What is Global Systemic Lupus Erythematous SLE Drug Market?
The Global Systemic Lupus Erythematous (SLE) Drug Market is a specialized segment within the pharmaceutical industry that focuses on the development and distribution of medications specifically designed to treat Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), a chronic autoimmune disease. SLE is characterized by the immune system mistakenly attacking healthy tissues, leading to inflammation and damage in various parts of the body, including the skin, joints, kidneys, and brain. The market for SLE drugs is driven by the need for effective treatments that can manage the symptoms and complications associated with this complex disease. The market encompasses a range of therapeutic options, including corticosteroids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs), antimalarials, BLyS-specific inhibitors or monoclonal antibodies (MAbs), immunosuppressive agents, and anticoagulants. These medications aim to reduce inflammation, suppress the overactive immune response, and prevent organ damage. The market is influenced by factors such as the prevalence of SLE, advancements in drug development, and the availability of innovative treatment options. As research continues to uncover new insights into the disease and its underlying mechanisms, the Global SLE Drug Market is expected to evolve, offering improved therapies for patients worldwide.
Corticosteroids, Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs), Anti-Inflammatories, Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs), Antimalarials, BLyS-specific Inhibitors or Monoclonal Antibodies (MAbS), Immunosuppressive Agents/Immune Modulators, Anticoagulants in the Global Systemic Lupus Erythematous SLE Drug Market:
Corticosteroids are a cornerstone in the treatment of SLE due to their potent anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. They work by reducing inflammation and suppressing the immune system's overactivity, which is crucial in managing the symptoms of SLE. However, long-term use of corticosteroids can lead to side effects such as weight gain, osteoporosis, and increased risk of infections, necessitating careful management by healthcare providers. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to alleviate pain and inflammation associated with SLE, particularly in cases involving joint pain and arthritis. While NSAIDs are effective in providing symptomatic relief, they do not address the underlying immune dysfunction in SLE. Anti-Inflammatories, including both corticosteroids and NSAIDs, play a vital role in managing acute flare-ups and controlling chronic inflammation. Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) are used to slow the progression of SLE and prevent long-term damage to organs and tissues. These drugs, such as methotrexate and azathioprine, work by modulating the immune system and reducing its attack on healthy tissues. Antimalarials, such as hydroxychloroquine, are a mainstay in SLE treatment due to their ability to reduce inflammation and prevent disease flares. They are particularly effective in managing skin and joint symptoms and have a favorable safety profile for long-term use. BLyS-specific inhibitors or Monoclonal Antibodies (MAbs), such as belimumab, target specific proteins involved in the immune response, offering a more targeted approach to SLE treatment. These biologic therapies have shown promise in reducing disease activity and are often used in patients who do not respond adequately to traditional therapies. Immunosuppressive Agents/Immune Modulators, such as mycophenolate mofetil and cyclophosphamide, are used to control severe SLE manifestations, particularly those affecting the kidneys and central nervous system. These drugs work by suppressing the immune system to prevent further damage to organs. Anticoagulants are sometimes prescribed to SLE patients who are at increased risk of blood clots, a common complication of the disease. By thinning the blood, anticoagulants help prevent clot formation and reduce the risk of serious events such as strokes and heart attacks. The Global SLE Drug Market is characterized by a diverse range of therapeutic options, each with its own mechanism of action and role in managing the disease. The choice of treatment is often tailored to the individual patient's needs, taking into account the severity of the disease, the organs affected, and the patient's overall health. As research continues to advance our understanding of SLE, new therapies are being developed that offer hope for more effective and personalized treatment options.
Intravenous, Oral, Topical, Others in the Global Systemic Lupus Erythematous SLE Drug Market:
The usage of Global Systemic Lupus Erythematous (SLE) Drug Market medications varies depending on the route of administration, which can significantly impact the effectiveness and convenience of treatment. Intravenous administration is often used for medications that require rapid action or when high doses are necessary, such as in severe cases of SLE. This route allows for the direct delivery of drugs into the bloodstream, ensuring quick and efficient distribution throughout the body. Intravenous administration is commonly used for biologic therapies, such as monoclonal antibodies, and for immunosuppressive agents during acute flare-ups. Oral administration is the most common route for SLE medications, offering convenience and ease of use for patients. Many corticosteroids, NSAIDs, DMARDs, and antimalarials are available in oral formulations, allowing patients to manage their condition at home. Oral medications are typically used for long-term management of SLE, helping to control symptoms and prevent disease progression. Topical administration is used for SLE medications that target skin manifestations of the disease. Topical corticosteroids and other anti-inflammatory creams can be applied directly to affected areas, providing localized relief from rashes and lesions. This route minimizes systemic exposure and reduces the risk of side effects associated with oral or intravenous administration. Other routes of administration, such as subcutaneous injections, are also used in the treatment of SLE. Subcutaneous injections are often employed for biologic therapies that require regular administration, offering a convenient alternative to intravenous infusions. The choice of administration route is influenced by factors such as the severity of the disease, the specific symptoms being treated, and the patient's preferences and lifestyle. Healthcare providers work closely with patients to determine the most appropriate route of administration, ensuring optimal treatment outcomes. As the Global SLE Drug Market continues to evolve, new formulations and delivery methods are being developed to enhance the effectiveness and convenience of SLE treatments, ultimately improving the quality of life for patients.
Global Systemic Lupus Erythematous SLE Drug Market Outlook:
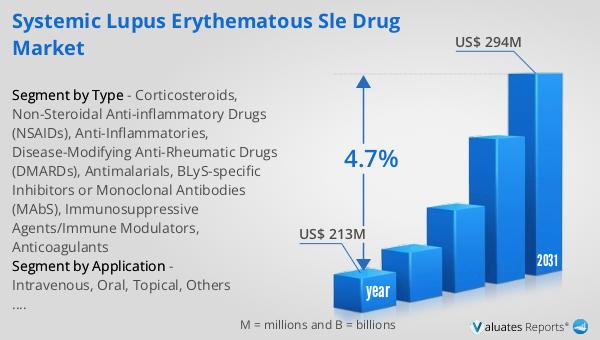
The global market for Systemic Lupus Erythematous (SLE) Drugs was valued at $213 million in 2024 and is anticipated to grow to a revised size of $294 million by 2031, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.7% over the forecast period. This growth is indicative of the increasing demand for effective treatments for SLE, driven by advancements in drug development and a better understanding of the disease. In the broader context, the global pharmaceutical market was valued at $1,475 billion in 2022, with a projected CAGR of 5% over the next six years. This growth is fueled by the continuous innovation and introduction of new therapies across various therapeutic areas. Comparatively, the chemical drug market is estimated to have grown from $1,005 billion in 2018 to $1,094 billion in 2022, highlighting the steady expansion of this segment within the pharmaceutical industry. The SLE Drug Market, while a niche segment, plays a crucial role in addressing the unmet medical needs of patients with this complex autoimmune disease. As research and development efforts continue to advance, the market is expected to offer more targeted and effective treatment options, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Systemic Lupus Erythematous SLE Drug Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 213 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 294 million |
| CAGR | 4.7% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Roche, Pfizer, Novartis, Bayer, Sanofi, GSK, ImmuPharma, Merck Serono, UCB, Amgen, HGS, Immunomedics, MedImmune |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |