What is Scientific Microscopy Cameras - Global Market?
Scientific microscopy cameras are specialized imaging devices used to capture detailed images through microscopes. These cameras are essential tools in various scientific fields, enabling researchers to observe and document microscopic structures and phenomena with high precision. The global market for scientific microscopy cameras is driven by advancements in technology and the increasing demand for high-resolution imaging in research and industrial applications. These cameras are used in life sciences, materials science, and other research areas to provide clear and accurate images that are crucial for analysis and documentation. The market is characterized by a range of products, including CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) and CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) cameras, each offering unique advantages in terms of sensitivity, speed, and image quality. As scientific research continues to evolve, the demand for advanced microscopy cameras is expected to grow, supporting innovations and discoveries across various disciplines. The market's growth is also influenced by the increasing adoption of digital imaging technologies and the need for efficient and reliable imaging solutions in laboratories and research institutions worldwide.
CCD Cameras, CMOS Cameras in the Scientific Microscopy Cameras - Global Market:
CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) and CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) cameras are two primary types of imaging sensors used in scientific microscopy cameras, each with distinct characteristics that cater to different research needs. CCD cameras have been traditionally favored for their high-quality image output and sensitivity to light, making them ideal for capturing detailed images in low-light conditions. This sensitivity is particularly beneficial in applications such as fluorescence microscopy, where capturing faint signals is crucial. CCD sensors work by transferring charge across the chip and reading it at one corner, which can result in slower image processing compared to CMOS sensors. However, their ability to produce images with low noise and high dynamic range makes them a preferred choice for applications requiring precise image quality. On the other hand, CMOS cameras have gained popularity due to their faster processing speeds and lower power consumption. Unlike CCD sensors, CMOS sensors convert light into electrical signals directly at each pixel, allowing for quicker image capture and processing. This speed advantage makes CMOS cameras suitable for applications requiring real-time imaging and high frame rates, such as live cell imaging and industrial inspection. Additionally, CMOS technology has advanced significantly, narrowing the gap in image quality between CMOS and CCD cameras. The choice between CCD and CMOS cameras often depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as the need for speed, sensitivity, or image quality. In the global market for scientific microscopy cameras, both CCD and CMOS cameras play vital roles, offering researchers and industries a range of options to meet their imaging needs. As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of both types of cameras are expected to improve, further enhancing their applications in scientific research and industrial processes. The ongoing development in sensor technology, coupled with the increasing demand for high-resolution and high-speed imaging, is likely to drive innovation and growth in the scientific microscopy camera market, providing researchers with more powerful tools to explore and understand the microscopic world.
Life Science Research, Industry & Manufacturing, Education, Pharmaceutical, Others in the Scientific Microscopy Cameras - Global Market:
Scientific microscopy cameras are utilized across various fields, each benefiting from the detailed imaging capabilities these devices offer. In life science research, these cameras are indispensable for studying cellular structures, biological processes, and molecular interactions. They enable researchers to capture high-resolution images of cells and tissues, facilitating a deeper understanding of biological functions and disease mechanisms. This capability is crucial for advancing research in areas such as cancer biology, neuroscience, and developmental biology. In the industry and manufacturing sector, scientific microscopy cameras are used for quality control and inspection processes. They help in identifying defects and ensuring the precision of components in fields like electronics, automotive, and materials science. The ability to capture detailed images of microscopic structures allows manufacturers to maintain high standards and improve product reliability. In education, these cameras serve as valuable tools for teaching and learning, providing students with the opportunity to observe and analyze microscopic specimens in real-time. This hands-on experience enhances understanding and engagement in scientific studies. In the pharmaceutical industry, scientific microscopy cameras play a critical role in drug discovery and development. They are used to study the effects of compounds on cellular structures and to monitor the interactions between drugs and biological targets. This information is vital for developing effective and safe medications. Beyond these areas, scientific microscopy cameras find applications in fields such as environmental science, where they are used to study microorganisms and pollutants, and in forensic science, where they assist in analyzing trace evidence. The versatility and precision of scientific microscopy cameras make them essential tools in a wide range of scientific and industrial applications, driving innovation and discovery across multiple disciplines.
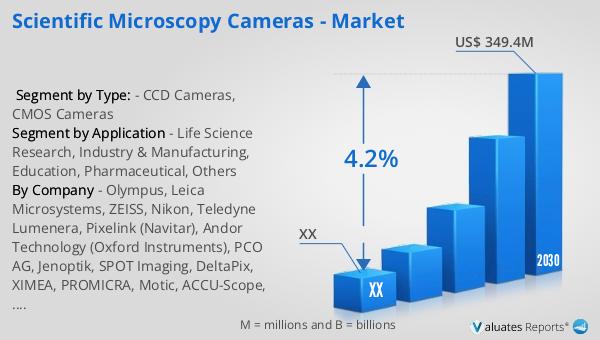
Scientific Microscopy Cameras - Global Market Outlook:
The global market for scientific microscopy cameras was valued at approximately $260 million in 2023 and is projected to reach around $349.4 million by 2030, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.2% from 2024 to 2030. These cameras are integral to various scientific applications, including life sciences, material science, and research, where they provide critical imaging capabilities. The growth in this market is driven by the increasing demand for high-resolution imaging solutions that support scientific research and industrial processes. As technology advances, the capabilities of scientific microscopy cameras continue to improve, offering enhanced sensitivity, speed, and image quality. This progress is essential for meeting the evolving needs of researchers and industries that rely on precise and reliable imaging tools. The market's expansion reflects the growing importance of digital imaging technologies in scientific and industrial applications, as well as the ongoing investment in research and development to create more advanced and efficient imaging solutions. As a result, scientific microscopy cameras are expected to play an increasingly vital role in supporting innovations and discoveries across various fields, contributing to the advancement of science and technology worldwide.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Scientific Microscopy Cameras - Market |
| Forecasted market size in 2030 | US$ 349.4 million |
| CAGR | 4.2% |
| Forecasted years | 2024 - 2030 |
| Segment by Type: |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| By Company | Olympus, Leica Microsystems, ZEISS, Nikon, Teledyne Lumenera, Pixelink (Navitar), Andor Technology (Oxford Instruments), PCO AG, Jenoptik, SPOT Imaging, DeltaPix, XIMEA, PROMICRA, Motic, ACCU-Scope, Guangzhou Micro-shot Technology |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
