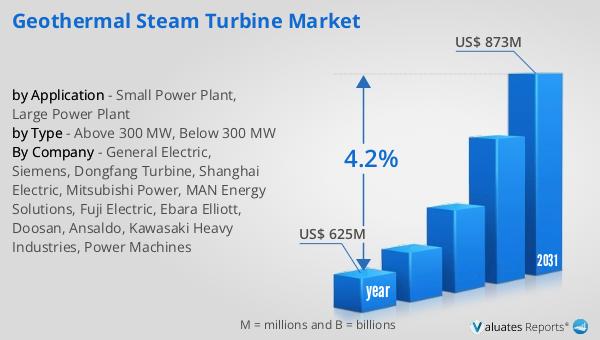
The outlook for the Global Geothermal Steam Turbine Market indicates a promising growth trajectory. In 2024, the market was valued at approximately US$ 625 million. By 2031, it is anticipated to reach an estimated size of US$ 873 million, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.2% over the forecast period. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for renewable energy sources and the global push towards reducing carbon emissions. Geothermal steam turbines play a crucial role in this transition, offering a reliable and sustainable solution for power generation. The market's expansion is supported by technological advancements that enhance the efficiency and performance of geothermal steam turbines, making them more cost-effective and environmentally friendly. Additionally, government policies and incentives aimed at promoting clean energy technologies further bolster the market's growth prospects. As countries around the world strive to meet their renewable energy targets, the Global Geothermal Steam Turbine Market is poised to play a significant role in the global energy landscape. The market's growth reflects the broader trend towards sustainable energy solutions, highlighting the importance of geothermal energy in achieving a low-carbon future. In conclusion, the Global Geothermal Steam Turbine Market is set to experience steady growth, driven by the increasing demand for clean energy and the ongoing efforts to combat climate change.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Geothermal Steam Turbine Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 625 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 873 million |
| CAGR | 4.2% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| by Type |
|
| by Application |
|
| Production by Region |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | General Electric, Siemens, Dongfang Turbine, Shanghai Electric, Mitsubishi Power, MAN Energy Solutions, Fuji Electric, Ebara Elliott, Doosan, Ansaldo, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Power Machines |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |