What is Carbon Cloth Gas Diffusion Layers - Global Market?
Carbon cloth gas diffusion layers (GDLs) are a critical component in the global market, particularly in the field of fuel cell technology. These layers are primarily used in proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) and play a vital role in the efficient operation of these cells. The GDLs are responsible for distributing gases evenly across the catalyst layer, facilitating the transport of reactants to the catalyst sites, and removing water produced during the electrochemical reactions. This ensures optimal performance and longevity of the fuel cells. The global market for carbon cloth GDLs is driven by the increasing demand for clean energy solutions and the growing adoption of fuel cell technologies in various applications, including transportation, stationary power generation, and portable power devices. As industries and governments worldwide focus on reducing carbon emissions and transitioning to sustainable energy sources, the demand for efficient and reliable fuel cell components like carbon cloth GDLs is expected to rise. The market is characterized by continuous advancements in material science and manufacturing techniques, aimed at improving the performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness of these diffusion layers.
Thickness<350μm, Thickness350~400μm, Thickness 400~450μm, Thickness >450μm in the Carbon Cloth Gas Diffusion Layers - Global Market:
In the global market for carbon cloth gas diffusion layers, thickness plays a crucial role in determining the performance and efficiency of fuel cells. The thickness of these layers can vary, typically categorized into four main segments: less than 350μm, 350-400μm, 400-450μm, and greater than 450μm. Each thickness range offers distinct advantages and is suited for specific applications. Layers with a thickness of less than 350μm are generally preferred for applications requiring high power density and rapid response times. These thinner layers facilitate efficient gas transport and water management, making them ideal for portable and automotive fuel cells where space and weight are critical considerations. On the other hand, layers with a thickness of 350-400μm strike a balance between mechanical strength and gas permeability. They are often used in stationary power applications where durability and long-term performance are prioritized. The 400-450μm thickness range is typically employed in applications that demand robust mechanical properties and enhanced water management capabilities. These layers are suitable for fuel cells operating under varying environmental conditions, ensuring consistent performance and reliability. Finally, layers with a thickness greater than 450μm are designed for heavy-duty applications where mechanical stability and durability are paramount. These thicker layers provide excellent support and protection for the catalyst layer, making them ideal for industrial and large-scale power generation applications. The choice of thickness is influenced by factors such as the specific requirements of the fuel cell application, operating conditions, and cost considerations. Manufacturers in the global market are continually innovating to develop carbon cloth GDLs with optimized thickness and properties to meet the evolving needs of the fuel cell industry.
Hydrogen-Oxygen Fuel Cell, Hydrocarbon Fuels Cell in the Carbon Cloth Gas Diffusion Layers - Global Market:
Carbon cloth gas diffusion layers are extensively used in hydrogen-oxygen fuel cells and hydrocarbon fuel cells, playing a pivotal role in their operation and efficiency. In hydrogen-oxygen fuel cells, these diffusion layers facilitate the even distribution of hydrogen and oxygen gases across the catalyst surface, ensuring efficient electrochemical reactions. The carbon cloth GDLs also aid in water management by allowing the produced water to be effectively removed from the cell, preventing flooding and maintaining optimal performance. This is particularly important in automotive applications where fuel cells are subjected to varying load conditions and require rapid response times. In hydrocarbon fuel cells, carbon cloth GDLs perform a similar function, ensuring the even distribution of hydrocarbon fuels and oxidants across the catalyst layer. These fuel cells often operate at higher temperatures and require robust diffusion layers that can withstand the harsh operating conditions. The carbon cloth GDLs provide the necessary mechanical support and thermal stability, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the fuel cells. Additionally, the porosity and hydrophobic properties of these layers are crucial in managing the water produced during the electrochemical reactions, preventing flooding and ensuring efficient gas transport. The use of carbon cloth GDLs in both hydrogen-oxygen and hydrocarbon fuel cells is driven by the need for high-performance, durable, and cost-effective solutions in the fuel cell industry. As the demand for clean energy technologies continues to grow, the role of carbon cloth GDLs in enhancing the performance and efficiency of fuel cells becomes increasingly important. Manufacturers are focused on developing advanced materials and manufacturing techniques to improve the properties of these diffusion layers, ensuring they meet the stringent requirements of modern fuel cell applications.
Carbon Cloth Gas Diffusion Layers - Global Market Outlook:
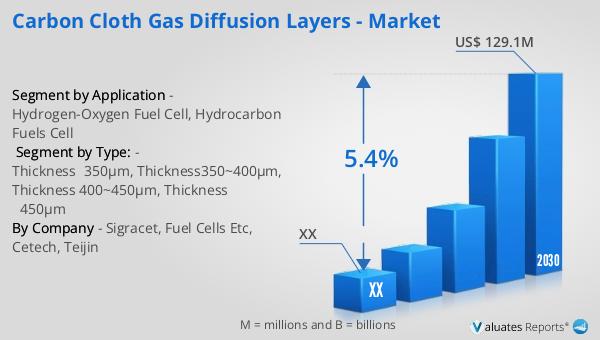
The global market for carbon cloth gas diffusion layers was valued at approximately $90 million in 2023. It is projected to grow to a revised size of $129.1 million by 2030, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.4% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2030. This growth is indicative of the increasing demand for fuel cell technologies and the critical role that carbon cloth GDLs play in their operation. In North America, the market for carbon cloth gas diffusion layers was valued at $ million in 2023, with expectations of reaching $ million by 2030. The growth in this region is driven by the adoption of fuel cell technologies in various applications, including transportation, stationary power generation, and portable power devices. The market dynamics are influenced by factors such as advancements in material science, manufacturing techniques, and the growing emphasis on clean energy solutions. As industries and governments worldwide focus on reducing carbon emissions and transitioning to sustainable energy sources, the demand for efficient and reliable fuel cell components like carbon cloth GDLs is expected to rise. The market is characterized by continuous advancements in material science and manufacturing techniques, aimed at improving the performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness of these diffusion layers.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Carbon Cloth Gas Diffusion Layers - Market |
| Forecasted market size in 2030 | US$ 129.1 million |
| CAGR | 5.4% |
| Forecasted years | 2024 - 2030 |
| Segment by Type: |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| By Company | Sigracet, Fuel Cells Etc, Cetech, Teijin |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
