What is Asphalt Chemical Modifiers - Global Market?
Asphalt chemical modifiers are specialized additives used to enhance the properties of asphalt, which is a key material in road construction and maintenance. These modifiers are crucial in improving the performance, durability, and longevity of asphalt pavements. The global market for asphalt chemical modifiers is driven by the increasing demand for high-performance road infrastructure, especially in regions experiencing rapid urbanization and industrialization. These modifiers help in addressing various challenges associated with asphalt, such as susceptibility to temperature variations, moisture damage, and heavy traffic loads. By incorporating chemical modifiers, asphalt can achieve better resistance to cracking, rutting, and aging, thereby extending the lifespan of roads and reducing maintenance costs. The market is characterized by a diverse range of products, each designed to meet specific performance requirements and environmental conditions. As the construction industry continues to evolve, the demand for innovative and sustainable asphalt solutions is expected to grow, further propelling the market for chemical modifiers. This growth is also supported by advancements in technology and increased awareness about the benefits of modified asphalt in enhancing road safety and efficiency.
Phosphoric Acid and Polyphosphoric Acid, Thermoplastic Elastomer, Thermoplastic Polymer, Thermosetting Polymer, Fiber, Others in the Asphalt Chemical Modifiers - Global Market:
Phosphoric acid and polyphosphoric acid are commonly used as asphalt chemical modifiers due to their ability to improve the high-temperature performance of asphalt. Phosphoric acid acts as a catalyst, enhancing the stiffness and elasticity of asphalt, which is crucial for roads exposed to high temperatures and heavy traffic. Polyphosphoric acid, on the other hand, offers even greater benefits by providing superior resistance to deformation and improving the overall durability of asphalt pavements. These acids are particularly effective in regions with extreme weather conditions, where maintaining road integrity is a significant challenge. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) are another category of asphalt modifiers that offer flexibility and resilience. TPEs are polymers that combine the properties of rubber and plastic, allowing asphalt to withstand temperature fluctuations without cracking. This makes them ideal for use in areas with varying climates. Thermoplastic polymers, similar to TPEs, enhance the flexibility and workability of asphalt, making it easier to apply and compact. They also contribute to the recyclability of asphalt, aligning with the growing emphasis on sustainable construction practices. Thermosetting polymers, unlike thermoplastics, form irreversible bonds upon curing, providing enhanced strength and stability to asphalt. These polymers are particularly useful in applications where long-term performance and resistance to chemical and physical stressors are required. Fibers, such as cellulose and synthetic fibers, are added to asphalt to improve its tensile strength and resistance to cracking. They act as reinforcement, distributing stress more evenly across the pavement and reducing the likelihood of surface damage. Other modifiers, including anti-stripping agents and adhesion promoters, are used to enhance the bond between asphalt and aggregates, preventing moisture-induced damage and ensuring the longevity of the pavement. The global market for asphalt chemical modifiers is diverse, with each type of modifier offering unique benefits tailored to specific environmental and performance needs. As infrastructure demands continue to rise, the role of these modifiers in creating durable, efficient, and sustainable road networks becomes increasingly important.
Hot Mix Asphalt, Cold Mix Asphalt, Warm Mix Asphalt in the Asphalt Chemical Modifiers - Global Market:
Asphalt chemical modifiers play a crucial role in the production and performance of different types of asphalt mixtures, including hot mix asphalt (HMA), cold mix asphalt (CMA), and warm mix asphalt (WMA). Hot mix asphalt is the most commonly used type, known for its durability and strength. It is produced by heating asphalt binder and aggregates to high temperatures, allowing for thorough mixing and compaction. Chemical modifiers are added to HMA to enhance its resistance to high temperatures, heavy traffic loads, and environmental stressors. These modifiers improve the elasticity and stiffness of the asphalt, reducing the risk of rutting and cracking. Cold mix asphalt, on the other hand, is produced without the need for high temperatures, making it a more environmentally friendly option. It is ideal for patching and repairing roads, especially in remote areas where hot mix plants are not accessible. Chemical modifiers in CMA help improve its workability and adhesion, ensuring a strong bond between the asphalt and aggregates even at lower temperatures. Warm mix asphalt is a relatively newer technology that allows for the production of asphalt at lower temperatures compared to HMA. This results in reduced energy consumption and emissions, making it a more sustainable option. Chemical modifiers in WMA facilitate the mixing and compaction process at lower temperatures, ensuring the asphalt maintains its performance characteristics. They also enhance the moisture resistance of WMA, reducing the risk of water damage and extending the lifespan of the pavement. The use of asphalt chemical modifiers in these different types of asphalt mixtures highlights their versatility and importance in modern road construction. By improving the performance and sustainability of asphalt, these modifiers contribute to the development of safer, more efficient, and longer-lasting road networks.
Asphalt Chemical Modifiers - Global Market Outlook:
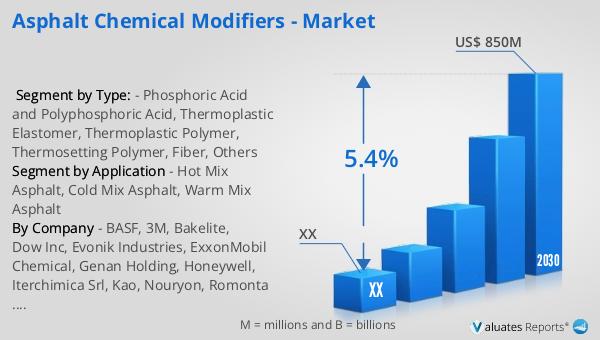
The global market for asphalt chemical modifiers was valued at approximately $570 million in 2023. It is projected to grow to a revised size of $850 million by 2030, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.4% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2030. This growth is indicative of the increasing demand for enhanced asphalt solutions in the construction industry. In North America, the market for asphalt chemical modifiers was valued at a certain amount in 2023 and is expected to reach a new value by 2030, with a specific CAGR during the forecast period. This regional growth is driven by the need for durable and sustainable road infrastructure, as well as advancements in construction technologies. The market outlook reflects the growing recognition of the benefits of using chemical modifiers in asphalt to improve road performance and longevity. As urbanization and industrialization continue to expand globally, the demand for high-quality road networks is expected to rise, further boosting the market for asphalt chemical modifiers. This positive market trajectory underscores the importance of innovation and sustainability in the construction sector, as stakeholders seek to address the challenges of modern infrastructure development.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Asphalt Chemical Modifiers - Market |
| Forecasted market size in 2030 | US$ 850 million |
| CAGR | 5.4% |
| Forecasted years | 2024 - 2030 |
| Segment by Type: |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| By Company | BASF, 3M, Bakelite, Dow Inc, Evonik Industries, ExxonMobil Chemical, Genan Holding, Honeywell, Iterchimica Srl, Kao, Nouryon, Romonta GmbH, Textile Rubber and Chemical Co |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |