What is Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment Drug - Global Market?
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a type of liver cancer that is becoming increasingly prevalent worldwide, prompting a significant focus on the development and distribution of treatment drugs. The global market for HCC treatment drugs encompasses a variety of therapeutic options designed to manage and treat this aggressive cancer. These drugs are crucial in improving patient outcomes and quality of life, as they target the cancer cells in the liver, aiming to slow down or stop their growth. The market is driven by factors such as the rising incidence of liver cancer, advancements in medical research, and the development of new and more effective treatment options. Pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in research and development to bring innovative drugs to the market, which is expected to expand as awareness and diagnosis rates increase. The global market for HCC treatment drugs is a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector, reflecting the urgent need for effective therapies in combating this challenging disease.
Chemotherapy Drug, Targeted Therapy Drug in the Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment Drug - Global Market:
Chemotherapy and targeted therapy drugs are two primary categories of treatment options within the global market for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Chemotherapy involves the use of powerful drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from dividing. These drugs are typically administered intravenously or orally and work by targeting rapidly dividing cells, a characteristic of cancer cells. However, chemotherapy can also affect healthy cells, leading to side effects such as fatigue, nausea, and hair loss. Despite these challenges, chemotherapy remains a cornerstone of cancer treatment due to its ability to reach cancer cells throughout the body. In the context of HCC, chemotherapy is often used in combination with other treatments to enhance its effectiveness. On the other hand, targeted therapy drugs represent a more modern approach to cancer treatment. These drugs are designed to specifically target cancer cells by interfering with specific molecules involved in tumor growth and progression. Unlike chemotherapy, targeted therapies aim to minimize damage to healthy cells, potentially reducing side effects. In the treatment of HCC, targeted therapies have shown promise in improving patient outcomes, particularly in cases where the cancer is advanced or has spread to other parts of the body. These therapies work by blocking the signals that tell cancer cells to grow and divide, effectively slowing down or stopping the progression of the disease. The development of targeted therapies has been fueled by advances in our understanding of the molecular and genetic basis of cancer, allowing for the creation of drugs that are tailored to the specific characteristics of a patient's tumor. As a result, targeted therapies are often used in conjunction with other treatments, such as surgery or radiation, to provide a comprehensive approach to cancer care. The global market for HCC treatment drugs is witnessing significant growth due to the increasing adoption of targeted therapies, which offer a more personalized and potentially more effective treatment option for patients. Pharmaceutical companies are actively engaged in research and development to discover new targets and develop drugs that can address the unmet needs of HCC patients. This has led to a robust pipeline of targeted therapies that are expected to drive market growth in the coming years. Overall, the global market for HCC treatment drugs is characterized by a diverse range of therapeutic options, with chemotherapy and targeted therapies playing a central role in the management of this challenging disease.
Below 29 Years, 30-49 Years, Above 50 Years in the Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment Drug - Global Market:
The usage of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) treatment drugs varies across different age groups, reflecting the unique needs and challenges faced by patients at different stages of life. For individuals below 29 years of age, the incidence of HCC is relatively low compared to older age groups. However, when HCC does occur in younger patients, it is often associated with underlying conditions such as hepatitis B or genetic disorders. In this age group, treatment strategies focus on aggressive management to achieve the best possible outcomes. Chemotherapy and targeted therapies are commonly used, with an emphasis on minimizing long-term side effects to preserve quality of life. For patients aged 30 to 49 years, the incidence of HCC begins to increase, often linked to lifestyle factors such as alcohol consumption and obesity, as well as chronic liver diseases. In this demographic, treatment approaches are tailored to the individual's overall health and the stage of the cancer. A combination of chemotherapy, targeted therapies, and surgical interventions may be employed to manage the disease effectively. The goal is to extend survival while maintaining a good quality of life, taking into consideration the patient's personal and professional responsibilities. For individuals above 50 years, the risk of developing HCC is significantly higher, often due to a lifetime of exposure to risk factors such as viral hepatitis and cirrhosis. In this age group, treatment decisions are influenced by the presence of comorbidities and the patient's overall health status. Chemotherapy and targeted therapies remain important components of the treatment regimen, but there is also a greater emphasis on palliative care to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. The global market for HCC treatment drugs is thus shaped by the diverse needs of patients across different age groups, with pharmaceutical companies striving to develop therapies that address the specific challenges faced by each demographic. As the population ages and the incidence of HCC continues to rise, the demand for effective and personalized treatment options is expected to grow, driving further innovation and expansion in the market.
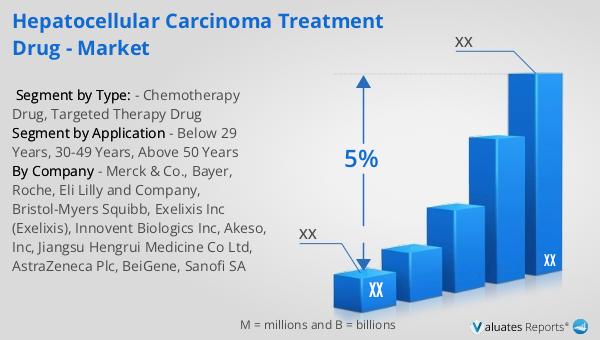
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment Drug - Global Market Outlook:
The global pharmaceutical market was valued at approximately 1,475 billion USD in 2022, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5% over the next six years. This growth is indicative of the increasing demand for pharmaceutical products worldwide, driven by factors such as an aging population, rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and advancements in medical technology. In comparison, the chemical drug market, a significant segment of the broader pharmaceutical industry, experienced growth from 1,005 billion USD in 2018 to an estimated 1,094 billion USD in 2022. This growth reflects the ongoing demand for chemical-based medications, which continue to play a crucial role in the treatment of various health conditions. The chemical drug market's expansion is supported by continuous research and development efforts aimed at improving drug efficacy and safety. As the pharmaceutical landscape evolves, both the overall market and the chemical drug segment are expected to continue their upward trajectory, driven by innovation and the need to address unmet medical needs. The interplay between these markets highlights the dynamic nature of the pharmaceutical industry and its critical role in global healthcare.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment Drug - Market |
| CAGR | 5% |
| Segment by Type: |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| By Company | Merck & Co., Bayer, Roche, Eli Lilly and Company, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Exelixis Inc (Exelixis), Innovent Biologics Inc, Akeso, Inc, Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine Co Ltd, AstraZeneca Plc, BeiGene, Sanofi SA |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |