What is Global Hospital Acquired Pneumonia Drugs Market?
The Global Hospital Acquired Pneumonia Drugs Market refers to the segment of the pharmaceutical industry that focuses on the development, production, and distribution of medications specifically designed to treat pneumonia acquired in hospital settings. Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) is a significant concern in healthcare facilities worldwide, as it is a common infection that patients can contract during their hospital stay, often leading to severe complications. The market for these drugs is driven by the need to effectively manage and treat HAP, which is caused by various bacteria, viruses, and fungi that thrive in hospital environments. The market encompasses a range of antibiotics and antiviral medications tailored to combat the specific pathogens responsible for HAP. As healthcare systems globally strive to improve patient outcomes and reduce hospital stays, the demand for effective HAP drugs continues to grow. This market is characterized by ongoing research and development efforts to create more effective treatments, as well as regulatory approvals that ensure the safety and efficacy of these drugs. The Global Hospital Acquired Pneumonia Drugs Market plays a crucial role in enhancing patient care and reducing the burden of hospital-acquired infections.
Phase II, Early Phase (Phase I & II) in the Global Hospital Acquired Pneumonia Drugs Market:
Phase II and Early Phase (Phase I & II) clinical trials are critical stages in the development of drugs for the Global Hospital Acquired Pneumonia Drugs Market. These phases are essential for evaluating the safety, efficacy, and optimal dosing of new medications intended to treat hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP). Phase I trials are the initial step in testing a new drug in humans. They primarily focus on assessing the safety profile of the drug, determining the appropriate dosage range, and identifying any potential side effects. These trials are usually conducted with a small group of healthy volunteers or patients and are crucial for establishing a foundation for further research. In the context of HAP drugs, Phase I trials help researchers understand how the drug interacts with the human body, its pharmacokinetics, and its pharmacodynamics. Once a drug successfully passes Phase I, it progresses to Phase II trials. Phase II trials involve a larger group of participants, typically patients who have the condition the drug is intended to treat—in this case, hospital-acquired pneumonia. The primary goal of Phase II is to evaluate the drug's efficacy and further assess its safety. Researchers aim to determine whether the drug has a therapeutic effect on HAP and to identify the optimal dose that provides the best balance between efficacy and safety. These trials are often randomized and controlled, meaning that participants are randomly assigned to receive either the experimental drug or a placebo, allowing researchers to compare outcomes and draw meaningful conclusions. Early Phase trials, which encompass both Phase I and Phase II, are crucial for identifying promising drug candidates that can proceed to later stages of development. They provide valuable data that inform decisions about whether to advance a drug to Phase III trials, where larger populations are studied to confirm efficacy and monitor adverse reactions. In the context of the Global Hospital Acquired Pneumonia Drugs Market, these early phases are particularly important due to the complexity of treating HAP. Hospital-acquired pneumonia is often caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria, making it challenging to develop effective treatments. Early Phase trials help identify drugs that can overcome these challenges and offer new hope for patients. The success of Phase II and Early Phase trials is vital for the overall progress of the Global Hospital Acquired Pneumonia Drugs Market. Positive results can lead to increased investment in research and development, as well as collaborations between pharmaceutical companies and healthcare institutions. These collaborations are essential for pooling resources, expertise, and data to accelerate the development of new treatments. Furthermore, regulatory agencies closely monitor these trials to ensure that any new drugs meet stringent safety and efficacy standards before they are approved for widespread use. In conclusion, Phase II and Early Phase (Phase I & II) trials are pivotal in the journey of developing new drugs for the Global Hospital Acquired Pneumonia Drugs Market. They provide the necessary evidence to support the advancement of promising drug candidates and contribute to the ongoing efforts to improve patient outcomes in hospital settings. As the demand for effective HAP treatments continues to rise, these trials play a crucial role in shaping the future of healthcare and addressing the challenges posed by hospital-acquired infections.
Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, Drug Store, E-Commerce in the Global Hospital Acquired Pneumonia Drugs Market:
The usage of drugs from the Global Hospital Acquired Pneumonia Drugs Market spans various distribution channels, including hospital pharmacies, retail pharmacies, drug stores, and e-commerce platforms. Each of these channels plays a unique role in ensuring that patients have access to the medications they need to treat hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP). Hospital pharmacies are a primary distribution point for HAP drugs, as they are directly linked to healthcare facilities where patients are treated. These pharmacies work closely with healthcare providers to ensure that the right medications are available for patients diagnosed with HAP. Hospital pharmacists play a crucial role in managing medication therapy, providing guidance on drug interactions, and ensuring that patients receive the appropriate dosage. The close proximity of hospital pharmacies to patients allows for timely access to medications, which is critical in managing acute infections like HAP. Retail pharmacies and drug stores also serve as important distribution channels for HAP drugs, particularly for patients who are discharged from the hospital but still require ongoing treatment. These pharmacies provide a convenient option for patients to fill their prescriptions and continue their medication regimen at home. Pharmacists in retail settings offer valuable counseling services, helping patients understand their treatment plan, potential side effects, and the importance of adherence to prescribed therapies. The accessibility of retail pharmacies and drug stores makes it easier for patients to obtain their medications, contributing to better health outcomes. E-commerce platforms have emerged as a growing channel for the distribution of HAP drugs, offering patients the convenience of ordering medications online and having them delivered to their doorstep. This option is particularly beneficial for patients with mobility issues or those living in remote areas where access to physical pharmacies may be limited. E-commerce platforms often provide detailed information about medications, including usage instructions and potential side effects, empowering patients to make informed decisions about their treatment. Additionally, online pharmacies may offer competitive pricing and discounts, making medications more affordable for patients. The integration of e-commerce into the distribution of HAP drugs reflects the broader trend of digital transformation in healthcare, where technology is leveraged to enhance patient access to essential medications. In summary, the Global Hospital Acquired Pneumonia Drugs Market relies on a diverse range of distribution channels to ensure that patients have access to the medications they need. Hospital pharmacies, retail pharmacies, drug stores, and e-commerce platforms each play a vital role in the supply chain, contributing to the timely and effective treatment of HAP. As healthcare systems continue to evolve, these channels will remain essential in meeting the needs of patients and improving outcomes for those affected by hospital-acquired pneumonia.
Global Hospital Acquired Pneumonia Drugs Market Outlook:
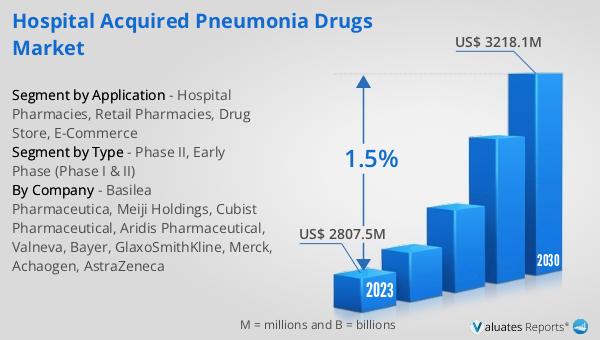
The worldwide market for Hospital Acquired Pneumonia Drugs was valued at approximately $2,983 million in 2024. It is anticipated to expand to a revised size of around $3,306 million by 2031, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 1.5% over the forecast period. This growth indicates a steady demand for medications that address hospital-acquired pneumonia, a significant concern in healthcare settings due to its impact on patient health and hospital resources. The market's expansion is driven by ongoing research and development efforts, as well as the introduction of new and more effective treatments. In parallel, the global market for medical devices is estimated to be valued at $603 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 5% over the next six years. This growth in the medical devices sector underscores the broader trend of increasing investment in healthcare technologies and innovations aimed at improving patient care and outcomes. The interplay between the pharmaceutical and medical device markets highlights the comprehensive approach needed to address complex healthcare challenges like hospital-acquired pneumonia. As these markets continue to evolve, they will play a crucial role in shaping the future of healthcare delivery and enhancing the quality of life for patients worldwide.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Hospital Acquired Pneumonia Drugs Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 2983 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 3306 million |
| CAGR | 1.5% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Basilea Pharmaceutica, Meiji Holdings, Cubist Pharmaceutical, Aridis Pharmaceutical, Valneva, Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Achaogen, AstraZeneca |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |