What is Global New Molecular Entity (NME) Drug Market?
The Global New Molecular Entity (NME) Drug Market represents a significant segment of the pharmaceutical industry, focusing on the development and commercialization of innovative drugs that contain active ingredients never before approved by regulatory agencies. These NMEs are crucial in addressing unmet medical needs and advancing therapeutic options for various diseases. Unlike generic drugs, which replicate existing medications, NMEs offer novel mechanisms of action, potentially leading to more effective treatments with fewer side effects. The market for NMEs is driven by ongoing research and development efforts, technological advancements, and the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases worldwide. Pharmaceutical companies invest heavily in the discovery and development of NMEs, as these drugs can command premium pricing and offer competitive advantages in the market. Regulatory pathways for NMEs are often rigorous, requiring extensive clinical trials to ensure safety and efficacy. However, successful approval can lead to significant market opportunities and the potential for substantial returns on investment. The NME market is characterized by its dynamic nature, with continuous innovation and a focus on personalized medicine, aiming to provide targeted therapies that improve patient outcomes. As such, the Global NME Drug Market plays a pivotal role in the evolution of modern healthcare.
Antibody, Polypeptide, Small Molecule Drug, Other in the Global New Molecular Entity (NME) Drug Market:
In the realm of the Global New Molecular Entity (NME) Drug Market, various types of drugs are developed, each with unique characteristics and applications. Antibody drugs, for instance, are a class of biologics that have gained prominence due to their specificity and ability to target particular antigens. These drugs are often used in the treatment of cancers and autoimmune diseases, where they can precisely target and neutralize disease-causing cells without affecting healthy ones. The development of monoclonal antibodies has revolutionized treatment protocols, offering new hope for patients with conditions that were previously difficult to manage. Polypeptide drugs, on the other hand, are composed of amino acid chains and are used in various therapeutic areas, including endocrinology and metabolic disorders. These drugs mimic natural hormones or enzymes in the body, providing a more natural approach to treatment. The stability and bioavailability of polypeptide drugs have been enhanced through advanced formulation techniques, making them a viable option for chronic disease management. Small molecule drugs, which are chemically synthesized, remain a cornerstone of the pharmaceutical industry. These drugs are typically easier to manufacture and can be administered orally, making them convenient for patients. They are used across a wide range of therapeutic areas, from cardiovascular diseases to neurological disorders. The versatility and cost-effectiveness of small molecule drugs ensure their continued relevance in the NME market. Other types of NMEs include nucleic acid-based drugs and gene therapies, which represent the cutting edge of medical innovation. These therapies aim to address genetic disorders at their source, offering the potential for curative treatments. The development of these advanced therapies is supported by breakthroughs in genomics and biotechnology, paving the way for personalized medicine. Each type of NME drug plays a crucial role in expanding the therapeutic arsenal available to healthcare providers, ultimately improving patient care and outcomes. The diversity of NMEs underscores the importance of continued investment in research and development, as well as collaboration between academia, industry, and regulatory bodies to bring these innovative treatments to market. As the NME Drug Market evolves, it will continue to drive advancements in medical science and offer new solutions to complex health challenges.
Hospital, Clinic in the Global New Molecular Entity (NME) Drug Market:
The usage of Global New Molecular Entity (NME) Drugs in hospitals and clinics is integral to modern healthcare delivery, providing cutting-edge treatment options for a variety of conditions. In hospitals, NMEs are often employed in specialized departments such as oncology, cardiology, and infectious diseases, where they offer targeted therapies that can significantly improve patient outcomes. For instance, in oncology departments, NMEs like monoclonal antibodies and small molecule inhibitors are used to treat various types of cancer, offering patients more effective and less toxic alternatives to traditional chemotherapy. These drugs can be administered as part of a comprehensive treatment plan, often in combination with surgery or radiation therapy, to enhance efficacy and reduce the risk of recurrence. In cardiology, NMEs are used to manage complex conditions such as heart failure and arrhythmias, providing novel mechanisms of action that can improve heart function and patient quality of life. Clinics, on the other hand, utilize NMEs in outpatient settings, where they are prescribed for chronic conditions such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis. The convenience of oral or injectable NMEs allows patients to manage their conditions effectively at home, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits. In addition, clinics often participate in clinical trials for NMEs, contributing to the development of new therapies and offering patients access to cutting-edge treatments before they become widely available. The integration of NMEs into hospital and clinic settings requires collaboration between healthcare providers, pharmacists, and patients to ensure optimal treatment outcomes. This includes careful consideration of dosing regimens, potential side effects, and patient education to maximize the benefits of these advanced therapies. As the NME Drug Market continues to grow, hospitals and clinics will play a crucial role in the adoption and implementation of these innovative treatments, ultimately enhancing the standard of care and improving patient health.
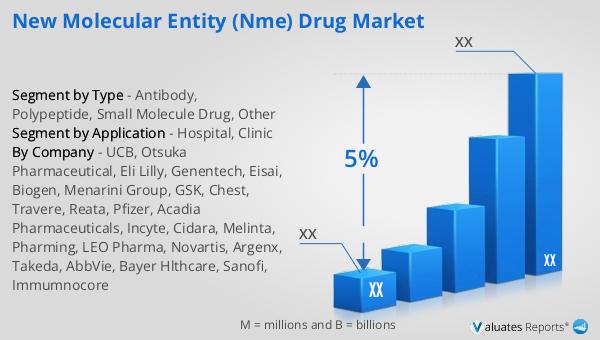
Global New Molecular Entity (NME) Drug Market Outlook:
In 2022, the global pharmaceutical market reached a valuation of 1,475 billion USD, demonstrating a steady growth trajectory with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5% projected over the next six years. This growth reflects the increasing demand for innovative and effective treatments across various therapeutic areas. In comparison, the chemical drug market has shown a more modest increase, rising from 1,005 billion USD in 2018 to 1,094 billion USD in 2022. This indicates a gradual expansion, driven by the development of new chemical entities and the ongoing need for traditional pharmaceuticals. The disparity in growth rates between the overall pharmaceutical market and the chemical drug segment highlights the dynamic nature of the industry, with biologics and NMEs playing an increasingly important role. As the market continues to evolve, the focus on personalized medicine and targeted therapies is expected to drive further innovation and investment in the pharmaceutical sector. The data underscores the importance of continued research and development efforts to meet the growing healthcare needs of the global population.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | New Molecular Entity (NME) Drug Market |
| CAGR | 5% |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| By Company | UCB, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Eli Lilly, Genentech, Eisai, Biogen, Menarini Group, GSK, Chest, Travere, Reata, Pfizer, Acadia Pharmaceuticals, Incyte, Cidara, Melinta, Pharming, LEO Pharma, Novartis, Argenx, Takeda, AbbVie, Bayer Hlthcare, Sanofi, Immumnocore |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |