What is Global Emergency Food Market?
The Global Emergency Food Market is a crucial segment of the food industry that focuses on providing essential nutrition during times of crisis. This market encompasses a wide range of food products designed to be stored for long periods and consumed when regular food supplies are disrupted. These disruptions can be due to natural disasters, wars, or other emergencies that make accessing fresh food challenging. Emergency food products are typically non-perishable, easy to prepare, and nutritionally balanced to sustain individuals during difficult times. They include items like canned goods, freeze-dried meals, and high-energy bars. The market is driven by the increasing frequency of natural disasters and geopolitical tensions, which have heightened the need for reliable food reserves. Additionally, growing awareness about emergency preparedness among individuals and governments has further fueled demand. Companies in this market are continually innovating to improve the taste, nutritional value, and shelf life of their products, ensuring they meet the diverse needs of consumers worldwide. As a result, the Global Emergency Food Market plays a vital role in enhancing food security and resilience in the face of unforeseen challenges.
High-calorie, Low-calorie in the Global Emergency Food Market:
In the Global Emergency Food Market, products are often categorized based on their caloric content, specifically into high-calorie and low-calorie options. High-calorie emergency foods are designed to provide a substantial amount of energy in a compact form, making them ideal for situations where individuals need to maintain their energy levels without access to regular meals. These foods are typically rich in carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, offering a balanced nutritional profile that supports physical activity and sustenance during emergencies. Common examples include energy bars, meal replacement shakes, and freeze-dried meals that can be easily rehydrated. These products are particularly valuable in scenarios where individuals are engaged in physically demanding tasks, such as rescue operations or military missions, where maintaining energy levels is crucial. On the other hand, low-calorie emergency foods are designed for situations where individuals may be less active or where rationing is necessary to extend food supplies over a longer period. These products focus on providing essential nutrients without excessive caloric intake, helping to prevent malnutrition while conserving resources. Low-calorie options often include soups, broths, and nutrient-dense snacks that offer vitamins and minerals without a high energy load. The choice between high-calorie and low-calorie emergency foods depends on the specific needs of the situation and the individuals involved. For instance, in a natural disaster scenario where people are displaced and have limited access to food, high-calorie options may be prioritized to ensure they receive adequate energy. Conversely, in a prolonged crisis where food supplies are limited, low-calorie options may be used to stretch resources while still providing necessary nutrition. The balance between these two types of emergency foods is crucial for effective crisis management, ensuring that individuals receive the right amount of energy and nutrients to sustain them through challenging times. Companies in the Global Emergency Food Market are continually innovating to improve the nutritional content and palatability of both high-calorie and low-calorie products. This includes developing new formulations that enhance taste, texture, and shelf life, making these foods more appealing and effective for consumers. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on incorporating sustainable and ethically sourced ingredients, reflecting broader trends in the food industry towards environmental responsibility. As the market evolves, the distinction between high-calorie and low-calorie emergency foods will continue to play a significant role in shaping product offerings and meeting the diverse needs of consumers worldwide.
Civil, Military in the Global Emergency Food Market:
The Global Emergency Food Market serves a critical role in various sectors, particularly in civil and military applications. In the civil sector, emergency food products are essential for disaster preparedness and response. Governments and humanitarian organizations stockpile these foods to ensure they can provide immediate relief to affected populations during natural disasters such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods. These foods are designed to be easily distributed and consumed, providing essential nutrition to individuals who may have lost access to regular food supplies. In addition to disaster response, emergency foods are also used in community preparedness programs, encouraging households to maintain a supply of non-perishable foods for potential emergencies. This proactive approach helps to enhance resilience and reduce the impact of crises on communities. In the military sector, emergency food products are a vital component of operational readiness. Military personnel often operate in challenging environments where access to fresh food is limited or non-existent. As such, they rely on specially designed rations that provide the necessary energy and nutrients to sustain them during missions. These rations, often referred to as Meals Ready-to-Eat (MREs), are compact, lightweight, and have a long shelf life, making them ideal for use in the field. The development of military rations has also influenced the broader emergency food market, with innovations in packaging, preservation, and nutritional content being adopted by civilian products. The use of emergency foods in both civil and military contexts highlights the importance of having reliable and effective food solutions during times of crisis. These products not only provide essential nutrition but also contribute to the overall resilience and preparedness of societies and organizations. As the frequency and intensity of emergencies continue to rise, the demand for high-quality emergency food products is expected to grow, driving further innovation and development in the market.
Global Emergency Food Market Outlook:
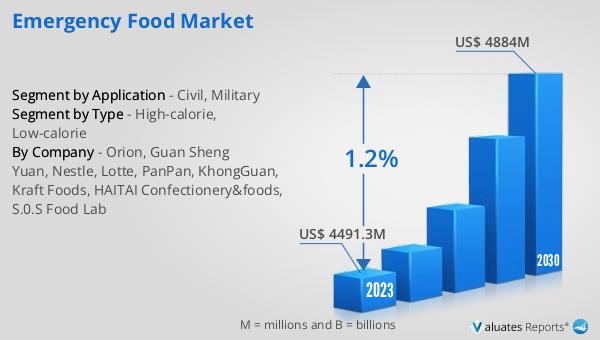
The global market for emergency food was valued at approximately $4,598 million in 2024, reflecting its significant role in addressing food security during crises. Over the years, this market has shown a steady growth trajectory, driven by increasing awareness of the importance of emergency preparedness and the rising frequency of natural and man-made disasters. By 2031, the market is projected to reach an estimated size of $4,989 million, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 1.2% during the forecast period. This growth is indicative of the ongoing demand for reliable and effective food solutions that can be deployed quickly and efficiently in times of need. The market's expansion is supported by advancements in food technology, which have improved the shelf life, nutritional content, and palatability of emergency food products. Additionally, the increasing involvement of governments and non-governmental organizations in disaster preparedness initiatives has further bolstered the market's growth prospects. As the global population continues to face various challenges, the importance of having a robust emergency food market cannot be overstated. It plays a crucial role in ensuring that individuals and communities have access to essential nutrition during times of crisis, thereby enhancing resilience and reducing the impact of emergencies on human lives.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Emergency Food Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 4598 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 4989 million |
| CAGR | 1.2% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Orion, Guan Sheng Yuan, Nestle, Lotte, PanPan, KhongGuan, Kraft Foods, HAITAI Confectionery&foods, S.0.S Food Lab |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
