What is Spent Fuel and Nuclear Waste Management - Global Market?
Spent fuel and nuclear waste management is a critical aspect of the global market, focusing on the safe handling, storage, and disposal of radioactive materials generated from nuclear reactors and other nuclear-related activities. Spent fuel refers to the used fuel that has been irradiated in a nuclear reactor and is no longer efficient for sustaining a nuclear reaction. This fuel, although no longer useful for energy production, remains highly radioactive and requires careful management to prevent environmental contamination and ensure public safety. Nuclear waste management encompasses a range of activities, including the transportation, storage, and disposal of radioactive waste materials. The global market for spent fuel and nuclear waste management is driven by the increasing demand for nuclear energy, which, while providing a low-carbon energy source, also generates significant amounts of radioactive waste. As countries continue to expand their nuclear power capabilities, the need for effective waste management solutions becomes increasingly important. This market involves various stakeholders, including government agencies, private companies, and international organizations, all working together to develop and implement strategies for the safe and efficient management of nuclear waste.
Low Level Waste, Intermediate Level Waste, High Level Waste in the Spent Fuel and Nuclear Waste Management - Global Market:
Low-level waste (LLW), intermediate-level waste (ILW), and high-level waste (HLW) are classifications of nuclear waste based on their radioactivity and the complexity of their management. LLW includes items like clothing, tools, and filters that have been exposed to radioactive materials but contain only small amounts of radioactivity. These materials are typically disposed of in near-surface disposal facilities, as they pose a relatively low risk to human health and the environment. The management of LLW is generally straightforward, involving containment and isolation until the radioactivity decays to safe levels. Intermediate-level waste, on the other hand, contains higher amounts of radioactivity and may require shielding during handling and transport. ILW includes resins, chemical sludges, and metal reactor components, which are more challenging to manage due to their higher radioactivity. Disposal of ILW often involves deep geological repositories, where the waste can be isolated from the biosphere for thousands of years. High-level waste is the most radioactive and hazardous form of nuclear waste, primarily consisting of spent nuclear fuel and waste materials from the reprocessing of spent fuel. HLW generates significant heat and requires cooling and shielding to protect human health and the environment. The management of HLW is complex and involves long-term strategies, including storage in specially designed facilities and eventual disposal in deep geological repositories. The global market for spent fuel and nuclear waste management is heavily influenced by the need to address these different types of waste, each requiring specific technologies and approaches to ensure safe and effective management. As countries continue to rely on nuclear power as a key energy source, the demand for advanced waste management solutions is expected to grow, driving innovation and investment in this critical sector.
Nuclear Power Industry, Defense and Research, Others in the Spent Fuel and Nuclear Waste Management - Global Market:
The usage of spent fuel and nuclear waste management in various sectors highlights the importance of this market in ensuring the safe and sustainable use of nuclear technology. In the nuclear power industry, spent fuel management is a crucial component of the overall nuclear fuel cycle. Nuclear power plants generate significant amounts of spent fuel, which must be carefully managed to prevent environmental contamination and ensure the safety of plant workers and the surrounding community. This involves the use of advanced storage technologies, such as dry cask storage and deep geological repositories, to safely contain and isolate radioactive materials. In the defense and research sectors, nuclear waste management plays a vital role in handling radioactive materials generated from military applications and scientific research. The defense sector, in particular, generates a variety of radioactive wastes from the production and maintenance of nuclear weapons, requiring specialized management strategies to ensure national security and environmental protection. Research facilities, on the other hand, produce radioactive waste from experiments and the development of new nuclear technologies, necessitating effective waste management solutions to support ongoing scientific advancements. Other sectors, such as medical and industrial applications, also contribute to the generation of nuclear waste, albeit on a smaller scale. These industries rely on nuclear technology for various purposes, including medical imaging and industrial radiography, and require appropriate waste management practices to handle the resulting radioactive materials. The global market for spent fuel and nuclear waste management is driven by the need to address the diverse requirements of these sectors, ensuring the safe and efficient handling of radioactive materials across different applications. As the demand for nuclear technology continues to grow, the importance of effective waste management solutions becomes increasingly critical, supporting the sustainable development of nuclear energy and technology.
Spent Fuel and Nuclear Waste Management - Global Market Outlook:
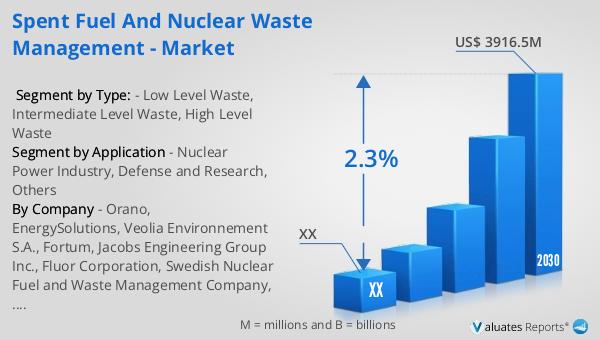
The global market for spent fuel and nuclear waste management was valued at approximately $3,344 million in 2023, with projections indicating a growth to around $3,916.5 million by 2030. This growth represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.3% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2030. The North American market, a significant player in this sector, was valued at an undisclosed amount in 2023, with expectations of reaching a similarly undisclosed figure by 2030, maintaining a steady CAGR throughout the forecast period. This market growth is driven by the increasing demand for nuclear energy and the corresponding need for effective waste management solutions. As countries continue to expand their nuclear power capabilities, the importance of safe and efficient spent fuel and nuclear waste management becomes paramount. The market involves various stakeholders, including government agencies, private companies, and international organizations, all working together to develop and implement strategies for the safe and efficient management of nuclear waste. This collaborative effort is essential to address the challenges associated with nuclear waste management and to ensure the sustainable development of nuclear energy and technology.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Spent Fuel and Nuclear Waste Management - Market |
| Forecasted market size in 2030 | US$ 3916.5 million |
| CAGR | 2.3% |
| Forecasted years | 2024 - 2030 |
| Segment by Type: |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| By Company | Orano, EnergySolutions, Veolia Environnement S.A., Fortum, Jacobs Engineering Group Inc., Fluor Corporation, Swedish Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Company, JGC Holdings Corporation, Westinghouse Electric Company LLC, Waste Control Specialists, LLC, Perma-Fix Environmental Services, Inc., US Ecology, Inc., Stericycle, Inc., SPIC Yuanda Environmental Protection Co., Ltd., Anhui Yingliu Electromechanical Co., Ltd. |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |