What is Global Central Venous Catheters Market?
The global Central Venous Catheters (CVC) market is a specialized segment within the medical devices industry, focusing on catheters that are inserted into large veins to administer medication, fluids, or to obtain blood tests. These catheters are crucial in critical care settings, such as intensive care units (ICUs), emergency rooms, and during major surgeries. The market encompasses a variety of CVCs designed for different medical needs and patient conditions. The demand for CVCs is driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, rising number of surgical procedures, and advancements in medical technology. Additionally, the aging population and the growing need for long-term intravenous therapies contribute to the market's expansion. The market is highly competitive, with numerous manufacturers striving to innovate and improve the safety and efficacy of their products. Overall, the global CVC market plays a vital role in modern healthcare, providing essential tools for patient management and treatment.
Single-lumen, Double-lumen, Triple-lumen, Other in the Global Central Venous Catheters Market:
Central Venous Catheters come in various types, including Single-lumen, Double-lumen, Triple-lumen, and other specialized designs, each serving distinct medical purposes. Single-lumen catheters have one channel or lumen, making them suitable for straightforward tasks like administering medication or fluids. They are often used in less complex medical situations where only one type of treatment is needed. Double-lumen catheters, on the other hand, have two separate channels, allowing for simultaneous administration of different medications or fluids. This dual functionality is particularly useful in more complex medical scenarios where multiple treatments are required concurrently. Triple-lumen catheters take this a step further by providing three separate channels, offering even greater versatility. These are commonly used in intensive care units (ICUs) and during major surgeries where multiple infusions, blood sampling, and monitoring are necessary. Other specialized CVCs include those designed for specific medical conditions or procedures, such as hemodialysis catheters, which are used for patients undergoing dialysis. These catheters are designed to handle the high flow rates required for effective dialysis treatment. Another example is antimicrobial-coated catheters, which are designed to reduce the risk of infections, a common complication associated with CVCs. The choice of catheter type depends on various factors, including the patient's condition, the duration of catheter use, and the specific medical requirements. For instance, in emergency situations where rapid access to the bloodstream is needed, a Single-lumen catheter might be preferred for its simplicity and ease of insertion. In contrast, for long-term treatments requiring multiple infusions, a Triple-lumen catheter might be more appropriate. The market for these different types of CVCs is influenced by the growing need for advanced medical treatments, the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and the rising number of surgical procedures. Manufacturers are continually innovating to improve the safety, efficacy, and ease of use of these catheters. For example, advancements in materials science have led to the development of more flexible and durable catheters, reducing the risk of complications such as catheter breakage or vein damage. Additionally, the incorporation of antimicrobial coatings and other infection-prevention technologies has significantly improved patient outcomes. The global market for CVCs is also shaped by regulatory standards and guidelines, which ensure the safety and effectiveness of these medical devices. Regulatory bodies in different regions have established stringent requirements for the design, manufacturing, and testing of CVCs, driving manufacturers to maintain high standards of quality and safety. Overall, the diverse range of CVCs available in the market caters to a wide array of medical needs, making them indispensable tools in modern healthcare.
Jugular Vein, Subclavian Vein, Femoral Vein, Other in the Global Central Venous Catheters Market:
Central Venous Catheters (CVCs) are utilized in various anatomical sites, including the Jugular Vein, Subclavian Vein, Femoral Vein, and other locations, each offering unique advantages and considerations. The Jugular Vein, located in the neck, is a common site for CVC insertion due to its accessibility and the relatively straightforward procedure required for catheter placement. This site is often preferred in emergency situations where rapid access to the central venous system is crucial. The Jugular Vein provides a direct route to the heart, making it ideal for administering medications, fluids, and for monitoring central venous pressure. However, the proximity to the carotid artery and the risk of puncturing it during insertion is a potential complication that requires careful technique and expertise. The Subclavian Vein, located beneath the collarbone, is another frequently used site for CVC insertion. This vein is favored for its relatively stable position and lower risk of infection compared to other sites. The Subclavian Vein is often chosen for long-term catheterization, such as in patients requiring prolonged intravenous therapies or total parenteral nutrition. The anatomical location of the Subclavian Vein also allows for greater patient mobility and comfort, as the catheter is less likely to interfere with daily activities. However, the insertion procedure can be technically challenging and carries a risk of complications such as pneumothorax (collapsed lung) if the pleura is accidentally punctured. The Femoral Vein, located in the groin area, is another option for CVC placement, particularly in emergency or critical care settings. The Femoral Vein is easily accessible and allows for rapid catheter insertion, making it suitable for situations where immediate central venous access is required. This site is often used in trauma patients or when other sites are not viable due to anatomical or medical reasons. However, the Femoral Vein is associated with a higher risk of infection and thrombosis (blood clots) compared to the Jugular and Subclavian veins. The proximity to the inguinal region also increases the risk of contamination, necessitating strict aseptic techniques during insertion and maintenance. Other sites for CVC insertion include the Basilic and Cephalic veins in the arm, which are used for peripherally inserted central catheters (PICCs). These sites are often chosen for patients requiring long-term intravenous therapies, such as chemotherapy or antibiotic treatment. PICCs offer the advantage of being less invasive and having a lower risk of complications compared to traditional CVCs. However, the insertion procedure is more time-consuming and requires specialized training and equipment. The choice of insertion site for CVCs depends on various factors, including the patient's medical condition, the duration of catheter use, and the specific clinical requirements. Each site offers unique benefits and challenges, and the decision must be made based on a thorough assessment of the patient's needs and the potential risks involved. The global market for CVCs is influenced by the growing demand for advanced medical treatments, the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and the rising number of surgical procedures. Manufacturers are continually innovating to improve the safety, efficacy, and ease of use of these catheters, ensuring that they remain indispensable tools in modern healthcare.
Global Central Venous Catheters Market Outlook:
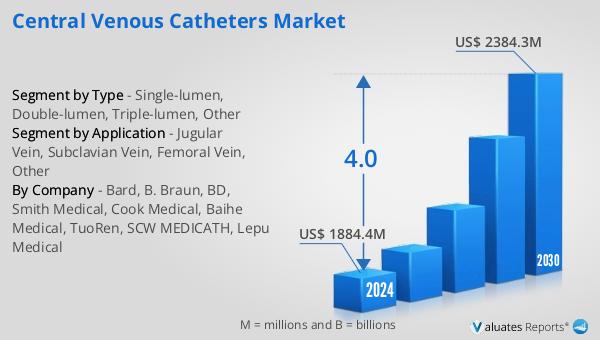
The global Central Venous Catheters market is anticipated to expand from US$ 1884.4 million in 2024 to US$ 2384.3 million by 2030, reflecting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 4.0% over the forecast period. The top four global manufacturers dominate the market, holding a collective share exceeding 60%. North America emerges as the largest market, accounting for over 40% of the total share, followed by China and Europe, each contributing approximately 35%. Among the various product types, Single-lumen catheters represent the largest segment, capturing over 40% of the market share.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Central Venous Catheters Market |
| Accounted market size in 2024 | US$ 1884.4 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2030 | US$ 2384.3 million |
| CAGR | 4.0 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecasted years | 2024 - 2030 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Segment by Region |
|
| By Company | Bard, B. Braun, BD, Smith Medical, Cook Medical, Baihe Medical, TuoRen, SCW MEDICATH, Lepu Medical |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
