What is Global Thin Films Photovoltaic Market?
The Global Thin Films Photovoltaic Market is a rapidly evolving segment within the renewable energy sector, focusing on the development and deployment of thin-film solar cells. These photovoltaic cells are characterized by their lightweight, flexible, and cost-effective nature compared to traditional silicon-based solar panels. Thin-film photovoltaics are made by depositing one or more thin layers of photovoltaic material onto a substrate, such as glass, plastic, or metal. This technology is gaining traction due to its ability to be integrated into a variety of surfaces, including building materials and portable devices. The market is driven by the increasing demand for sustainable energy solutions, advancements in technology, and supportive government policies promoting renewable energy adoption. As the world shifts towards cleaner energy sources, the Global Thin Films Photovoltaic Market is poised to play a significant role in meeting the growing energy needs while reducing carbon footprints. The versatility and adaptability of thin-film photovoltaics make them an attractive option for diverse applications, from residential rooftops to large-scale utility projects, contributing to the global transition towards a more sustainable energy future.
Organic Photovoltaic, Inorganic Photovoltaic in the Global Thin Films Photovoltaic Market:
Organic Photovoltaic (OPV) and Inorganic Photovoltaic technologies are two primary categories within the Global Thin Films Photovoltaic Market, each offering unique advantages and challenges. Organic Photovoltaics are based on carbon-based materials and polymers, which provide the benefit of flexibility and lightweight properties. These materials can be processed at low temperatures, allowing for the production of solar cells on flexible substrates, such as plastic films. This flexibility opens up a wide range of applications, including integration into clothing, portable electronics, and building materials. OPVs are also known for their potential to be produced at a lower cost compared to traditional solar cells, due to the use of abundant and inexpensive organic materials. However, OPVs face challenges in terms of efficiency and stability, as they generally have lower power conversion efficiencies and shorter lifespans compared to inorganic counterparts. Research and development efforts are ongoing to improve the performance and durability of OPVs, making them more competitive in the market. In contrast, Inorganic Photovoltaics are based on inorganic materials, such as cadmium telluride (CdTe), copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS), and amorphous silicon (a-Si). These materials are known for their higher efficiency and stability compared to organic materials. Inorganic thin-film solar cells have been widely adopted in various applications due to their proven performance and reliability. CdTe and CIGS, in particular, have shown significant promise in achieving high power conversion efficiencies, making them popular choices for large-scale solar installations. The manufacturing process for inorganic photovoltaics typically involves vacuum deposition techniques, which can be more complex and costly compared to the solution-based processes used for OPVs. However, the higher efficiency and longer lifespan of inorganic solar cells often justify the additional manufacturing costs. The Global Thin Films Photovoltaic Market is witnessing a growing interest in hybrid approaches that combine the advantages of both organic and inorganic materials. These hybrid solar cells aim to leverage the flexibility and low-cost production of organic materials with the high efficiency and stability of inorganic materials. By integrating the strengths of both technologies, hybrid solar cells have the potential to offer improved performance and broader application possibilities. As research and development in this area continue to advance, hybrid thin-film photovoltaics could play a crucial role in the future of solar energy. Overall, the Global Thin Films Photovoltaic Market is characterized by a dynamic interplay between organic and inorganic technologies, each contributing to the diversification and expansion of solar energy applications. As the market continues to evolve, advancements in material science, manufacturing processes, and device architectures are expected to drive further improvements in the efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and versatility of thin-film solar cells. This ongoing innovation will be essential in meeting the increasing global demand for renewable energy solutions and supporting the transition towards a more sustainable energy future.
