What is Olfactory Neuroblastoma (ONB) - Global Market?
Olfactory Neuroblastoma (ONB) is a rare type of cancer that originates in the upper part of the nasal cavity, specifically in the olfactory epithelium, which is responsible for the sense of smell. This tumor is also known as esthesioneuroblastoma and is characterized by its aggressive nature and potential to spread to other parts of the body, including the brain and lymph nodes. The global market for ONB is driven by the need for effective diagnosis and treatment options, given the complexity and rarity of the disease. Advances in medical technology and increased awareness among healthcare professionals have contributed to the growth of this market. The market encompasses various diagnostic tools, surgical procedures, and therapeutic approaches aimed at managing ONB. As research continues to evolve, the market is expected to expand, offering new opportunities for healthcare providers and patients alike. The focus is on improving patient outcomes through early detection and personalized treatment plans, which are crucial in managing this challenging condition.
Chemotherapy, Immunotherapy in the Olfactory Neuroblastoma (ONB) - Global Market:
Chemotherapy and immunotherapy are two pivotal treatment modalities in the management of Olfactory Neuroblastoma (ONB), each offering unique mechanisms of action and therapeutic benefits. Chemotherapy involves the use of potent drugs to target and destroy rapidly dividing cancer cells. In the context of ONB, chemotherapy is often employed as an adjuvant treatment, meaning it is used in conjunction with other therapies such as surgery or radiation. The primary goal of chemotherapy in ONB is to reduce the size of the tumor, eliminate any remaining cancer cells post-surgery, and prevent metastasis. Common chemotherapeutic agents used in ONB include cisplatin, etoposide, and cyclophosphamide, among others. These drugs work by interfering with the DNA replication process of cancer cells, thereby inhibiting their growth and proliferation. However, chemotherapy is not without its challenges. Patients often experience side effects such as nausea, fatigue, and increased susceptibility to infections due to the impact of these drugs on healthy cells. Despite these challenges, chemotherapy remains a cornerstone in the treatment of ONB, particularly in cases where the tumor is inoperable or has spread to other regions. Immunotherapy, on the other hand, represents a more targeted approach to cancer treatment. It harnesses the body's immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. In recent years, immunotherapy has gained traction as a promising treatment option for various cancers, including ONB. This approach involves the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies, and cancer vaccines to enhance the immune response against tumor cells. One of the key advantages of immunotherapy is its ability to provide a more personalized treatment experience, as it can be tailored to the specific genetic makeup of the patient's tumor. This precision medicine approach has shown potential in improving treatment outcomes and reducing the likelihood of recurrence. However, immunotherapy is not without its limitations. The response to treatment can vary significantly among patients, and some may experience immune-related side effects such as inflammation and autoimmune reactions. Despite these challenges, ongoing research and clinical trials continue to explore the potential of immunotherapy in ONB, with the aim of improving its efficacy and minimizing adverse effects. The global market for ONB treatments, including chemotherapy and immunotherapy, is driven by several factors. The increasing incidence of ONB, coupled with advancements in diagnostic techniques, has led to a greater demand for effective treatment options. Additionally, the growing emphasis on personalized medicine and targeted therapies has spurred interest in immunotherapy as a viable treatment modality. Pharmaceutical companies and research institutions are investing heavily in the development of novel drugs and treatment protocols to address the unmet needs in ONB management. Furthermore, collaborations between academic institutions, healthcare providers, and industry players are fostering innovation and accelerating the translation of research findings into clinical practice. As a result, the ONB treatment market is poised for significant growth, with chemotherapy and immunotherapy playing central roles in shaping the future of cancer care.
Hospital, Clinic in the Olfactory Neuroblastoma (ONB) - Global Market:
The usage of Olfactory Neuroblastoma (ONB) treatments in hospitals and clinics is integral to the comprehensive management of this rare cancer. Hospitals, being the primary centers for cancer treatment, play a crucial role in the diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up care of ONB patients. In a hospital setting, a multidisciplinary team of specialists, including oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, and pathologists, collaborates to develop individualized treatment plans for patients. This team-based approach ensures that all aspects of the patient's care are addressed, from initial diagnosis to post-treatment monitoring. Hospitals are equipped with advanced diagnostic tools such as MRI and CT scans, which are essential for accurately staging the tumor and planning surgical interventions. Surgical resection remains a primary treatment modality for ONB, and hospitals provide the necessary infrastructure and expertise to perform complex surgeries with precision and care. In addition to surgery, hospitals offer a range of adjuvant therapies, including chemotherapy and radiation therapy, to enhance treatment outcomes. Chemotherapy is administered in a controlled hospital environment, where patients can be closely monitored for any adverse reactions. The hospital setting also facilitates the administration of immunotherapy, which may require specialized equipment and expertise. Furthermore, hospitals are often involved in clinical trials, providing patients with access to cutting-edge treatments and experimental therapies that may not be available in other settings. This access to innovative treatment options is a significant advantage for ONB patients, as it offers the potential for improved outcomes and quality of life. Clinics, on the other hand, serve as important centers for ongoing care and support for ONB patients. While they may not have the same level of resources as hospitals, clinics provide essential services such as routine check-ups, follow-up care, and supportive therapies. Clinics are often more accessible to patients, offering a convenient location for regular appointments and consultations. In a clinic setting, healthcare providers focus on monitoring the patient's progress, managing any side effects of treatment, and addressing any concerns or complications that may arise. Clinics also play a vital role in patient education, providing information on disease management, lifestyle modifications, and coping strategies to help patients navigate their cancer journey. The integration of hospital and clinic services is crucial for ensuring continuity of care for ONB patients. Effective communication and coordination between these two settings enable seamless transitions between different phases of treatment and care. For instance, a patient may undergo surgery and initial chemotherapy in a hospital, followed by regular follow-up appointments and supportive care in a clinic. This integrated approach ensures that patients receive comprehensive and consistent care throughout their treatment journey. Moreover, the collaboration between hospitals and clinics fosters a supportive network for patients, providing them with access to a wide range of resources and expertise. As the global market for ONB treatments continues to evolve, the role of hospitals and clinics in delivering high-quality care remains paramount, ensuring that patients receive the best possible outcomes.
Olfactory Neuroblastoma (ONB) - Global Market Outlook:
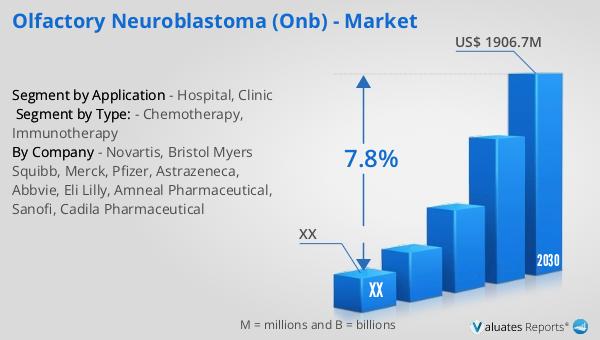
The global market for Olfactory Neuroblastoma (ONB) was valued at approximately $1,139 million in 2023, with projections indicating a growth to around $1,906.7 million by 2030. This represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2030. The North American segment of the ONB market was also assessed in 2023, although specific figures were not provided. However, it is anticipated to experience growth at a certain CAGR throughout the same forecast period. This market expansion is driven by several factors, including advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic technologies, increased awareness among healthcare professionals, and a growing emphasis on personalized medicine. The rising incidence of ONB and the need for effective treatment options further contribute to the market's growth. As research and development efforts continue to advance, the ONB market is expected to offer new opportunities for healthcare providers, pharmaceutical companies, and patients. The focus remains on improving patient outcomes through early detection, innovative treatment approaches, and comprehensive care strategies. This market outlook underscores the importance of continued investment in research and collaboration among industry stakeholders to address the challenges associated with ONB and enhance the quality of care for patients worldwide.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Olfactory Neuroblastoma (ONB) - Market |
| Forecasted market size in 2030 | US$ 1906.7 million |
| CAGR | 7.8% |
| Forecasted years | 2024 - 2030 |
| Segment by Type: |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| By Company | Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck, Pfizer, Astrazeneca, Abbvie, Eli Lilly, Amneal Pharmaceutical, Sanofi, Cadila Pharmaceutical |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
