What is Absorbable Ophthalmic Surgical Sutures - Global Market?
Absorbable ophthalmic surgical sutures are specialized threads used in eye surgeries to close wounds or incisions. These sutures are designed to be absorbed by the body over time, eliminating the need for removal and reducing the risk of infection. The global market for these sutures is driven by the increasing prevalence of eye disorders and the growing number of ophthalmic surgeries worldwide. As the population ages, conditions such as cataracts, glaucoma, and retinal disorders become more common, necessitating surgical interventions that often require sutures. Technological advancements in suture materials and manufacturing processes have also contributed to market growth, offering surgeons more options in terms of suture strength, absorption rate, and biocompatibility. Additionally, the rising demand for minimally invasive surgeries has spurred the development of finer, more precise sutures that facilitate quicker recovery and less scarring. The market is further bolstered by the expansion of healthcare infrastructure in emerging economies, where access to advanced surgical procedures is improving. Overall, the absorbable ophthalmic surgical sutures market is poised for steady growth as it continues to adapt to the evolving needs of both patients and healthcare providers.
Monofilament Suture, Multifilament Suture in the Absorbable Ophthalmic Surgical Sutures - Global Market:
Monofilament and multifilament sutures are two primary types of absorbable ophthalmic surgical sutures, each with distinct characteristics and applications. Monofilament sutures are made from a single strand of material, which gives them a smooth surface that reduces tissue drag during insertion. This feature is particularly beneficial in delicate ophthalmic surgeries where minimizing tissue trauma is crucial. Monofilament sutures are less likely to harbor bacteria, making them a preferred choice in procedures where infection risk must be minimized. However, their smooth surface can make them more challenging to handle and knot securely, requiring skilled surgical techniques. On the other hand, multifilament sutures are composed of multiple strands twisted or braided together, providing greater flexibility and ease of handling. This structure allows for more secure knotting, which can be advantageous in surgeries requiring precise suture placement. The braided nature of multifilament sutures can increase tissue drag, potentially causing more trauma during insertion, but advancements in coating technologies have mitigated this issue by providing smoother surfaces. Multifilament sutures may also have a higher risk of bacterial colonization due to their braided structure, but they offer superior tensile strength, making them suitable for surgeries where suture strength is paramount. In the global market, the choice between monofilament and multifilament sutures often depends on the specific requirements of the surgical procedure, the surgeon's preference, and the patient's condition. Both types of sutures are available in various materials, such as polyglycolic acid, polylactic acid, and polydioxanone, each offering different absorption rates and biocompatibility profiles. The development of new materials and coatings continues to enhance the performance of both monofilament and multifilament sutures, expanding their applications in ophthalmic surgeries. As the demand for advanced surgical solutions grows, manufacturers are investing in research and development to create sutures that offer optimal balance between strength, flexibility, and absorption. This ongoing innovation is crucial in addressing the diverse needs of the global ophthalmic surgical community, ensuring that surgeons have access to the best tools for achieving successful patient outcomes.
Hospital, Clinic in the Absorbable Ophthalmic Surgical Sutures - Global Market:
Absorbable ophthalmic surgical sutures play a vital role in both hospital and clinic settings, where they are used to facilitate healing after eye surgeries. In hospitals, these sutures are commonly employed in complex procedures such as cataract extraction, corneal transplants, and retinal detachment repairs. The use of absorbable sutures in these settings is advantageous because it reduces the need for follow-up visits to remove sutures, thereby decreasing the overall burden on hospital resources and improving patient convenience. Hospitals often have access to a wide range of suture materials and sizes, allowing surgeons to select the most appropriate suture for each specific procedure. The availability of advanced surgical equipment and skilled personnel in hospitals further enhances the effectiveness of absorbable sutures in promoting optimal healing outcomes. In clinics, absorbable ophthalmic surgical sutures are frequently used in less invasive procedures, such as pterygium excision and minor eyelid surgeries. Clinics benefit from the use of these sutures as they enable quick and efficient procedures, often performed on an outpatient basis. The absorbable nature of the sutures ensures that patients do not need to return for suture removal, which is particularly beneficial in clinic settings where resources may be more limited than in hospitals. The use of absorbable sutures in clinics also aligns with the growing trend towards minimally invasive surgeries, which prioritize patient comfort and faster recovery times. Both hospitals and clinics rely on the versatility and reliability of absorbable ophthalmic surgical sutures to deliver high-quality care to patients undergoing eye surgeries. The choice of suture type and material is often guided by the specific needs of the procedure, the surgeon's expertise, and the patient's individual circumstances. As the global market for absorbable ophthalmic surgical sutures continues to expand, healthcare providers in both hospitals and clinics are increasingly able to access a diverse array of suture options, ensuring that they can provide the best possible care for their patients.
Absorbable Ophthalmic Surgical Sutures - Global Market Outlook:
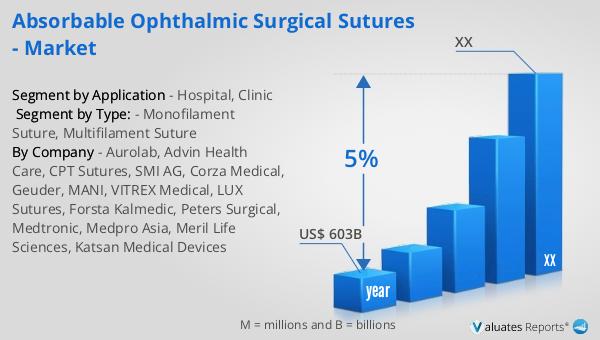
Our research indicates that the global market for medical devices, including absorbable ophthalmic surgical sutures, is projected to reach approximately $603 billion in 2023. This substantial market size reflects the growing demand for advanced medical technologies and innovations that enhance patient care and surgical outcomes. Over the next six years, the market is expected to experience a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5%, driven by factors such as the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, an aging population, and the expansion of healthcare infrastructure in emerging economies. The steady growth of the medical device market underscores the importance of continuous research and development efforts to meet the evolving needs of healthcare providers and patients worldwide. As the market expands, manufacturers are likely to focus on developing new materials and technologies that improve the performance and safety of medical devices, including absorbable ophthalmic surgical sutures. This growth trajectory presents significant opportunities for stakeholders across the healthcare industry, from manufacturers and suppliers to healthcare providers and patients, as they work together to advance the field of medical technology and improve health outcomes globally.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Absorbable Ophthalmic Surgical Sutures - Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 603 billion |
| CAGR | 5% |
| Base Year | year |
| Segment by Type: |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| By Company | Aurolab, Advin Health Care, CPT Sutures, SMI AG, Corza Medical, Geuder, MANI, VITREX Medical, LUX Sutures, Forsta Kalmedic, Peters Surgical, Medtronic, Medpro Asia, Meril Life Sciences, Katsan Medical Devices |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
