What is Global Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Market?
The Global Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Market is a specialized segment within the pharmaceutical industry that focuses on a class of medications used primarily for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. These medications mimic the action of the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), a hormone that stimulates insulin secretion in response to meals, thereby helping to regulate blood sugar levels. The market for these drugs has been expanding due to the increasing prevalence of diabetes worldwide, driven by factors such as aging populations, rising obesity rates, and sedentary lifestyles. The GLP-1 receptor agonists not only help in controlling blood sugar but also offer additional benefits like weight loss and cardiovascular protection, making them a preferred choice among healthcare providers. The market is characterized by intense competition among pharmaceutical companies, each striving to innovate and improve the efficacy and safety profiles of their products. As awareness about diabetes management grows, the demand for GLP-1 receptor agonists is expected to continue its upward trajectory, supported by ongoing research and development efforts aimed at enhancing patient outcomes and expanding therapeutic applications.
Exenatide, Liraglutide, Lixisenatide, Albiglutide, Others in the Global Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Market:
Exenatide, Liraglutide, Lixisenatide, Albiglutide, and other GLP-1 receptor agonists represent a significant portion of the Global Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Market, each offering unique benefits and characteristics. Exenatide, one of the first GLP-1 receptor agonists introduced, is known for its twice-daily or once-weekly dosing options, providing flexibility for patients. It works by enhancing insulin secretion, suppressing glucagon release, and slowing gastric emptying, which collectively help in managing blood glucose levels. Liraglutide, on the other hand, is administered once daily and has gained attention not only for its efficacy in glycemic control but also for its cardiovascular benefits, as demonstrated in clinical trials. This has made it a popular choice for patients with type 2 diabetes who are at risk of cardiovascular diseases. Lixisenatide, with its once-daily dosing, offers a convenient option for patients and has shown effectiveness in reducing postprandial glucose levels, which is crucial for comprehensive diabetes management. Albiglutide, although less commonly used, provides a once-weekly dosing regimen, appealing to patients seeking less frequent injections. Each of these medications has been developed with a focus on improving patient adherence and minimizing side effects, such as nausea and gastrointestinal discomfort, which are common with GLP-1 receptor agonists. The market also includes other emerging GLP-1 receptor agonists that are in various stages of development, aiming to offer even more advanced solutions for diabetes management. These drugs are continually being evaluated for their potential in treating other conditions, such as obesity and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), expanding their therapeutic scope. The competition among these drugs is fierce, with pharmaceutical companies investing heavily in research and development to differentiate their products and capture a larger market share. As the understanding of GLP-1 receptor agonists evolves, the market is poised for further growth, driven by innovations that enhance efficacy, safety, and patient convenience.
Solid Tumors, Blood-related Tumors in the Global Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Market:
The usage of Global Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists extends beyond diabetes management, with emerging research exploring their potential in treating various types of tumors, including solid tumors and blood-related tumors. In the context of solid tumors, GLP-1 receptor agonists are being investigated for their ability to modulate metabolic pathways that are often dysregulated in cancer cells. These drugs may influence tumor growth by affecting glucose metabolism, which is a critical energy source for rapidly proliferating cancer cells. Additionally, GLP-1 receptor agonists have shown promise in reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which are implicated in cancer progression. While the research is still in its early stages, these findings suggest that GLP-1 receptor agonists could become a valuable adjunct therapy in oncology, potentially enhancing the efficacy of existing cancer treatments. In the realm of blood-related tumors, such as leukemia and lymphoma, GLP-1 receptor agonists are being studied for their potential to improve metabolic health and immune function. These drugs may help in modulating the immune response, which is crucial for targeting and eliminating cancerous cells. Furthermore, by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing hyperglycemia, GLP-1 receptor agonists could potentially mitigate some of the metabolic complications associated with cancer and its treatment. The exploration of GLP-1 receptor agonists in oncology is a testament to the versatility of these drugs and their potential to address unmet medical needs beyond diabetes. As research progresses, it is hoped that these medications will offer new therapeutic avenues for patients with cancer, improving outcomes and quality of life. The integration of GLP-1 receptor agonists into cancer treatment regimens will require rigorous clinical trials to establish their safety and efficacy, but the preliminary data is promising and underscores the importance of continued investigation in this area.
Global Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Market Outlook:
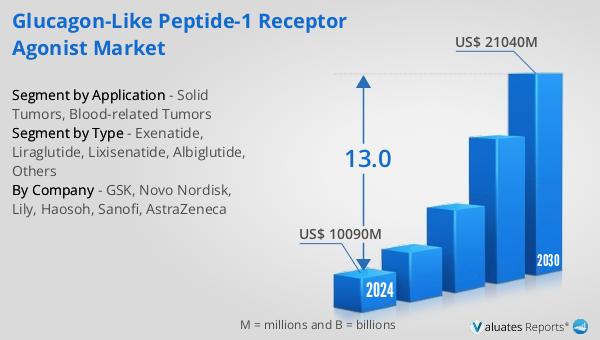
The outlook for the Global Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Market is promising, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. The market is expected to expand from approximately US$ 10,090 million in 2024 to around US$ 21,040 million by 2030, reflecting a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.0% during the forecast period. This growth is driven by the increasing prevalence of diabetes and the rising demand for effective and convenient treatment options. The broader medical devices market, estimated at US$ 603 billion in 2023, is also on an upward trajectory, with a projected CAGR of 5% over the next six years. This growth is indicative of the overall expansion in healthcare technologies and innovations aimed at improving patient care. The GLP-1 receptor agonist market is poised to benefit from these trends, as advancements in drug delivery systems and personalized medicine continue to enhance the therapeutic landscape. The competitive nature of the market, coupled with ongoing research and development efforts, is expected to drive further innovations and improvements in GLP-1 receptor agonists, ultimately benefiting patients and healthcare providers alike. As the market evolves, stakeholders will need to navigate regulatory challenges and address patient needs to fully capitalize on the opportunities presented by this dynamic and rapidly growing segment.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Market |
| Accounted market size in 2024 | US$ 10090 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2030 | US$ 21040 million |
| CAGR | 13.0 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2030 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| By Company | GSK, Novo Nordisk, Lily, Haosoh, Sanofi, AstraZeneca |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
