What is Self-expanding NiTi Alloy Stent - Global Market?
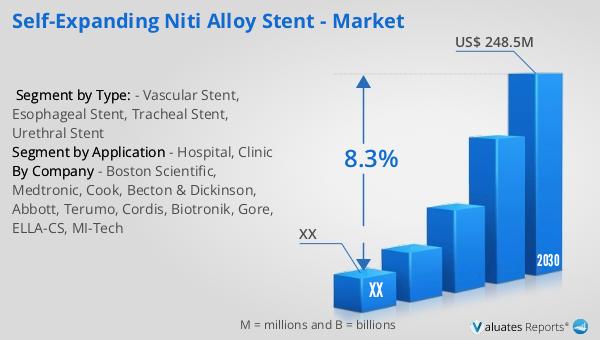
The self-expanding NiTi alloy stent is a medical device used globally to treat various conditions by providing support to tubular structures within the body. Made from a nickel-titanium alloy, these stents are known for their unique ability to expand and conform to the shape of the vessel or duct they are placed in, providing a minimally invasive solution to blockages or narrowing. The global market for these stents was valued at approximately $142 million in 2023, with projections indicating growth to $248.5 million by 2030, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.3% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is driven by increasing demand for minimally invasive procedures, advancements in stent technology, and a rising prevalence of conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, esophageal cancer, and other ailments that require stenting. The self-expanding nature of these stents allows for easier placement and reduced risk of complications, making them a preferred choice in many medical scenarios. As the global medical device market, estimated at $603 billion in 2023, continues to grow at a CAGR of 5% over the next six years, the demand for innovative solutions like the NiTi alloy stent is expected to rise, further fueling market expansion.
Vascular Stent, Esophageal Stent, Tracheal Stent, Urethral Stent in the Self-expanding NiTi Alloy Stent - Global Market:
The self-expanding NiTi alloy stent is utilized in various medical applications, including vascular, esophageal, tracheal, and urethral stenting. In vascular applications, these stents are primarily used to treat conditions such as peripheral artery disease and coronary artery disease. The stent is inserted into the narrowed or blocked artery, where it expands to restore blood flow, reducing symptoms like pain and fatigue. The flexibility and biocompatibility of the NiTi alloy make it ideal for navigating the complex vascular system, ensuring that the stent conforms to the vessel's natural shape and minimizes the risk of restenosis, or re-narrowing of the artery. In esophageal applications, self-expanding NiTi alloy stents are used to treat conditions like esophageal cancer or strictures caused by radiation therapy or other factors. These stents help maintain the patency of the esophagus, allowing patients to swallow food and liquids more easily. The stent's ability to expand and adapt to the esophageal anatomy reduces the risk of migration and improves patient comfort. Tracheal stents made from NiTi alloy are used to address tracheal stenosis or collapse, conditions that can lead to breathing difficulties. The stent provides structural support to the trachea, ensuring an open airway and improving respiratory function. The self-expanding nature of the stent allows for easy placement and adjustment, reducing the need for additional interventions. In urethral applications, these stents are used to treat urethral strictures, which can cause urinary retention and discomfort. The stent is placed in the urethra, where it expands to relieve the obstruction and restore normal urine flow. The biocompatibility and flexibility of the NiTi alloy ensure that the stent conforms to the urethral anatomy, minimizing irritation and the risk of infection. Overall, the self-expanding NiTi alloy stent offers a versatile and effective solution for a range of medical conditions, providing patients with improved quality of life and reducing the need for more invasive surgical procedures.
Hospital, Clinic in the Self-expanding NiTi Alloy Stent - Global Market:
In hospitals, the use of self-expanding NiTi alloy stents is widespread due to their versatility and effectiveness in treating various conditions. These stents are often used in the cardiology department for procedures such as angioplasty, where they are inserted into narrowed or blocked coronary arteries to restore blood flow and prevent heart attacks. The self-expanding nature of the stent allows for precise placement and reduces the risk of complications, making it a preferred choice for many cardiologists. In addition to cardiology, these stents are also used in the gastroenterology department to treat conditions like esophageal cancer or strictures. The stent is placed in the esophagus to maintain patency and allow patients to swallow food and liquids more easily. The flexibility and biocompatibility of the NiTi alloy make it ideal for use in the delicate esophageal tissue, reducing the risk of migration and improving patient comfort. In the pulmonology department, self-expanding NiTi alloy stents are used to treat tracheal stenosis or collapse, conditions that can lead to breathing difficulties. The stent provides structural support to the trachea, ensuring an open airway and improving respiratory function. The self-expanding nature of the stent allows for easy placement and adjustment, reducing the need for additional interventions. In urology, these stents are used to treat urethral strictures, which can cause urinary retention and discomfort. The stent is placed in the urethra, where it expands to relieve the obstruction and restore normal urine flow. The biocompatibility and flexibility of the NiTi alloy ensure that the stent conforms to the urethral anatomy, minimizing irritation and the risk of infection. In clinics, the use of self-expanding NiTi alloy stents is also common, particularly in outpatient settings where minimally invasive procedures are preferred. These stents are often used in procedures such as endoscopy or bronchoscopy, where they can be inserted into the esophagus or trachea to treat strictures or obstructions. The self-expanding nature of the stent allows for quick and easy placement, reducing the need for anesthesia and minimizing recovery time. Overall, the use of self-expanding NiTi alloy stents in hospitals and clinics provides patients with a safe and effective treatment option for a range of conditions, improving their quality of life and reducing the need for more invasive surgical procedures.
Self-expanding NiTi Alloy Stent - Global Market Outlook:
The global market for self-expanding NiTi alloy stents was valued at approximately $142 million in 2023, with projections indicating growth to $248.5 million by 2030, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.3% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is driven by increasing demand for minimally invasive procedures, advancements in stent technology, and a rising prevalence of conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, esophageal cancer, and other ailments that require stenting. The self-expanding nature of these stents allows for easier placement and reduced risk of complications, making them a preferred choice in many medical scenarios. As the global medical device market, estimated at $603 billion in 2023, continues to grow at a CAGR of 5% over the next six years, the demand for innovative solutions like the NiTi alloy stent is expected to rise, further fueling market expansion.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Self-expanding NiTi Alloy Stent - Market |
| Forecasted market size in 2030 | US$ 248.5 million |
| CAGR | 8.3% |
| Forecasted years | 2024 - 2030 |
| Segment by Type: |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| By Company | Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Cook, Becton & Dickinson, Abbott, Terumo, Cordis, Biotronik, Gore, ELLA-CS, MI-Tech |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
