What is Global Viral Gene Therapy Market?
The global viral gene therapy market is a rapidly evolving field that focuses on using viral vectors to deliver therapeutic genes into patients' cells to treat various genetic disorders and diseases. This innovative approach leverages the natural ability of viruses to introduce genetic material into host cells. By modifying these viruses to carry therapeutic genes instead of their own viral genes, scientists can target and correct genetic defects at the molecular level. The market encompasses a wide range of applications, including the treatment of inherited genetic disorders, cancers, and other serious conditions. The growing interest in gene therapy is driven by its potential to provide long-lasting and potentially curative treatments, which traditional therapies often cannot achieve. As research advances and more gene therapies receive regulatory approval, the global viral gene therapy market is expected to expand significantly, offering new hope for patients with previously untreatable conditions.
Integrating Viral Vectors, Non-Integrating Viral Vectors in the Global Viral Gene Therapy Market:
Integrating viral vectors and non-integrating viral vectors are two primary types of vectors used in the global viral gene therapy market, each with distinct characteristics and applications. Integrating viral vectors, such as lentiviruses and retroviruses, incorporate the therapeutic gene into the host cell's genome. This integration ensures that the therapeutic gene is passed on to daughter cells during cell division, making it particularly useful for treating conditions that require long-term gene expression. However, the integration process carries a risk of insertional mutagenesis, where the insertion of the viral DNA disrupts normal cellular genes, potentially leading to cancer or other issues. On the other hand, non-integrating viral vectors, such as adenoviruses and adeno-associated viruses (AAV), deliver the therapeutic gene without integrating it into the host genome. This approach reduces the risk of insertional mutagenesis but may require repeated administrations to maintain therapeutic levels of gene expression, especially in rapidly dividing cells. Adenoviruses are known for their high transduction efficiency and ability to infect a wide range of cell types, making them suitable for applications where transient gene expression is sufficient. AAVs, in particular, have gained popularity due to their low immunogenicity and ability to achieve long-term gene expression in non-dividing cells, making them ideal for treating chronic conditions. The choice between integrating and non-integrating vectors depends on various factors, including the nature of the disease, the target cell type, and the desired duration of gene expression. Researchers and clinicians must carefully consider these factors to select the most appropriate vector for each specific application. As the field of gene therapy continues to advance, ongoing research aims to improve the safety and efficacy of both integrating and non-integrating viral vectors, expanding their potential to treat a broader range of diseases.
Metabolic Diseases, Cardiovascular Diseases, Muscular Diseases, Hematologic Diseases, Ophthalmologic Diseases, Infectious Diseases, Others in the Global Viral Gene Therapy Market:
The global viral gene therapy market has shown promising potential in treating a variety of diseases, including metabolic, cardiovascular, muscular, hematologic, ophthalmologic, and infectious diseases, among others. In the realm of metabolic diseases, gene therapy aims to correct genetic defects that lead to metabolic dysfunctions, such as lysosomal storage disorders and phenylketonuria. By introducing functional copies of the defective genes, gene therapy can restore normal metabolic processes and alleviate symptoms. For cardiovascular diseases, gene therapy focuses on repairing or regenerating damaged heart tissues, improving blood flow, and reducing the risk of heart failure. This can be achieved by delivering genes that promote angiogenesis or by correcting genetic mutations that cause inherited heart conditions. Muscular diseases, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, can also benefit from gene therapy by introducing genes that produce functional dystrophin protein, thereby improving muscle strength and function. Hematologic diseases, including hemophilia and sickle cell anemia, are prime candidates for gene therapy due to the accessibility of blood cells for genetic modification. By correcting the underlying genetic defects, gene therapy can provide long-term relief from these debilitating conditions. Ophthalmologic diseases, such as Leber congenital amaurosis and retinitis pigmentosa, have seen significant advancements with gene therapy, offering the potential to restore vision in patients with inherited retinal disorders. Infectious diseases, including HIV and hepatitis, are also being targeted by gene therapy approaches that aim to enhance the immune system's ability to fight off infections or to directly target and eliminate the pathogens. The versatility of viral gene therapy extends to other areas as well, including cancer treatment, where it can be used to deliver genes that induce tumor cell death or enhance the immune response against cancer cells. As research progresses, the global viral gene therapy market continues to expand its reach, offering new treatment options for a wide range of diseases that were previously considered untreatable.
Global Viral Gene Therapy Market Outlook:
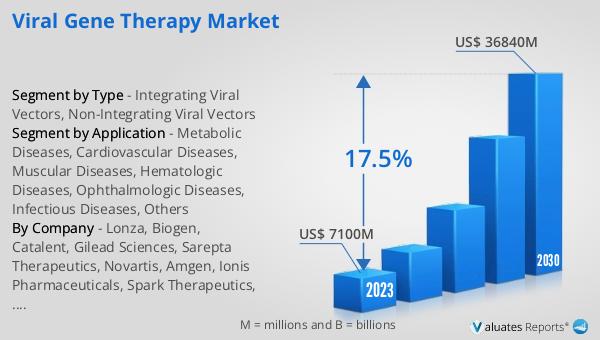
The global viral gene therapy market was valued at $7.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $36.84 billion by 2030, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.5% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2030. This substantial growth is driven by the increasing prevalence of genetic disorders and the rising demand for innovative treatments that offer long-term and potentially curative benefits. Advances in gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR-Cas9, and improvements in viral vector design and delivery methods have significantly enhanced the safety and efficacy of gene therapies, further fueling market growth. Additionally, the growing number of clinical trials and regulatory approvals for gene therapy products are contributing to the market's expansion. As more gene therapies become available, they are expected to address a broader range of diseases, providing new hope for patients with conditions that currently have limited treatment options. The global viral gene therapy market's impressive growth trajectory underscores the transformative potential of this cutting-edge field in revolutionizing the treatment landscape for various genetic and acquired diseases.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Viral Gene Therapy Market |
| Accounted market size in 2023 | US$ 7100 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2030 | US$ 36840 million |
| CAGR | 17.5% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecasted years | 2024 - 2030 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| By Company | Lonza, Biogen, Catalent, Gilead Sciences, Sarepta Therapeutics, Novartis, Amgen, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Spark Therapeutics, Shanghai Sunway Biotech, SIBIONO, AnGes, Orchard Therapeutics |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
