What is Global Biomedical Polymers Market?
The Global Biomedical Polymers Market is a rapidly evolving sector that focuses on the development and application of polymer materials in the medical field. These polymers are specially designed to meet the stringent requirements of medical applications, such as biocompatibility, sterilizability, and mechanical properties. Biomedical polymers are used in a wide range of medical devices and products, including surgical instruments, implants, drug delivery systems, and tissue engineering scaffolds. The market is driven by the increasing demand for advanced medical devices, the growing prevalence of chronic diseases, and the rising aging population. Additionally, technological advancements in polymer science and the increasing focus on personalized medicine are further propelling the growth of this market. The global biomedical polymers market is characterized by a high level of innovation and competition, with numerous companies investing in research and development to create new and improved polymer materials. The market is also influenced by regulatory standards and policies, which ensure the safety and efficacy of biomedical polymers used in medical applications. Overall, the global biomedical polymers market plays a crucial role in the advancement of medical technology and the improvement of patient care.
Natural Type, Synthetic Type in the Global Biomedical Polymers Market:
Biomedical polymers can be broadly categorized into two types: natural and synthetic. Natural biomedical polymers are derived from biological sources, such as plants, animals, and microorganisms. These polymers include materials like collagen, gelatin, chitosan, and alginate. Natural polymers are often favored for their biocompatibility and biodegradability, making them suitable for applications where temporary support or gradual degradation is required. For example, collagen is widely used in wound dressings and tissue engineering due to its excellent biocompatibility and ability to promote cell growth. Chitosan, derived from the shells of crustaceans, is used in drug delivery systems and wound healing applications due to its antimicrobial properties and ability to form hydrogels. On the other hand, synthetic biomedical polymers are man-made materials that are engineered to meet specific medical requirements. These polymers include materials like polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polylactic acid (PLA). Synthetic polymers offer greater control over their properties, such as mechanical strength, flexibility, and degradation rate, making them suitable for a wide range of medical applications. For instance, polyethylene is commonly used in joint replacement implants due to its high wear resistance and durability. PLA, a biodegradable polymer, is used in sutures and drug delivery systems where gradual degradation is desired. Both natural and synthetic biomedical polymers have their unique advantages and limitations, and the choice of polymer depends on the specific requirements of the medical application. The development of hybrid polymers, which combine the properties of both natural and synthetic materials, is an emerging trend in the biomedical polymers market. These hybrid materials aim to offer the best of both worlds, providing the biocompatibility and biodegradability of natural polymers along with the tunable properties of synthetic polymers. Overall, the diversity of biomedical polymers and their ability to be tailored to specific medical needs make them invaluable in the advancement of medical technology and patient care.
Surgical Sutures, Controlled Release of Drugs, Others in the Global Biomedical Polymers Market:
Biomedical polymers are extensively used in various medical applications, including surgical sutures, controlled release of drugs, and other medical devices. In the area of surgical sutures, biomedical polymers play a crucial role in wound closure and healing. Polymers such as polyglycolic acid (PGA) and polylactic acid (PLA) are commonly used to manufacture absorbable sutures that gradually degrade in the body, eliminating the need for suture removal and reducing the risk of infection. These sutures provide temporary support to the wound, allowing it to heal naturally over time. Non-absorbable sutures made from polymers like polypropylene and nylon are used in situations where long-term support is required. In the controlled release of drugs, biomedical polymers are used to create drug delivery systems that release therapeutic agents at a controlled rate over a specified period. Polymers such as poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) are used to encapsulate drugs in microspheres or nanoparticles, providing a sustained release of the drug and improving its efficacy. This approach is particularly beneficial for chronic conditions that require long-term medication, as it reduces the frequency of drug administration and enhances patient compliance. Biomedical polymers are also used in other medical applications, such as tissue engineering, where they serve as scaffolds to support the growth and regeneration of tissues. Polymers like collagen and hyaluronic acid are used to create scaffolds that mimic the natural extracellular matrix, promoting cell attachment and proliferation. Additionally, biomedical polymers are used in the manufacturing of medical devices such as catheters, stents, and prosthetic implants. These polymers provide the necessary mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and sterilizability required for these devices to function effectively in the body. Overall, the versatility and adaptability of biomedical polymers make them essential in a wide range of medical applications, contributing to the advancement of medical technology and the improvement of patient outcomes.
Global Biomedical Polymers Market Outlook:
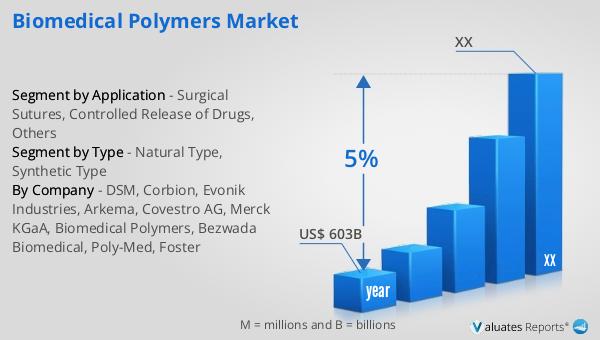
According to our research, the global market for medical devices is projected to reach approximately US$ 603 billion in 2023, with an anticipated growth rate of 5% annually over the next six years. This growth is driven by several factors, including the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, the aging population, and the rising demand for advanced medical technologies. The medical device industry encompasses a wide range of products, from simple bandages and surgical instruments to complex diagnostic equipment and implantable devices. The continuous innovation and development of new medical devices are essential to meet the evolving needs of healthcare providers and patients. Additionally, the regulatory landscape for medical devices is becoming increasingly stringent, with a focus on ensuring the safety and efficacy of these products. Companies operating in this market are investing heavily in research and development to create innovative solutions that address unmet medical needs and improve patient care. The growing adoption of digital health technologies, such as telemedicine and wearable devices, is also contributing to the expansion of the medical device market. These technologies enable remote monitoring and management of health conditions, providing patients with greater convenience and access to healthcare services. Overall, the global medical device market is poised for significant growth, driven by technological advancements, increasing healthcare expenditure, and the rising demand for high-quality medical care.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Biomedical Polymers Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 603 billion |
| CAGR | 5% |
| Base Year | year |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | DSM, Corbion, Evonik Industries, Arkema, Covestro AG, Merck KGaA, Biomedical Polymers, Bezwada Biomedical, Poly-Med, Foster |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
