What is Global Antidiabetic Drug Market?
The global antidiabetic drug market is a crucial segment of the pharmaceutical industry, focusing on medications designed to manage diabetes, a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is primarily categorized into two types: Type I, where the body fails to produce insulin, and Type II, where the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn't produce enough. The market for antidiabetic drugs is driven by the increasing prevalence of diabetes worldwide, attributed to factors such as aging populations, rising obesity rates, and sedentary lifestyles. These drugs aim to regulate blood sugar levels, thereby preventing complications associated with diabetes, such as cardiovascular diseases, nerve damage, and kidney failure. The market encompasses a variety of drug classes, each targeting different mechanisms of action to control blood glucose levels. The continuous advancements in drug development, coupled with growing awareness about diabetes management, are propelling the market forward. As healthcare systems globally strive to improve diabetes care, the demand for effective antidiabetic medications continues to rise, making this market a vital component of the broader pharmaceutical landscape.
Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors, Biguanides, Sulphonylureas, Glp-1 Agonist, Meglitinides, Dpp-4 Inhibitors, Sglt–2, Thiazolodinediones in the Global Antidiabetic Drug Market:
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, biguanides, sulphonylureas, GLP-1 agonists, meglitinides, DPP-4 inhibitors, SGLT-2 inhibitors, and thiazolidinediones represent diverse classes of drugs within the global antidiabetic drug market, each playing a unique role in managing diabetes. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, such as acarbose, work by slowing down the digestion of carbohydrates in the intestines, thereby reducing the post-meal rise in blood glucose levels. Biguanides, with metformin being the most common, decrease glucose production in the liver and improve insulin sensitivity, making them a first-line treatment for Type II diabetes. Sulphonylureas, like glipizide and glyburide, stimulate the pancreas to release more insulin, helping to lower blood sugar levels. GLP-1 agonists, including drugs like liraglutide, mimic the incretin hormones that increase insulin secretion and decrease glucagon release, also promoting weight loss, which is beneficial for many Type II diabetes patients. Meglitinides, such as repaglinide, are similar to sulphonylureas but act faster and for a shorter duration, providing flexibility in managing blood sugar levels around meals. DPP-4 inhibitors, like sitagliptin, prolong the action of incretin hormones, enhancing insulin secretion and suppressing glucagon release. SGLT-2 inhibitors, including canagliflozin, work by preventing glucose reabsorption in the kidneys, leading to glucose excretion through urine, which also aids in weight loss and blood pressure reduction. Thiazolidinediones, such as pioglitazone, improve insulin sensitivity by acting on fat cells and muscle tissues. Each of these drug classes offers distinct mechanisms and benefits, allowing healthcare providers to tailor diabetes treatment plans to individual patient needs, thereby optimizing blood sugar control and minimizing the risk of complications. The diversity and specificity of these medications underscore the complexity of diabetes management and the importance of personalized treatment strategies in achieving optimal health outcomes for patients worldwide.
Type I Diabetes, Type II Diabetes in the Global Antidiabetic Drug Market:
The usage of antidiabetic drugs in managing Type I and Type II diabetes varies significantly due to the distinct nature of these conditions. Type I diabetes, an autoimmune disorder, requires lifelong insulin therapy as the body cannot produce insulin. Patients with Type I diabetes rely on insulin injections or insulin pumps to maintain blood glucose levels within a target range. While insulin remains the cornerstone of Type I diabetes management, adjunctive therapies such as amylin analogs may be used to further stabilize blood sugar levels. In contrast, Type II diabetes, characterized by insulin resistance and often associated with lifestyle factors, offers a broader range of pharmacological options. Metformin, a biguanide, is typically the first-line treatment for Type II diabetes due to its efficacy, safety profile, and cost-effectiveness. As the disease progresses, additional medications from various classes, such as sulphonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors, or SGLT-2 inhibitors, may be introduced to achieve better glycemic control. GLP-1 agonists and thiazolidinediones are also commonly used in Type II diabetes management, particularly in patients who require additional weight management benefits. The choice of medication is influenced by factors such as the patient's overall health, risk of hypoglycemia, weight considerations, and the presence of comorbidities. The global antidiabetic drug market continues to evolve, with ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving the efficacy and safety of existing treatments, as well as introducing novel therapies. This dynamic landscape underscores the importance of personalized medicine in diabetes care, where treatment plans are tailored to meet the unique needs of each patient, ultimately enhancing their quality of life and reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Global Antidiabetic Drug Market Outlook:
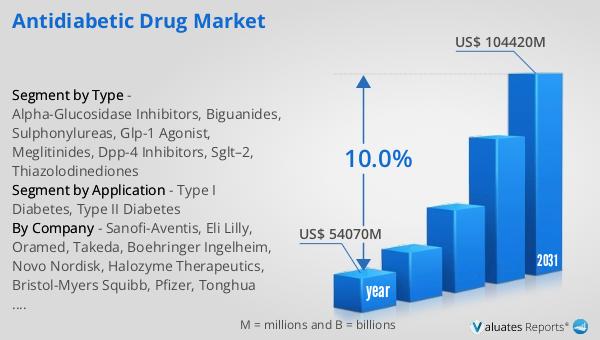
In 2024, the global antidiabetic drug market was valued at approximately $54,070 million, with projections indicating a significant growth trajectory, reaching an estimated $104,420 million by 2031. This growth, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.0%, reflects the increasing demand for effective diabetes management solutions. Despite efforts in diet, exercise, and diabetes education, many patients still require pharmacological intervention to achieve optimal blood glucose control, underscoring the critical role of antidiabetic drugs. In comparison, the broader pharmaceutical market was valued at $1,475 billion in 2022, with a projected CAGR of 5% over the next six years. The chemical drug market, a subset of the pharmaceutical industry, saw an increase from $1,005 billion in 2018 to $1,094 billion in 2022. These figures highlight the robust growth of the antidiabetic drug market relative to the overall pharmaceutical sector, driven by the rising prevalence of diabetes and the continuous innovation in drug development. As healthcare systems worldwide prioritize diabetes management, the demand for effective and accessible antidiabetic medications is expected to remain strong, contributing to the market's expansion and the improvement of patient outcomes globally.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Antidiabetic Drug Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 54070 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 104420 million |
| CAGR | 10.0% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Sanofi-Aventis, Eli Lilly, Oramed, Takeda, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, Halozyme Therapeutics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Tonghua Dongbao, Biocon, Wockhardt |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
