What is Global Back-Illuminated Medical Grade CMOS Image Sensor Market?
The Global Back-Illuminated Medical Grade CMOS Image Sensor Market is a specialized segment within the broader medical imaging technology industry. These sensors are crucial components in medical imaging devices, offering enhanced image quality by capturing more light and reducing noise, which is particularly beneficial in low-light conditions. Unlike traditional front-illuminated sensors, back-illuminated sensors have their photodiodes positioned closer to the light source, allowing for more efficient light capture. This technology is pivotal in medical applications where precision and clarity are paramount, such as in endoscopy, ophthalmology, and other diagnostic imaging fields. The demand for these sensors is driven by the increasing need for high-resolution imaging in medical diagnostics, which aids in accurate disease detection and monitoring. As healthcare providers continue to seek advanced imaging solutions to improve patient outcomes, the market for back-illuminated medical grade CMOS image sensors is expected to grow, driven by technological advancements and the rising prevalence of chronic diseases that require detailed imaging for effective management. The integration of these sensors into medical devices not only enhances diagnostic capabilities but also supports the trend towards minimally invasive procedures, which are becoming increasingly popular in modern medicine.
Passive Pixel CMOS Sensor, Active Pixel CMOS Sensor in the Global Back-Illuminated Medical Grade CMOS Image Sensor Market:
In the realm of Global Back-Illuminated Medical Grade CMOS Image Sensors, two primary types of sensors are prevalent: Passive Pixel CMOS Sensors (PPS) and Active Pixel CMOS Sensors (APS). Passive Pixel CMOS Sensors are the simpler of the two, characterized by their straightforward design where each pixel in the sensor array is connected to a common output line. This design allows for the capture of images by accumulating charge in each pixel, which is then read out sequentially. However, the simplicity of PPS comes with limitations, such as lower sensitivity and slower readout speeds, making them less suitable for applications requiring high-speed imaging or low-light performance. Despite these limitations, PPS can be advantageous in applications where cost and power consumption are critical factors, as their simpler design typically results in lower manufacturing costs and reduced power requirements. On the other hand, Active Pixel CMOS Sensors represent a more advanced technology, offering significant improvements over their passive counterparts. In APS, each pixel contains its own amplifier, which boosts the signal before it is read out. This design enhances the sensor's sensitivity and speed, making APS ideal for applications that demand high-resolution and high-speed imaging. The integration of amplifiers within each pixel also reduces noise, resulting in clearer and more detailed images. This is particularly beneficial in medical imaging, where precision and clarity are essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. The ability of APS to perform well in low-light conditions further extends their applicability in medical settings, where lighting conditions can vary significantly. The choice between Passive Pixel and Active Pixel CMOS Sensors in the Global Back-Illuminated Medical Grade CMOS Image Sensor Market largely depends on the specific requirements of the medical application. For instance, in applications where high-speed imaging is crucial, such as in dynamic imaging of moving organs or tissues, APS would be the preferred choice due to their superior speed and sensitivity. Conversely, in applications where cost and power efficiency are more critical, such as in portable or battery-operated medical devices, PPS might be more suitable. Moreover, the ongoing advancements in CMOS sensor technology continue to blur the lines between these two types of sensors. Innovations such as the development of hybrid sensors that combine the benefits of both PPS and APS are emerging, offering even greater flexibility and performance in medical imaging applications. These advancements are driven by the increasing demand for more sophisticated imaging solutions that can provide detailed insights into the human body, aiding in early disease detection and improving patient outcomes. In conclusion, both Passive Pixel and Active Pixel CMOS Sensors play vital roles in the Global Back-Illuminated Medical Grade CMOS Image Sensor Market. While PPS offers advantages in terms of cost and power efficiency, APS provides superior performance in terms of speed, sensitivity, and image quality. The choice between the two depends on the specific needs of the medical application, with ongoing technological advancements continuing to enhance the capabilities and applications of these sensors in the medical field. As the demand for high-quality medical imaging continues to grow, the role of CMOS sensors in meeting this demand will only become more significant, driving further innovation and development in this critical area of medical technology.