Residential, Utility, Commercial, Military, Others in the Global Thin Films Photovoltaic Market:
The Global Thin Films Photovoltaic Market finds its usage across various sectors, including residential, utility, commercial, military, and others, each benefiting from the unique properties of thin-film solar technology. In the residential sector, thin-film photovoltaics are increasingly being used for rooftop installations due to their lightweight and flexible nature. These solar panels can be easily integrated into existing structures without the need for significant structural reinforcement, making them an attractive option for homeowners looking to reduce their energy bills and carbon footprint. Additionally, the aesthetic appeal of thin-film solar panels, which can be designed to blend seamlessly with roofing materials, further enhances their adoption in residential applications. In the utility sector, thin-film photovoltaics are employed in large-scale solar farms and power plants to generate electricity for the grid. The ability to produce thin-film solar panels at a lower cost compared to traditional silicon-based panels makes them an economically viable option for utility-scale projects. Moreover, the high efficiency and reliability of certain inorganic thin-film technologies, such as CdTe and CIGS, make them suitable for deployment in harsh environmental conditions, ensuring consistent energy production over time. Commercial applications of thin-film photovoltaics include their integration into building facades, windows, and other architectural elements. The flexibility and lightweight properties of thin-film solar cells allow for innovative design possibilities, enabling architects and builders to incorporate solar energy generation into the very fabric of commercial buildings. This not only helps businesses reduce their energy costs but also enhances their sustainability credentials, which is increasingly important in today's environmentally conscious market. In the military sector, thin-film photovoltaics are used to power portable electronic devices, communication equipment, and remote installations. The lightweight and flexible nature of thin-film solar panels makes them ideal for use in rugged and remote environments where traditional power sources may be unavailable or impractical. Military applications often require reliable and efficient energy solutions, and the advancements in thin-film photovoltaic technology have made it a valuable asset for defense operations. Beyond these primary sectors, thin-film photovoltaics are also finding applications in other areas, such as transportation and consumer electronics. In the transportation sector, thin-film solar panels are being integrated into vehicles, including cars, buses, and even aircraft, to provide auxiliary power and improve fuel efficiency. In consumer electronics, the flexibility and lightweight properties of thin-film solar cells make them suitable for powering portable devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and wearable technology. Overall, the versatility and adaptability of thin-film photovoltaics make them a valuable asset across a wide range of applications. As the Global Thin Films Photovoltaic Market continues to grow, the ongoing advancements in technology and manufacturing processes are expected to further expand the potential uses of thin-film solar cells, contributing to the global transition towards a more sustainable and energy-efficient future.
Global Thin Films Photovoltaic Market Outlook:
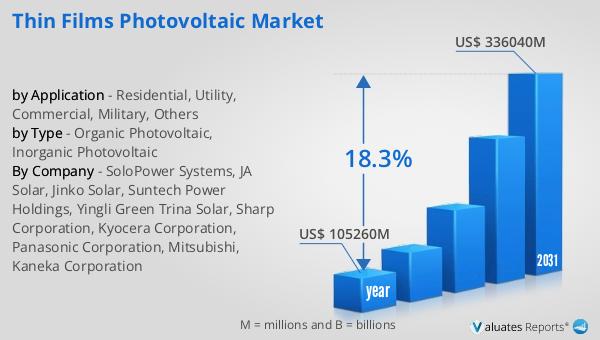
The worldwide market for Thin Films Photovoltaic was estimated to be worth $105.26 billion in 2024, and it is anticipated to expand to a revised valuation of $336.04 billion by 2031, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.3% throughout the forecast period. This significant growth trajectory underscores the increasing demand for renewable energy solutions and the pivotal role that thin-film photovoltaics are expected to play in the global energy landscape. The market's robust expansion is driven by several factors, including technological advancements that enhance the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of thin-film solar cells, as well as supportive government policies and incentives aimed at promoting the adoption of clean energy technologies. Additionally, the growing awareness of environmental issues and the need to reduce carbon emissions are further propelling the demand for sustainable energy solutions, contributing to the market's upward momentum. As the market continues to evolve, the ongoing innovation and development in thin-film photovoltaic technology are expected to unlock new opportunities and applications, solidifying its position as a key player in the transition towards a more sustainable and energy-efficient future.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Thin Films Photovoltaic Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 105260 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 336040 million |
| CAGR | 18.3% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| by Type |
|
| by Application |
|
| Production by Region |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | SoloPower Systems, JA Solar, Jinko Solar, Suntech Power Holdings, Yingli Green Trina Solar, Sharp Corporation, Kyocera Corporation, Panasonic Corporation, Mitsubishi, Kaneka Corporation |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
