What is Global Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market?
The Global Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market is a rapidly evolving sector within the pharmaceutical industry, focusing on innovative cancer treatments. Immune checkpoint inhibitors are a class of drugs that help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively. These inhibitors target specific proteins, such as PD-1, PD-L1, and CTLA-4, which act as brakes on the immune system, preventing it from attacking cancer cells. By blocking these proteins, immune checkpoint inhibitors unleash the immune system's full potential to combat cancer. This market has gained significant attention due to the increasing prevalence of various cancers and the growing demand for more effective and less toxic cancer therapies. The market is characterized by a robust pipeline of new drugs, ongoing clinical trials, and strategic collaborations among pharmaceutical companies to enhance research and development efforts. As a result, the Global Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market is poised for substantial growth, driven by advancements in biotechnology and a deeper understanding of cancer immunology. The market's expansion is also supported by regulatory approvals and the adoption of these therapies in clinical practice, offering hope to patients worldwide.
PD-1/PD-L1, CTLA-4 in the Global Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market:
PD-1 (Programmed Death-1) and PD-L1 (Programmed Death-Ligand 1) are critical components in the immune checkpoint pathway, playing a significant role in the Global Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market. PD-1 is a receptor found on the surface of T-cells, which are essential players in the immune response. When PD-1 binds to its ligand, PD-L1, which is often expressed on cancer cells, it sends an inhibitory signal to the T-cell, effectively turning off its ability to attack the cancer cell. This mechanism is a way for cancer cells to evade the immune system. Immune checkpoint inhibitors targeting PD-1 and PD-L1 work by blocking this interaction, thereby reactivating T-cells to recognize and destroy cancer cells. CTLA-4 (Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte-Associated Protein 4) is another checkpoint protein that plays a crucial role in regulating immune responses. CTLA-4 is expressed on T-cells and acts as an "off" switch when bound to its ligands, CD80/CD86, on antigen-presenting cells. By inhibiting CTLA-4, immune checkpoint inhibitors enhance T-cell activation and proliferation, boosting the immune system's ability to fight cancer. The development of PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors has revolutionized cancer treatment, offering new hope for patients with various types of cancer. These inhibitors have shown remarkable efficacy in treating cancers that were previously considered difficult to manage, such as melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, and renal cell carcinoma. The success of these therapies has spurred extensive research and development efforts, leading to the introduction of several new drugs in the market. Pharmaceutical companies are actively investing in clinical trials to explore the potential of PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors in combination with other treatments, such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapies. This approach aims to enhance the overall efficacy of cancer treatment and overcome resistance mechanisms that may develop with monotherapy. The Global Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market is witnessing a surge in collaborations and partnerships among key players to accelerate the development of novel therapies and expand their product portfolios. These strategic alliances are crucial for sharing expertise, resources, and technology, ultimately driving innovation in the field. Additionally, regulatory agencies worldwide are recognizing the potential of immune checkpoint inhibitors and are granting approvals for their use in various cancer indications. This regulatory support is facilitating the rapid adoption of these therapies in clinical practice, benefiting patients across the globe. The market's growth is also fueled by the increasing prevalence of cancer, rising awareness about immunotherapy, and the demand for personalized medicine. As researchers continue to unravel the complexities of the immune system and its interactions with cancer, the Global Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market is expected to witness significant advancements, offering new avenues for cancer treatment and improving patient outcomes.
Lung Cancer, Colorectal Cancer, Breast Cancer, Prostate Cancer, Melanoma, Blood Cancer, Other in the Global Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market:
The Global Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market has made significant strides in the treatment of various cancers, including lung cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, melanoma, blood cancer, and others. In lung cancer, particularly non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), immune checkpoint inhibitors have become a cornerstone of treatment. Drugs targeting PD-1 and PD-L1 have demonstrated improved survival rates and are often used in combination with chemotherapy to enhance efficacy. In colorectal cancer, immune checkpoint inhibitors are primarily used for patients with microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) tumors, which are more responsive to immunotherapy. These inhibitors offer a promising option for patients who have exhausted other treatment avenues. Breast cancer, particularly triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), has also seen advancements with the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors. TNBC is an aggressive form of breast cancer with limited treatment options, and the introduction of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors has provided new hope for patients. In prostate cancer, immune checkpoint inhibitors are being explored in combination with other therapies to improve outcomes, especially in advanced stages of the disease. Melanoma, a type of skin cancer, was one of the first cancers to benefit from immune checkpoint inhibitors. The introduction of CTLA-4 and PD-1 inhibitors has significantly improved survival rates for patients with advanced melanoma, transforming the treatment landscape. Blood cancers, such as Hodgkin lymphoma, have also shown responsiveness to immune checkpoint inhibitors, particularly PD-1 inhibitors, offering a new line of treatment for patients who have relapsed or are refractory to conventional therapies. Beyond these specific cancers, immune checkpoint inhibitors are being investigated for their potential in treating other malignancies, including gastric cancer, bladder cancer, and head and neck cancers. The versatility of these inhibitors in targeting various cancer types underscores their importance in the Global Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market. As research continues to explore the full potential of these therapies, the market is expected to expand further, providing more patients with access to life-saving treatments. The integration of immune checkpoint inhibitors into standard cancer care represents a paradigm shift in oncology, offering a more targeted and less toxic approach to cancer treatment.
Global Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market Outlook:
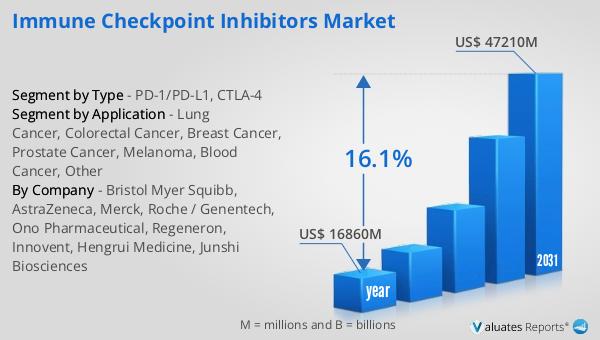
In 2024, the global market for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors was valued at approximately $16.86 billion. This market is anticipated to experience significant growth, reaching an estimated size of $47.21 billion by 2031. This expansion reflects a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.1% over the forecast period. The robust growth of this market can be attributed to several factors, including the increasing prevalence of cancer worldwide and the rising demand for innovative cancer therapies. Immune checkpoint inhibitors have emerged as a promising class of drugs, offering new hope for patients with various types of cancer. These inhibitors work by unleashing the immune system's ability to recognize and attack cancer cells, providing a more targeted and less toxic approach to treatment. The market's growth is further supported by ongoing research and development efforts, leading to the introduction of new drugs and the exploration of combination therapies. Additionally, regulatory approvals and the adoption of these therapies in clinical practice are driving the market's expansion. As the understanding of cancer immunology continues to evolve, the Global Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market is poised for substantial growth, offering new avenues for cancer treatment and improving patient outcomes.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 16860 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 47210 million |
| CAGR | 16.1% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Bristol Myer Squibb, AstraZeneca, Merck, Roche / Genentech, Ono Pharmaceutical, Regeneron, Innovent, Hengrui Medicine, Junshi Biosciences |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |