What is Global Drug based on CAR T-Cell Market?
Global Drug based on CAR T-Cell Market refers to a specialized segment within the pharmaceutical industry that focuses on the development and commercialization of therapies using Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-cells. These are genetically engineered T-cells designed to target and destroy cancer cells, offering a novel approach to cancer treatment. CAR T-cell therapies have shown significant promise, particularly in treating certain types of blood cancers, by harnessing the body's immune system to fight the disease. The market for these drugs is driven by advancements in biotechnology, increasing prevalence of cancer, and the need for more effective treatments. As research progresses, the potential applications of CAR T-cell therapies are expanding beyond hematological malignancies to include solid tumors, further broadening the market scope. The global interest in CAR T-cell therapies is also fueled by the potential for personalized medicine, as these treatments can be tailored to individual patients' genetic profiles, enhancing their efficacy and reducing side effects. The market is characterized by intense research and development activities, collaborations between biotech firms and academic institutions, and significant investments from pharmaceutical companies aiming to bring these innovative therapies to market.
CD19-targeted, BCMA-targeted in the Global Drug based on CAR T-Cell Market:
CD19-targeted and BCMA-targeted therapies are two prominent categories within the Global Drug based on CAR T-Cell Market, each focusing on different antigens associated with specific types of cancer. CD19-targeted CAR T-cell therapies are primarily used in the treatment of B-cell malignancies, such as certain types of lymphomas and leukemias. CD19 is a protein found on the surface of B-cells, and targeting it allows CAR T-cells to specifically attack and eliminate cancerous B-cells. This approach has shown remarkable success in clinical trials, leading to the approval of several CD19-targeted therapies for use in patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell cancers. The development of these therapies involves complex processes, including the extraction of a patient's T-cells, their genetic modification to express the CAR targeting CD19, and their expansion before being reintroduced into the patient's body. This personalized treatment has revolutionized the approach to treating B-cell malignancies, offering hope to patients who have exhausted other treatment options. On the other hand, BCMA-targeted CAR T-cell therapies are designed to treat multiple myeloma, a cancer of plasma cells. BCMA, or B-cell maturation antigen, is a protein expressed on the surface of malignant plasma cells, making it an ideal target for CAR T-cell therapy. The development of BCMA-targeted therapies has been driven by the need for more effective treatments for multiple myeloma, particularly for patients who have relapsed or are resistant to existing therapies. Similar to CD19-targeted therapies, the process involves engineering a patient's T-cells to express a CAR that targets BCMA, allowing for the selective destruction of cancerous plasma cells. Clinical trials have demonstrated significant efficacy of BCMA-targeted therapies, with many patients achieving deep and durable responses. The success of these therapies has spurred further research into optimizing their design, improving their safety profile, and exploring combination strategies with other treatments to enhance their effectiveness. Both CD19-targeted and BCMA-targeted CAR T-cell therapies represent significant advancements in the field of oncology, offering new hope to patients with limited treatment options. The development and commercialization of these therapies are supported by a robust pipeline of clinical trials, ongoing research into new targets, and collaborations between biotech companies and academic institutions. As the understanding of CAR T-cell biology continues to evolve, there is potential for these therapies to be applied to a broader range of cancers, including solid tumors, further expanding their impact on the global drug market. The success of CD19-targeted and BCMA-targeted therapies underscores the transformative potential of CAR T-cell technology in cancer treatment, paving the way for the development of next-generation therapies that could offer even greater efficacy and safety for patients worldwide.