Hospital, Clinic, Others in the Global Back-Illuminated Medical Grade CMOS Image Sensor Market:
The Global Back-Illuminated Medical Grade CMOS Image Sensor Market finds extensive usage across various healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, and other medical facilities. In hospitals, these sensors are integral to a wide range of imaging devices used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. For instance, in radiology departments, back-illuminated CMOS sensors are employed in digital X-ray systems, CT scanners, and MRI machines, where they contribute to producing high-resolution images that are crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. The enhanced sensitivity and low-light performance of these sensors make them particularly valuable in capturing detailed images of internal organs and tissues, aiding in the early detection of diseases and monitoring of treatment progress. In clinics, where space and resources may be more limited compared to larger hospitals, the compact and efficient design of back-illuminated CMOS sensors is particularly advantageous. These sensors are used in portable imaging devices, such as handheld ultrasound machines and point-of-care diagnostic tools, enabling healthcare providers to perform imaging procedures at the patient's bedside or in remote locations. This flexibility is essential for improving access to diagnostic services, particularly in underserved areas where traditional imaging infrastructure may be lacking. The ability to obtain high-quality images quickly and efficiently supports timely decision-making and enhances the overall quality of care provided in clinical settings. Beyond hospitals and clinics, the Global Back-Illuminated Medical Grade CMOS Image Sensor Market also extends to other areas of healthcare, including research institutions and specialized medical facilities. In research settings, these sensors are used in advanced imaging systems for studying complex biological processes and developing new diagnostic and therapeutic techniques. The high resolution and sensitivity of back-illuminated CMOS sensors enable researchers to capture detailed images at the cellular and molecular levels, facilitating groundbreaking discoveries in fields such as oncology, neurology, and cardiology. Additionally, specialized medical facilities, such as ophthalmology centers and dental clinics, also benefit from the capabilities of back-illuminated CMOS sensors. In ophthalmology, these sensors are used in devices like fundus cameras and optical coherence tomography (OCT) systems, where they provide high-resolution images of the retina and other structures of the eye, aiding in the diagnosis and management of various eye conditions. Similarly, in dental imaging, these sensors contribute to producing detailed images of teeth and surrounding structures, supporting accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Overall, the versatility and advanced imaging capabilities of back-illuminated CMOS sensors make them indispensable across a wide range of healthcare settings. Their ability to deliver high-quality images in various conditions enhances the diagnostic and therapeutic capabilities of medical professionals, ultimately improving patient outcomes. As the demand for advanced imaging solutions continues to grow, the role of these sensors in healthcare is expected to expand further, driving innovation and improving the quality of care provided to patients worldwide.
Global Back-Illuminated Medical Grade CMOS Image Sensor Market Outlook:
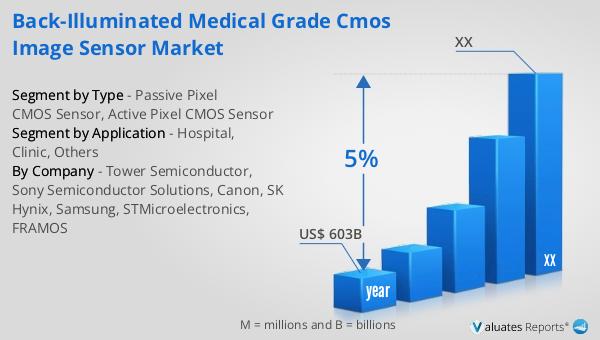
Our analysis indicates that the worldwide market for medical devices is projected to reach approximately $603 billion in 2023, with an anticipated growth rate of 5% annually over the next six years.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Back-Illuminated Medical Grade CMOS Image Sensor Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 603 billion |
| CAGR | 5% |
| Base Year | year |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Segment by Region |
|
| By Company | Tower Semiconductor, Sony Semiconductor Solutions, Canon, SK Hynix, Samsung, STMicroelectronics, FRAMOS |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
