What is Foam Wound Dressings - Global Market?
Foam wound dressings are a significant component of the global medical supplies market, designed to manage and treat various types of wounds. These dressings are made from a hydrophilic polyurethane foam that is highly absorbent, providing a moist environment conducive to healing while protecting the wound from external contaminants. The global market for foam wound dressings is driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic wounds, such as diabetic foot ulcers, pressure ulcers, and venous leg ulcers, which require effective management to prevent complications. Additionally, the rise in surgical procedures and the growing awareness of advanced wound care products contribute to the market's expansion. Foam wound dressings are favored for their versatility, as they can be used on a wide range of wound types and are available in various forms, including adhesive and non-adhesive options. Their ability to conform to the wound bed, provide cushioning, and maintain a moist environment makes them an essential tool in wound management. As healthcare systems worldwide continue to focus on improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs, the demand for effective wound care solutions like foam wound dressings is expected to grow.
Adhesive Foam Dressing, Non-Adhesive Foam Dressing in the Foam Wound Dressings - Global Market:
Adhesive foam dressings are a popular choice in the foam wound dressings market due to their ease of use and secure fit. These dressings come with an adhesive border that helps them stay in place, reducing the need for frequent changes and minimizing the risk of wound contamination. They are particularly useful for wounds located in areas that are difficult to dress or where movement might dislodge a non-adhesive dressing. Adhesive foam dressings are designed to absorb exudate while maintaining a moist wound environment, which is crucial for promoting faster healing. They are often used in the treatment of moderate to heavily exuding wounds, such as pressure ulcers, leg ulcers, and surgical wounds. The adhesive border is typically made from a hypoallergenic material to minimize skin irritation, making these dressings suitable for patients with sensitive skin. On the other hand, non-adhesive foam dressings are preferred in situations where the wound area is large or irregularly shaped, or where the skin surrounding the wound is fragile or damaged. These dressings do not have an adhesive border, allowing them to be easily removed and repositioned without causing trauma to the wound or surrounding skin. Non-adhesive foam dressings are often secured with secondary dressings, such as bandages or tapes, to ensure they stay in place. They are ideal for wounds that require frequent inspection or dressing changes, as they can be removed and reapplied with minimal disruption to the healing process. Both adhesive and non-adhesive foam dressings play a crucial role in the global market for foam wound dressings, offering healthcare providers and patients a range of options to suit different wound care needs. The choice between adhesive and non-adhesive dressings often depends on the specific requirements of the wound, the patient's skin condition, and the level of exudate. As the demand for advanced wound care products continues to rise, manufacturers are focusing on developing innovative foam dressings that offer enhanced performance, comfort, and ease of use. This includes the incorporation of antimicrobial agents to reduce the risk of infection, as well as the development of dressings with improved absorbency and breathability. The global market for foam wound dressings is expected to benefit from these advancements, as they provide healthcare professionals with more effective tools for managing complex wounds.
Hospital, Clinic, Other in the Foam Wound Dressings - Global Market:
Foam wound dressings are widely used in various healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, and other medical facilities, due to their effectiveness in managing a range of wound types. In hospitals, foam wound dressings are commonly used in surgical wards, intensive care units, and emergency departments to treat post-operative wounds, pressure ulcers, and traumatic injuries. Their ability to absorb large amounts of exudate and maintain a moist wound environment makes them ideal for use in acute care settings, where wound healing needs to be optimized to reduce the risk of complications and shorten hospital stays. In clinics, foam wound dressings are often used in outpatient settings to manage chronic wounds, such as diabetic foot ulcers and venous leg ulcers. These dressings provide a convenient and effective solution for patients who require regular wound care but do not need to be hospitalized. The ease of application and removal of foam dressings makes them suitable for use by healthcare professionals and caregivers in home care settings, allowing patients to receive ongoing wound care without the need for frequent clinic visits. In addition to hospitals and clinics, foam wound dressings are also used in other healthcare settings, such as nursing homes, rehabilitation centers, and home healthcare. In nursing homes, foam dressings are used to manage pressure ulcers and other chronic wounds in elderly patients, who are often at higher risk of developing such conditions due to limited mobility and underlying health issues. In rehabilitation centers, foam dressings are used to protect and promote healing of wounds in patients recovering from surgery or injury. The versatility and effectiveness of foam wound dressings make them a valuable tool in the management of wounds across various healthcare settings. As the global population continues to age and the prevalence of chronic conditions increases, the demand for effective wound care solutions like foam wound dressings is expected to grow. Healthcare providers are increasingly recognizing the importance of using advanced wound care products to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs, driving the adoption of foam wound dressings in hospitals, clinics, and other medical facilities worldwide.
Foam Wound Dressings - Global Market Outlook:
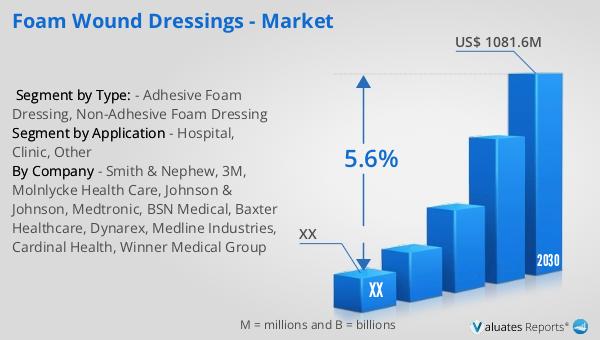
The global market for foam wound dressings was valued at approximately $742.5 million in 2023, with projections indicating a growth to around $1,081.6 million by 2030. This growth is expected to occur at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.6% from 2024 to 2030. In North America, the market for foam wound dressings was valued at a significant amount in 2023, with expectations of reaching a higher value by 2030, following a similar growth trajectory during the forecast period. This upward trend in the foam wound dressings market can be attributed to several factors, including the increasing prevalence of chronic wounds, advancements in wound care technology, and a growing awareness of the benefits of advanced wound care products. The demand for foam wound dressings is also driven by the rising number of surgical procedures and the need for effective post-operative wound management. As healthcare systems worldwide continue to focus on improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs, the adoption of foam wound dressings is expected to increase, contributing to the market's growth. The North American market, in particular, is anticipated to experience significant growth due to the region's advanced healthcare infrastructure, high prevalence of chronic wounds, and increasing adoption of advanced wound care products.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Foam Wound Dressings - Market |
| Forecasted market size in 2030 | US$ 1081.6 million |
| CAGR | 5.6% |
| Forecasted years | 2024 - 2030 |
| Segment by Type: |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| By Company | Smith & Nephew, 3M, Molnlycke Health Care, Johnson & Johnson, Medtronic, BSN Medical, Baxter Healthcare, Dynarex, Medline Industries, Cardinal Health, Winner Medical Group |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
