What is Global Epilepsy Drug Market?
The global epilepsy drug market is a specialized segment of the pharmaceutical industry focused on the development and distribution of medications designed to manage and treat epilepsy, a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures. This market encompasses a wide range of drugs that aim to control seizures, improve the quality of life for patients, and reduce the frequency and severity of epileptic episodes. The market is driven by factors such as the increasing prevalence of epilepsy worldwide, advancements in drug formulations, and a growing awareness of the condition. Pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in research and development to create more effective and safer medications, catering to the diverse needs of epilepsy patients. The market is also influenced by regulatory approvals, patent expirations, and the introduction of generic drugs, which can impact pricing and accessibility. As the understanding of epilepsy and its underlying causes continues to evolve, the global epilepsy drug market is poised to adapt and expand, offering new opportunities for innovation and improved patient outcomes.
First Generation Drugs, Second Generation Drugs, Third Generation Drugs in the Global Epilepsy Drug Market:
First-generation epilepsy drugs, also known as traditional antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), have been the cornerstone of epilepsy treatment for decades. These medications, including phenobarbital, phenytoin, carbamazepine, and valproic acid, were among the first to be developed and have a long history of use. They work by stabilizing electrical activity in the brain, thereby reducing the likelihood of seizures. Despite their effectiveness, first-generation drugs often come with a range of side effects, such as dizziness, fatigue, and cognitive impairment, which can impact a patient's quality of life. Additionally, these drugs may interact with other medications, necessitating careful management by healthcare providers. Second-generation epilepsy drugs emerged as an improvement over their predecessors, offering better tolerability and fewer side effects. These include medications like lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and topiramate. Second-generation drugs are often used when patients do not respond well to first-generation treatments or experience intolerable side effects. They provide more options for personalized treatment plans, allowing healthcare providers to tailor therapy to individual patient needs. Third-generation epilepsy drugs represent the latest advancements in epilepsy treatment. These newer medications, such as lacosamide, perampanel, and brivaracetam, are designed to offer even greater efficacy and safety. They often target specific types of seizures or epilepsy syndromes, providing more precise treatment options. Third-generation drugs are typically used when patients have not achieved adequate seizure control with earlier treatments or when they experience significant side effects. The development of these drugs reflects ongoing research efforts to better understand epilepsy and improve patient outcomes. As the global epilepsy drug market continues to evolve, the introduction of new medications and treatment strategies will play a crucial role in enhancing the quality of life for individuals living with epilepsy.
Hospital, Clinic, Others in the Global Epilepsy Drug Market:
The global epilepsy drug market plays a vital role in various healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, and other medical facilities. In hospitals, epilepsy drugs are often used in emergency situations to manage acute seizures and stabilize patients. Hospital settings provide access to a wide range of diagnostic tools and specialized care, allowing for comprehensive evaluation and treatment of epilepsy. Inpatient care may be necessary for patients experiencing severe or frequent seizures, and hospital-based neurologists and epileptologists work closely with patients to develop effective treatment plans. Clinics, on the other hand, serve as primary care settings for many epilepsy patients. In these environments, healthcare providers focus on long-term management of the condition, monitoring patients' progress, and adjusting medications as needed. Clinics offer a more personalized approach to care, with regular follow-up appointments and ongoing support for patients and their families. This setting is particularly important for individuals with well-controlled epilepsy who require routine check-ups and medication management. Other settings, such as specialized epilepsy centers and research institutions, also contribute to the global epilepsy drug market. These facilities often focus on advanced diagnostic techniques, clinical trials, and the development of new treatment options. They play a crucial role in advancing the understanding of epilepsy and improving therapeutic outcomes. Additionally, community health programs and support groups provide education and resources for epilepsy patients, helping to raise awareness and reduce stigma associated with the condition. Overall, the global epilepsy drug market is integral to the comprehensive care of individuals with epilepsy, offering a range of treatment options and support services across various healthcare settings.
Global Epilepsy Drug Market Outlook:
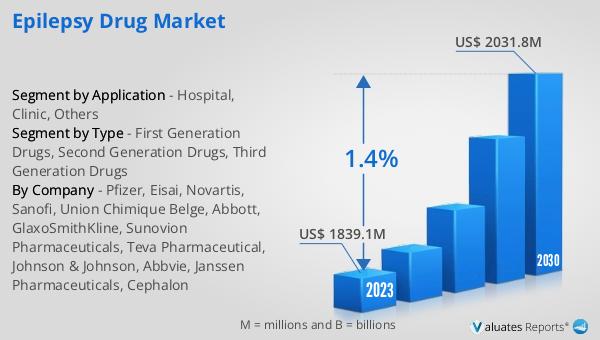
The global market for epilepsy drugs was valued at $1,891 million in 2024 and is anticipated to grow to a revised size of $2,084 million by 2031, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 1.4% during the forecast period. This growth is modest compared to the broader pharmaceutical market, which was valued at $1,475 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5% over the next six years. In contrast, the chemical drug market is projected to increase from $1,005 billion in 2018 to $1,094 billion in 2022. These figures highlight the unique dynamics of the epilepsy drug market, which is influenced by factors such as the introduction of generic drugs, patent expirations, and the development of new treatment options. While the growth rate of the epilepsy drug market may be slower than that of the overall pharmaceutical industry, it remains a critical segment focused on addressing the needs of individuals with epilepsy. The market's evolution is driven by ongoing research and development efforts, as well as the increasing prevalence of epilepsy worldwide. As new drugs are introduced and existing treatments are refined, the global epilepsy drug market will continue to play a vital role in improving patient outcomes and enhancing the quality of life for those living with epilepsy.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Epilepsy Drug Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 1891 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 2084 million |
| CAGR | 1.4% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Pfizer, Eisai, Novartis, Sanofi, Union Chimique Belge, Abbott, GlaxoSmithKline, Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, Teva Pharmaceutical, Johnson & Johnson, Abbvie, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Cephalon |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