Lymphoma, Multiple Myeloma in the Global Drug based on CAR T-Cell Market:
The usage of Global Drug based on CAR T-Cell Market in treating lymphoma and multiple myeloma highlights the transformative potential of this innovative therapy. In the case of lymphoma, particularly B-cell lymphomas, CAR T-cell therapy has emerged as a groundbreaking treatment option. Lymphoma is a type of blood cancer that affects the lymphatic system, and B-cell lymphomas are among the most common subtypes. Traditional treatments for lymphoma include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and stem cell transplants, but these approaches may not be effective for all patients, especially those with relapsed or refractory disease. CAR T-cell therapy offers a new avenue for treatment by genetically modifying a patient's T-cells to target and destroy cancerous B-cells. This personalized approach has shown remarkable efficacy in clinical trials, with many patients achieving complete remission. The success of CAR T-cell therapy in treating lymphoma has led to its approval by regulatory agencies and its incorporation into treatment guidelines for certain types of B-cell lymphomas. In the context of multiple myeloma, CAR T-cell therapy targeting BCMA has shown significant promise. Multiple myeloma is a cancer of plasma cells, and despite advances in treatment, it remains an incurable disease with a high rate of relapse. BCMA-targeted CAR T-cell therapy represents a novel approach to treating multiple myeloma by specifically targeting and eliminating malignant plasma cells. Clinical trials have demonstrated impressive response rates, with many patients experiencing deep and durable remissions. This has led to the approval of BCMA-targeted CAR T-cell therapies for patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma, providing a new treatment option for those who have exhausted other therapies. The development of BCMA-targeted therapies has also spurred further research into optimizing their design, improving their safety profile, and exploring combination strategies with other treatments to enhance their effectiveness. The application of CAR T-cell therapy in lymphoma and multiple myeloma underscores the potential of this technology to revolutionize cancer treatment. By harnessing the power of the immune system, CAR T-cell therapy offers a targeted and personalized approach to treating these challenging diseases. The success of CAR T-cell therapy in these areas has also paved the way for further research into expanding its use to other types of cancer, including solid tumors. As the understanding of CAR T-cell biology continues to evolve, there is potential for these therapies to be applied to a broader range of cancers, further expanding their impact on the global drug market. The development and commercialization of CAR T-cell therapies are supported by a robust pipeline of clinical trials, ongoing research into new targets, and collaborations between biotech companies and academic institutions. As a result, CAR T-cell therapy represents a significant advancement in the field of oncology, offering new hope to patients with limited treatment options and paving the way for the development of next-generation therapies that could offer even greater efficacy and safety for patients worldwide.
Global Drug based on CAR T-Cell Market Outlook:
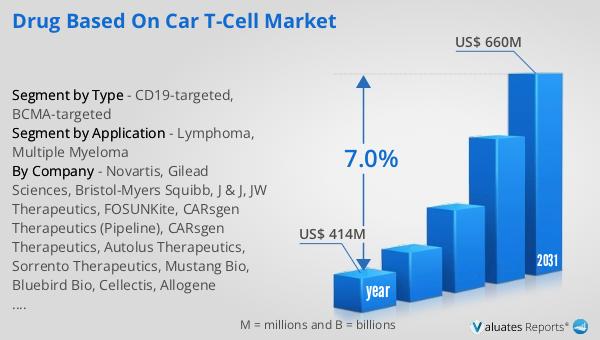
The global market for drugs based on CAR T-Cell was valued at $414 million in 2024 and is anticipated to grow to a revised size of $660 million by 2031, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.0% during the forecast period. This growth is indicative of the increasing demand and advancements in CAR T-cell therapies, driven by their potential to revolutionize cancer treatment. In comparison, the global pharmaceutical market was valued at $1,475 billion in 2022, with a projected CAGR of 5% over the next six years. This highlights the rapid growth and significant interest in CAR T-cell therapies within the broader pharmaceutical landscape. Additionally, the chemical drug market is estimated to have increased from $1,005 billion in 2018 to $1,094 billion in 2022, showcasing a steady growth trajectory. The CAR T-cell market, although smaller in size compared to the overall pharmaceutical and chemical drug markets, represents a highly specialized and innovative segment with the potential for significant impact on cancer treatment. The increasing investment in research and development, coupled with the growing number of clinical trials and regulatory approvals, is expected to drive the continued growth of the CAR T-cell market, offering new hope to patients and transforming the landscape of cancer therapy.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Drug based on CAR T-Cell Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 414 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 660 million |
| CAGR | 7.0% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| By Company | Novartis, Gilead Sciences, Bristol-Myers Squibb, J & J, JW Therapeutics, FOSUNKite, CARsgen Therapeutics (Pipeline), CARsgen Therapeutics, Autolus Therapeutics, Sorrento Therapeutics, Mustang Bio, Bluebird Bio, Cellectis, Allogene Therapeutics, Celyad |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |