What is Contactless Inductive Charging - Global Market?
Contactless inductive charging, often referred to as wireless charging, is a technology that allows devices to be charged without the need for physical connectors or cables. This method of charging is gaining significant traction globally due to its convenience and efficiency. The technology works by using electromagnetic fields to transfer energy between two objects. Typically, a charging pad or station generates an electromagnetic field, and when a compatible device is placed on or near this pad, it receives the energy and converts it into electrical power to charge its battery. This method is not only convenient but also reduces wear and tear on device ports and cables, enhancing the longevity of both the device and its accessories. The global market for contactless inductive charging is expanding rapidly, driven by the increasing adoption of smartphones, wearable devices, and electric vehicles, all of which benefit from the ease and efficiency of wireless charging. As more industries and consumers recognize the advantages of this technology, its application is expected to broaden, further fueling market growth.
Magnetic Resonance, Electromagnetic Induction in the Contactless Inductive Charging - Global Market:
Magnetic resonance and electromagnetic induction are two fundamental principles that underpin contactless inductive charging technology. Electromagnetic induction, discovered by Michael Faraday in the 19th century, involves the generation of an electric current in a conductor by changing the magnetic field around it. In the context of wireless charging, this principle is applied by creating a magnetic field through a coil in the charging pad. When a device with a compatible coil is placed within this field, an electric current is induced in the device's coil, which is then used to charge the battery. This method is highly efficient for short distances and is commonly used in charging smartphones and other small devices. On the other hand, magnetic resonance involves the transfer of energy between two coils that are tuned to resonate at the same frequency. This method allows for greater flexibility in terms of distance and alignment between the charger and the device. Magnetic resonance is particularly useful for charging larger devices or multiple devices simultaneously, as it can transmit energy over a wider area. Both technologies have their advantages and limitations, and the choice between them often depends on the specific requirements of the application. For instance, electromagnetic induction is typically more efficient for close-range charging, while magnetic resonance offers more flexibility and can be more effective in scenarios where precise alignment is difficult to achieve. As the global market for contactless inductive charging continues to grow, advancements in both electromagnetic induction and magnetic resonance are expected to enhance the efficiency, range, and versatility of wireless charging solutions. These improvements will likely lead to broader adoption across various industries, from consumer electronics to automotive and beyond. The ongoing development of these technologies is crucial for meeting the increasing demand for convenient and efficient charging solutions in a world that is becoming increasingly reliant on portable electronic devices.
Smart Phone, Wearable Device, Tablet Computer, Car in the Contactless Inductive Charging - Global Market:
The usage of contactless inductive charging is becoming increasingly prevalent across a range of devices, including smartphones, wearable devices, tablet computers, and cars. For smartphones, wireless charging offers a seamless and convenient way to keep devices powered without the hassle of plugging and unplugging cables. Many modern smartphones are equipped with wireless charging capabilities, allowing users to simply place their phones on a charging pad to recharge. This not only simplifies the charging process but also reduces wear on charging ports, which can be a common point of failure in smartphones. Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, also benefit from contactless inductive charging. Given their small size and the need for frequent charging, wireless charging provides a practical solution that eliminates the need for tiny, fiddly connectors. Users can easily charge their wearables by placing them on a compatible charging dock or pad, ensuring they are always ready to use. Tablet computers, which often have larger batteries than smartphones, can also take advantage of wireless charging technology. While the charging process may take longer due to the larger battery capacity, the convenience of being able to charge without cables is a significant advantage, especially in environments where multiple devices are used, such as in offices or educational settings. In the automotive industry, contactless inductive charging is being explored as a solution for electric vehicles (EVs). Wireless charging pads can be installed in garages or parking spaces, allowing EVs to be charged simply by parking over the pad. This technology has the potential to make charging EVs as easy as parking them, which could significantly enhance the user experience and encourage the adoption of electric vehicles. As the technology continues to evolve, it is likely that we will see even more innovative applications of contactless inductive charging across various sectors.
Contactless Inductive Charging - Global Market Outlook:
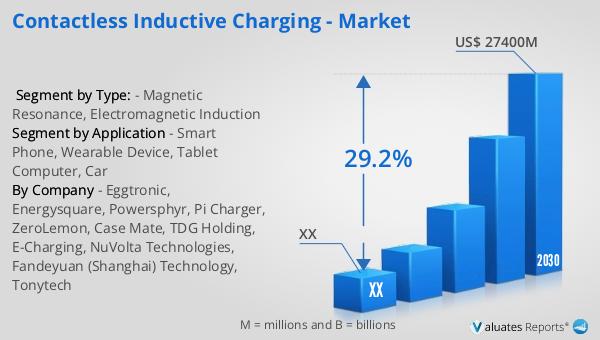
The global market for contactless inductive charging was valued at approximately $4,563 million in 2023. It is projected to grow significantly, reaching an estimated size of $27,400 million by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 29.2% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2030. This impressive growth is driven by the increasing demand for convenient, efficient, and safe charging solutions across various industries. Contactless inductive charging operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a magnetic field is established between the charger and the device to transmit energy. This method eliminates the need for physical connectors, reducing wear and tear on devices and cables, and providing a more reliable and user-friendly charging experience. As more consumers and industries recognize the benefits of wireless charging, its adoption is expected to accelerate, further driving market expansion. The technology's ability to enhance the user experience by simplifying the charging process and reducing the risk of damage to devices is a key factor contributing to its growing popularity. With ongoing advancements in wireless charging technology, the market is poised for continued growth and innovation in the coming years.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Contactless Inductive Charging - Market |
| Forecasted market size in 2030 | US$ 27400 million |
| CAGR | 29.2% |
| Forecasted years | 2024 - 2030 |
| Segment by Type: |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| By Company | Eggtronic, Energysquare, Powersphyr, Pi Charger, ZeroLemon, Case Mate, TDG Holding, E-Charging, NuVolta Technologies, Fandeyuan (Shanghai) Technology, Tonytech |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
