What is Global Synthetic Antibody Market?
The Global Synthetic Antibody Market is a rapidly evolving sector within the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries. Synthetic antibodies are engineered proteins designed to mimic the immune system's ability to fight off harmful pathogens. Unlike traditional antibodies derived from living organisms, synthetic antibodies are created using advanced technologies that allow for precise targeting and enhanced stability. This market is driven by the increasing demand for targeted therapies in treating various diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, and infectious diseases. The ability of synthetic antibodies to be customized for specific antigens makes them a valuable tool in both therapeutic and diagnostic applications. Additionally, advancements in genetic engineering and biotechnology have facilitated the development of more efficient and cost-effective synthetic antibodies, further propelling market growth. As healthcare systems worldwide continue to seek innovative solutions for complex medical challenges, the Global Synthetic Antibody Market is poised for significant expansion, offering promising opportunities for research, development, and commercialization. The market's growth is also supported by collaborations between biotech companies and research institutions, aiming to harness the full potential of synthetic antibodies in improving patient outcomes and advancing personalized medicine.
Recombinant Antibodies, Non-Immunoglobulin Derived Synthetic Antibodies in the Global Synthetic Antibody Market:
Recombinant antibodies and non-immunoglobulin derived synthetic antibodies are two pivotal components of the Global Synthetic Antibody Market. Recombinant antibodies are produced using recombinant DNA technology, which involves inserting the gene encoding the desired antibody into a host cell, such as bacteria or yeast, to produce the antibody in large quantities. This method allows for the production of highly specific and consistent antibodies, which are crucial for both therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. Recombinant antibodies offer several advantages over traditional monoclonal antibodies, including reduced risk of contamination, improved scalability, and the ability to engineer antibodies with enhanced properties, such as increased affinity and stability. These attributes make recombinant antibodies an attractive option for developing targeted therapies for a wide range of diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, and infectious diseases. On the other hand, non-immunoglobulin derived synthetic antibodies represent a novel class of binding proteins that are engineered to mimic the antigen-binding properties of traditional antibodies without being derived from immunoglobulin structures. These synthetic antibodies are designed using advanced protein engineering techniques, allowing for the creation of highly specific and stable binding proteins that can be tailored to target specific antigens. Non-immunoglobulin derived synthetic antibodies offer several advantages, including smaller size, increased stability, and the ability to penetrate tissues more effectively than traditional antibodies. These properties make them particularly useful in applications where traditional antibodies may be limited, such as in targeting intracellular antigens or crossing the blood-brain barrier. The development of non-immunoglobulin derived synthetic antibodies is an exciting area of research, with the potential to revolutionize the field of targeted therapies and diagnostics. As the Global Synthetic Antibody Market continues to grow, the demand for both recombinant antibodies and non-immunoglobulin derived synthetic antibodies is expected to increase, driven by the need for more effective and personalized treatment options. The ongoing advancements in biotechnology and protein engineering are likely to further enhance the capabilities of these synthetic antibodies, opening up new possibilities for their use in a wide range of medical applications. The collaboration between academic institutions, biotech companies, and pharmaceutical firms is crucial in driving innovation and translating research findings into clinical applications. As a result, the Global Synthetic Antibody Market is poised for significant growth, offering promising opportunities for the development of novel therapies and diagnostics that can improve patient outcomes and address unmet medical needs.
Cancer, Poisoning, Viral Infections, Septicemia, Autoimmune Diseases, Others in the Global Synthetic Antibody Market:
The Global Synthetic Antibody Market plays a crucial role in addressing various medical conditions, including cancer, poisoning, viral infections, septicemia, autoimmune diseases, and others. In the field of cancer treatment, synthetic antibodies are used to develop targeted therapies that specifically attack cancer cells while sparing healthy tissues. This targeted approach helps to minimize side effects and improve the efficacy of cancer treatments. Synthetic antibodies can be engineered to recognize specific antigens expressed on the surface of cancer cells, allowing for precise targeting and destruction of these cells. In cases of poisoning, synthetic antibodies can be used as antidotes to neutralize toxins and prevent further harm to the body. These antibodies are designed to bind to specific toxins, rendering them inactive and facilitating their removal from the body. This application is particularly valuable in cases of snake bites, drug overdoses, and exposure to chemical agents. In the realm of viral infections, synthetic antibodies are being developed to target and neutralize specific viruses, offering a promising approach to treating diseases such as HIV, influenza, and COVID-19. These antibodies can be engineered to block viral entry into host cells or to enhance the immune system's ability to clear the infection. In the treatment of septicemia, synthetic antibodies can be used to target and neutralize bacterial toxins, reducing inflammation and preventing organ damage. This approach has the potential to improve outcomes in patients with severe bacterial infections and sepsis. Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, are characterized by the immune system attacking the body's own tissues. Synthetic antibodies can be designed to modulate the immune response, reducing inflammation and preventing tissue damage. This targeted approach offers a more precise and effective treatment option compared to traditional immunosuppressive therapies. Beyond these specific applications, synthetic antibodies are also being explored for use in a variety of other medical conditions, including neurological disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic disorders. The versatility and specificity of synthetic antibodies make them a valuable tool in the development of personalized medicine, allowing for tailored treatment approaches that address the unique needs of individual patients. As research and development in the field of synthetic antibodies continue to advance, the potential applications of these innovative therapies are expected to expand, offering new hope for patients with a wide range of medical conditions.
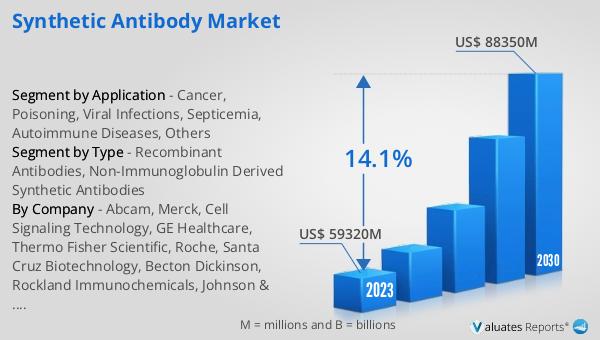
Global Synthetic Antibody Market Outlook:
The outlook for the Global Synthetic Antibody Market is promising, with significant growth anticipated in the coming years. In 2023, the market was valued at approximately $59,320 million, reflecting the increasing demand for innovative therapeutic and diagnostic solutions. By 2030, the market is expected to reach an impressive $88,350 million, driven by a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.1% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2030. This robust growth is indicative of the expanding applications of synthetic antibodies in various medical fields, including oncology, infectious diseases, and autoimmune disorders. The market's expansion is also supported by ongoing advancements in biotechnology and protein engineering, which are enhancing the capabilities and efficiency of synthetic antibodies. Additionally, the growing emphasis on personalized medicine and targeted therapies is fueling the demand for synthetic antibodies, as they offer the potential for more precise and effective treatment options. The collaboration between academic institutions, biotech companies, and pharmaceutical firms is playing a crucial role in driving innovation and translating research findings into clinical applications. As a result, the Global Synthetic Antibody Market is poised for significant growth, offering promising opportunities for the development of novel therapies and diagnostics that can improve patient outcomes and address unmet medical needs.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Synthetic Antibody Market |
| Accounted market size in 2023 | US$ 59320 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2030 | US$ 88350 million |
| CAGR | 14.1% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecasted years | 2024 - 2030 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Abcam, Merck, Cell Signaling Technology, GE Healthcare, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Roche, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Becton Dickinson, Rockland Immunochemicals, Johnson & Johnson |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
