What is Global Antihypertensive Market?
The Global Antihypertensive Market is a significant segment of the pharmaceutical industry, focusing on medications designed to manage high blood pressure, a condition known as hypertension. Hypertension is a prevalent health issue worldwide, affecting millions of people and increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other serious health problems. The market encompasses a wide range of drugs, each targeting different mechanisms within the body to lower blood pressure. These medications are crucial in preventing the complications associated with hypertension and improving the quality of life for patients. The market is driven by factors such as the rising prevalence of hypertension due to lifestyle changes, an aging population, and increased awareness about the condition. Additionally, advancements in medical research and technology have led to the development of more effective antihypertensive drugs, further propelling market growth. The market is also influenced by healthcare policies, economic factors, and the availability of generic drugs, which make these medications more accessible to a broader population. Overall, the Global Antihypertensive Market plays a vital role in the healthcare sector, addressing a critical need for effective hypertension management.
Diuretics, Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs), Calcium Channel Blockers, Beta Blockers, Alpha Blockers, Vasodilators & Renin Inhibitors in the Global Antihypertensive Market:
Diuretics, Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs), Calcium Channel Blockers, Beta Blockers, Alpha Blockers, Vasodilators, and Renin Inhibitors are the primary classes of drugs within the Global Antihypertensive Market, each offering unique mechanisms to combat high blood pressure. Diuretics, often referred to as water pills, help the kidneys remove excess salt and water from the body, reducing blood volume and, consequently, blood pressure. They are usually the first line of treatment for hypertension due to their effectiveness and affordability. ACE Inhibitors work by blocking the formation of a hormone called angiotensin II, which normally causes blood vessels to constrict. By inhibiting this hormone, ACE Inhibitors help blood vessels relax and widen, making it easier for blood to flow and reducing blood pressure. ARBs, on the other hand, block the action of angiotensin II directly at the receptor level, providing a similar effect to ACE Inhibitors but often with fewer side effects. Calcium Channel Blockers prevent calcium from entering the cells of the heart and blood vessel walls, leading to relaxed blood vessels and lower blood pressure. These are particularly effective in treating hypertension in older adults and those of African descent. Beta Blockers reduce blood pressure by slowing down the heart rate and decreasing the force of heart contractions, which reduces the amount of blood the heart pumps into the arteries. They are often used in combination with other antihypertensive drugs for better efficacy. Alpha Blockers work by relaxing certain muscles and helping small blood vessels remain open, which improves blood flow and lowers blood pressure. Vasodilators directly relax the muscles in the blood vessel walls, causing the vessels to widen and blood pressure to decrease. They are typically used in severe cases of hypertension or when other medications are not effective. Lastly, Renin Inhibitors target the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system by inhibiting the activity of renin, an enzyme involved in blood pressure regulation. This class of drugs is relatively new and is often used when other treatments have not been successful. Each of these drug classes plays a crucial role in the comprehensive management of hypertension, offering healthcare providers a range of options to tailor treatment plans to individual patient needs. The diversity of these medications reflects the complexity of hypertension as a condition and the necessity for personalized treatment approaches to achieve optimal outcomes.
Hospital Pharmacy, Retail Pharmacy, Online Pharmacy, Others in the Global Antihypertensive Market:
The usage of antihypertensive medications spans various distribution channels, including hospital pharmacies, retail pharmacies, online pharmacies, and others, each playing a vital role in ensuring patient access to these essential drugs. Hospital pharmacies are integral in the immediate management of hypertension, especially in acute settings where patients may present with dangerously high blood pressure levels. In such environments, healthcare professionals can quickly administer antihypertensive medications to stabilize patients, often using intravenous formulations for rapid effect. Hospital pharmacies also play a crucial role in educating patients about their condition and the importance of adhering to prescribed medication regimens upon discharge. Retail pharmacies are perhaps the most common point of access for antihypertensive medications, providing a convenient option for patients to fill their prescriptions. Pharmacists in these settings offer valuable counseling services, helping patients understand their medications, potential side effects, and the importance of lifestyle modifications in managing hypertension. The accessibility of retail pharmacies ensures that patients can maintain a consistent supply of their medications, which is critical for effective long-term management of hypertension. Online pharmacies have gained popularity in recent years, offering patients the convenience of ordering medications from the comfort of their homes. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with mobility issues or those living in remote areas where access to traditional pharmacies may be limited. Online pharmacies often provide competitive pricing and home delivery services, making it easier for patients to adhere to their treatment plans. However, it is essential for patients to ensure they are purchasing from reputable sources to avoid counterfeit medications. Other distribution channels, such as community health centers and government programs, also play a role in providing access to antihypertensive medications, particularly for underserved populations. These programs often offer medications at reduced costs or even for free, helping to address disparities in healthcare access and improve outcomes for individuals with hypertension. Overall, the diverse distribution channels for antihypertensive medications reflect the importance of making these drugs readily available to patients, ensuring that they can effectively manage their condition and reduce the risk of complications.
Global Antihypertensive Market Outlook:
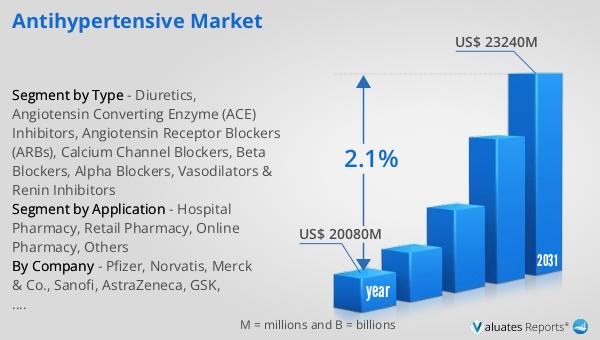
The global market for antihypertensive medications was valued at approximately $20,080 million in 2024, with projections indicating an increase to around $23,240 million by 2031, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.1% over the forecast period. This growth is indicative of the ongoing demand for effective hypertension management solutions, driven by factors such as an aging population and increasing prevalence of lifestyle-related health conditions. In comparison, the broader global pharmaceutical market was valued at $1,475 billion in 2022, with an expected CAGR of 5% over the next six years. This growth trajectory highlights the robust expansion of the pharmaceutical industry as a whole, driven by advancements in medical research, technology, and an increasing focus on personalized medicine. Within this context, the chemical drug market, a significant component of the pharmaceutical industry, was estimated to grow from $1,005 billion in 2018 to $1,094 billion in 2022. This growth underscores the continued importance of chemical drugs, including antihypertensive medications, in addressing a wide range of health conditions. The steady growth of the antihypertensive market, although at a slightly lower rate compared to the overall pharmaceutical market, reflects the critical role these medications play in managing a prevalent and potentially life-threatening condition. As healthcare systems worldwide continue to prioritize the management of chronic diseases, the demand for effective antihypertensive therapies is expected to remain strong, contributing to the overall growth of the pharmaceutical industry.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Antihypertensive Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 20080 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 23240 million |
| CAGR | 2.1% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Pfizer, Norvatis, Merck & Co., Sanofi, AstraZeneca, GSK, Daiichi-Sankyo, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bayer, Johnson & Johnson, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Tekeda, Ranbaxy Laboratories, Shihuida Pharm, Second Pharmaceutical, Lupin Limited., Yangtze River Pharmaceutical, Hengrui Medicine, Qilu Pharmaceutical, HUALON, Dawnrays, HISUN Pharmceutical |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |