What is Global Antibacterial Therapeutic Market?
The Global Antibacterial Therapeutic Market is a crucial segment of the pharmaceutical industry, focusing on the development and distribution of medications designed to combat bacterial infections. These therapeutic agents are essential in treating a wide range of bacterial diseases, from minor infections to life-threatening conditions. The market encompasses a variety of antibacterial drugs, each targeting specific types of bacteria and infections. With the rise of antibiotic resistance, the demand for innovative and effective antibacterial therapies has increased significantly. This market is driven by the need to address both common and emerging bacterial threats, ensuring public health safety. The global reach of this market highlights its importance, as bacterial infections are a universal concern, affecting populations worldwide. The market's growth is fueled by ongoing research and development efforts, aiming to discover new drugs and improve existing ones to enhance their efficacy and reduce side effects. As healthcare systems worldwide strive to manage and prevent bacterial infections, the Global Antibacterial Therapeutic Market plays a pivotal role in providing the necessary tools and treatments to achieve these goals. The market's evolution is closely tied to advancements in medical science and technology, which continue to shape its trajectory.
Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Quinolone, Aminoglycosides, Monobactams, Carbapenems, Macrolides, Others in the Global Antibacterial Therapeutic Market:
Penicillins are among the oldest and most widely used classes of antibiotics in the Global Antibacterial Therapeutic Market. They work by inhibiting the synthesis of bacterial cell walls, leading to the destruction of the bacteria. Penicillins are effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria, making them a staple in treating infections like strep throat, pneumonia, and syphilis. Cephalosporins, similar to penicillins, also target bacterial cell wall synthesis but are often used when patients are allergic to penicillins or when bacteria have developed resistance. They are categorized into generations, each with varying effectiveness against different bacteria. Quinolones, another class of antibiotics, work by interfering with bacterial DNA replication. They are particularly effective against urinary tract infections and certain types of pneumonia. Aminoglycosides, known for their potency, are used to treat severe infections caused by gram-negative bacteria. However, their use is limited due to potential side effects like kidney damage and hearing loss. Monobactams, a newer class, are effective against aerobic gram-negative bacteria and are often used in patients with penicillin allergies. Carbapenems are broad-spectrum antibiotics used for severe or high-risk bacterial infections, especially those resistant to other antibiotics. They are considered last-resort antibiotics due to their effectiveness against multi-drug resistant bacteria. Macrolides, such as erythromycin, are used to treat respiratory infections, skin infections, and sexually transmitted diseases. They work by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. The "Others" category includes various antibiotics that don't fit into the main classes but are crucial in treating specific infections. Each of these classes plays a vital role in the Global Antibacterial Therapeutic Market, addressing different bacterial threats and contributing to the overall effort to combat bacterial infections. The development and use of these antibiotics are guided by the need to balance efficacy with safety, minimizing side effects while maximizing therapeutic outcomes. As bacterial resistance continues to evolve, the market must adapt by developing new antibiotics and improving existing ones to ensure effective treatment options remain available. The interplay between these different classes of antibiotics highlights the complexity and importance of the Global Antibacterial Therapeutic Market in maintaining public health.
Oral, Topical, Parenteral, Others in the Global Antibacterial Therapeutic Market:
The usage of antibacterial therapeutics in the Global Antibacterial Therapeutic Market spans several administration routes, each tailored to specific types of infections and patient needs. Oral administration is one of the most common methods, involving the ingestion of antibiotics in pill or liquid form. This route is convenient and effective for treating a wide range of infections, including respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, and skin infections. Oral antibiotics are preferred for their ease of use and ability to be administered outside of a hospital setting, making them accessible for outpatient treatment. Topical administration involves applying antibiotics directly to the skin or mucous membranes. This method is particularly useful for treating localized infections, such as skin infections, eye infections, and certain types of ear infections. Topical antibiotics minimize systemic exposure, reducing the risk of side effects and drug interactions. Parenteral administration, which includes intravenous and intramuscular injections, is used for severe infections that require rapid and high concentrations of antibiotics in the bloodstream. This route is often employed in hospital settings for conditions like sepsis, severe pneumonia, and complicated urinary tract infections. Parenteral antibiotics provide immediate therapeutic effects, making them crucial for life-threatening infections. The "Others" category encompasses various administration routes, such as inhalation for respiratory infections and rectal administration for specific cases. Each route of administration in the Global Antibacterial Therapeutic Market is chosen based on the infection's severity, location, and the patient's overall health condition. The diversity in administration methods ensures that antibacterial therapies can be tailored to meet individual patient needs, optimizing treatment outcomes. As the market continues to evolve, the development of new administration technologies and formulations will play a key role in enhancing the effectiveness and accessibility of antibacterial treatments. The careful selection of administration routes is essential in maximizing the therapeutic benefits of antibiotics while minimizing potential risks, contributing to the overall success of the Global Antibacterial Therapeutic Market.
Global Antibacterial Therapeutic Market Outlook:
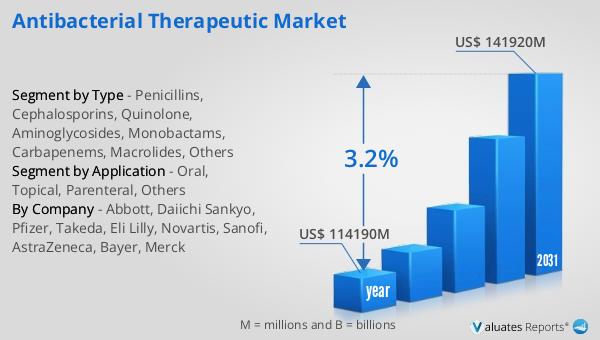
The worldwide market for Antibacterial Therapeutics was valued at $114.19 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to expand to $141.92 billion by 2031, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.2% over the forecast period. In contrast, the global pharmaceutical market was valued at $1.475 trillion in 2022, with an expected growth rate of 5% over the next six years. Meanwhile, the chemical drug market is projected to grow from $1.005 trillion in 2018 to $1.094 trillion by 2022. This comparison highlights the significant role of the Antibacterial Therapeutic Market within the broader pharmaceutical landscape. Despite its slower growth rate compared to the overall pharmaceutical market, the Antibacterial Therapeutic Market remains a critical component due to the ongoing need for effective treatments against bacterial infections. The market's growth is driven by factors such as the increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, the demand for new and improved antibacterial agents, and the continuous advancements in medical research and technology. As the market evolves, it will continue to play a vital role in addressing global health challenges, ensuring the availability of effective antibacterial therapies for diverse populations worldwide.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Antibacterial Therapeutic Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 114190 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 141920 million |
| CAGR | 3.2% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| By Company | Abbott, Daiichi Sankyo, Pfizer, Takeda, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Merck |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |