What is Global Parenteral Drugs Market?
The Global Parenteral Drugs Market refers to the segment of the pharmaceutical industry that focuses on drugs administered through non-oral means, typically via injections. This market is crucial because it encompasses medications that are delivered directly into the body, bypassing the digestive system, which allows for rapid absorption and immediate effect. Parenteral drugs are essential in treating patients who cannot take medications orally due to various reasons such as unconsciousness, severe nausea, or when the drug is not effective if taken orally. The market includes a wide range of products such as vaccines, biologics, and small molecule drugs. It is driven by factors like the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, advancements in biologics, and the growing demand for biologic drugs. The market is also influenced by technological advancements in drug delivery systems, which enhance the efficacy and safety of parenteral drugs. The global reach of this market is significant, as it caters to the needs of healthcare systems worldwide, providing critical treatments for a variety of conditions. The market's growth is supported by ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving drug formulations and delivery methods.
LVP Drug, SVP Drug in the Global Parenteral Drugs Market:
In the Global Parenteral Drugs Market, Large Volume Parenteral (LVP) and Small Volume Parenteral (SVP) drugs play pivotal roles. LVPs are typically solutions that are administered in volumes greater than 100 milliliters. They are often used for fluid replacement, electrolyte balance, and providing essential nutrients to patients who cannot consume food orally. LVPs are crucial in hospital settings where patients require intravenous therapy for hydration, nutrition, or medication delivery. These solutions are typically packaged in large bags or bottles and are administered through an intravenous drip. The demand for LVPs is driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, the rising number of surgeries, and the growing geriatric population, which often requires long-term care and intravenous therapy. On the other hand, SVPs are administered in volumes less than 100 milliliters and are used for delivering medications that require precise dosing. SVPs include a wide range of products such as vaccines, insulin, and other injectable medications. They are typically packaged in ampoules, vials, or pre-filled syringes, making them convenient for single-dose administration. The demand for SVPs is driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cancer, and autoimmune disorders, which require regular administration of injectable medications. Additionally, the growing trend towards self-administration of drugs, facilitated by advancements in drug delivery devices, is boosting the demand for SVPs. Both LVPs and SVPs are subject to stringent regulatory requirements to ensure their safety, efficacy, and quality. Manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and comply with regulations set by health authorities such as the FDA and EMA. The production of parenteral drugs involves complex processes that require specialized equipment and facilities to maintain sterility and prevent contamination. The market for LVPs and SVPs is highly competitive, with numerous players vying for market share. Companies are investing in research and development to innovate and improve their product offerings. This includes developing new formulations, enhancing drug stability, and improving delivery systems to enhance patient compliance and outcomes. The market is also witnessing a trend towards the use of biologics and biosimilars, which are driving the demand for parenteral drugs. Biologics are complex molecules derived from living organisms and are often administered parenterally due to their large size and sensitivity to degradation in the digestive system. Biosimilars, which are similar to biologics but not identical, are gaining traction as cost-effective alternatives to branded biologics. The increasing adoption of biologics and biosimilars is expected to drive the growth of the parenteral drugs market in the coming years. Furthermore, the market is witnessing a shift towards the use of pre-filled syringes and auto-injectors, which offer convenience and ease of use for patients. These devices are particularly beneficial for patients who require regular injections, as they reduce the risk of dosing errors and improve patient compliance. The growing trend towards personalized medicine is also influencing the market, as it requires precise dosing and targeted delivery of medications. In conclusion, the Global Parenteral Drugs Market is a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector that plays a critical role in modern healthcare. The demand for LVPs and SVPs is driven by various factors, including the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, advancements in biologics, and the growing trend towards self-administration of drugs. The market is characterized by intense competition, with companies investing in research and development to innovate and improve their product offerings. The future of the market looks promising, with ongoing advancements in drug delivery systems and the increasing adoption of biologics and biosimilars expected to drive growth.
Hospitals, Medical Centers, Others in the Global Parenteral Drugs Market:
The Global Parenteral Drugs Market finds extensive usage across various healthcare settings, including hospitals, medical centers, and other facilities. In hospitals, parenteral drugs are indispensable due to their ability to deliver rapid therapeutic effects, which is crucial in emergency and critical care situations. Hospitals rely heavily on parenteral drugs for treating patients who are unable to take oral medications, such as those who are unconscious, undergoing surgery, or suffering from severe gastrointestinal issues. The use of parenteral drugs in hospitals is also prevalent in the administration of chemotherapy, antibiotics, and pain management medications. The ability to administer drugs intravenously allows for precise control over dosing and ensures that the medication is delivered directly into the bloodstream, providing immediate therapeutic effects. This is particularly important in critical care units, where patients require constant monitoring and rapid intervention. Medical centers, which often serve as outpatient facilities, also utilize parenteral drugs for various treatments. These centers cater to patients who require regular administration of medications such as insulin, biologics, and vaccines. The convenience of parenteral administration allows patients to receive their treatments without the need for hospitalization, reducing healthcare costs and improving patient outcomes. Medical centers often provide specialized services such as infusion therapy, where patients receive medications through an intravenous line over a period of time. This is particularly beneficial for patients with chronic conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and Crohn's disease, who require regular infusions of biologic drugs. In addition to hospitals and medical centers, parenteral drugs are also used in other healthcare settings such as nursing homes, home healthcare, and ambulatory care centers. Nursing homes often cater to elderly patients who may have difficulty swallowing pills or require medications that are not available in oral form. Parenteral drugs provide a viable alternative for these patients, ensuring they receive the necessary treatments to manage their health conditions. Home healthcare services have also seen an increase in the use of parenteral drugs, as more patients opt for receiving treatments in the comfort of their homes. This is facilitated by advancements in drug delivery devices, such as pre-filled syringes and auto-injectors, which allow patients or caregivers to administer medications safely and effectively. The growing trend towards home healthcare is driven by the desire to reduce hospital stays, lower healthcare costs, and improve patient quality of life. Ambulatory care centers, which provide same-day surgical and medical procedures, also utilize parenteral drugs for pre-operative and post-operative care. These centers offer a range of services, including minor surgeries, diagnostic procedures, and pain management, all of which may require the use of parenteral drugs. The ability to administer medications quickly and effectively is crucial in these settings, where patients are often discharged on the same day. In conclusion, the Global Parenteral Drugs Market plays a vital role in various healthcare settings, providing essential treatments for patients who require rapid and effective medication delivery. The use of parenteral drugs in hospitals, medical centers, and other facilities is driven by the need for immediate therapeutic effects, precise dosing, and the ability to treat patients who cannot take oral medications. The market is supported by advancements in drug delivery systems and the growing trend towards home healthcare, which is expected to drive further growth in the coming years.
Global Parenteral Drugs Market Outlook:
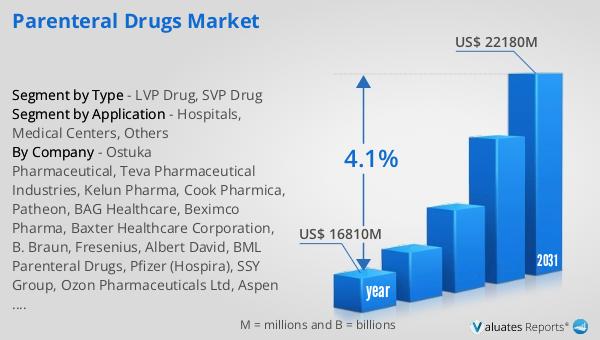
The worldwide market for Parenteral Drugs was estimated to be worth $16,810 million in 2024, and it is anticipated to expand to a revised valuation of $22,180 million by 2031, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.1% throughout the forecast period. This growth trajectory underscores the increasing demand and reliance on parenteral drugs in the healthcare sector. The broader pharmaceutical market, which encompasses parenteral drugs, is valued at approximately $1.47 trillion, with an expected CAGR of around 5% over the next six years. This indicates a robust growth potential for the pharmaceutical industry as a whole, driven by factors such as the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, advancements in drug development, and the increasing adoption of biologics and biosimilars. The parenteral drugs market, in particular, is poised for growth due to its critical role in delivering medications that require rapid absorption and immediate therapeutic effects. The market's expansion is further supported by technological advancements in drug delivery systems, which enhance the safety, efficacy, and convenience of parenteral drug administration. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, the demand for parenteral drugs is expected to rise, driven by the need for effective treatments for a wide range of medical conditions. The market's growth is also influenced by the increasing trend towards personalized medicine, which requires precise dosing and targeted delivery of medications. Overall, the Global Parenteral Drugs Market is set to experience significant growth in the coming years, driven by a combination of factors that highlight its importance in modern healthcare.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Parenteral Drugs Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 16810 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 22180 million |
| CAGR | 4.1% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type | |
| Segment by Application |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Ostuka Pharmaceutical, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Kelun Pharma, Cook Pharmica, Patheon, BAG Healthcare, Beximco Pharma, Baxter Healthcare Corporation, B. Braun, Fresenius, Albert David, BML Parenteral Drugs, Pfizer (Hospira), SSY Group, Ozon Pharmaceuticals Ltd, Aspen Holdings, PSI Ltd, Cisen, AXA Parenterals Ltd, Acebright, Southwest Pharmaceutical, Abbott |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
