What is Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management - Global Market?
Nuclear fuel and waste management is a critical component of the global energy market, focusing on the handling, storage, and disposal of nuclear materials used in power generation. Nuclear fuel refers to the materials used in nuclear reactors to produce energy, typically uranium or plutonium. Once these materials have been used, they become radioactive waste, which poses significant challenges for safe disposal. The global market for nuclear fuel and waste management encompasses a range of activities, including the mining and processing of uranium, the fabrication of nuclear fuel, and the management of spent fuel and radioactive waste. This market is driven by the need for sustainable and safe energy solutions, as well as the imperative to minimize environmental impacts. As countries continue to rely on nuclear power to meet their energy needs, the demand for effective nuclear fuel and waste management solutions is expected to grow. This market involves various stakeholders, including governments, energy companies, and environmental organizations, all working together to ensure the safe and efficient use of nuclear energy. The development of advanced technologies and regulatory frameworks is crucial to addressing the challenges associated with nuclear fuel and waste management, ensuring a sustainable future for nuclear energy.
Near Surface Proposal, Deep Geological Proposal in the Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management - Global Market:
In the realm of nuclear fuel and waste management, two primary strategies have emerged to address the disposal of radioactive waste: the Near Surface Proposal and the Deep Geological Proposal. The Near Surface Proposal involves the disposal of low-level radioactive waste in facilities located near the earth's surface. These facilities are designed to contain and isolate waste for a period of time until its radioactivity decreases to safe levels. This approach is typically used for waste that has a relatively short half-life and poses a lower risk to the environment and human health. Near surface disposal facilities are engineered to prevent the release of radioactive materials into the environment, using barriers and containment systems to ensure safety. This method is cost-effective and suitable for managing waste generated from medical, industrial, and research activities. On the other hand, the Deep Geological Proposal is designed for the disposal of high-level radioactive waste, which remains hazardous for thousands of years. This approach involves burying waste deep underground in stable geological formations, such as granite or clay, which provide natural barriers to prevent the migration of radioactive materials. Deep geological repositories are engineered to withstand geological events, such as earthquakes, and are designed to isolate waste for the long term. This method is considered the most secure and sustainable solution for managing high-level waste, as it minimizes the risk of environmental contamination and human exposure. The development of deep geological repositories requires extensive research and planning, as well as collaboration between governments, scientists, and local communities. Both the Near Surface and Deep Geological Proposals are essential components of a comprehensive nuclear waste management strategy, ensuring the safe and responsible disposal of radioactive materials. As the global demand for nuclear energy continues to rise, the implementation of these proposals will play a crucial role in addressing the challenges associated with nuclear waste management. The success of these strategies depends on the development of advanced technologies, robust regulatory frameworks, and public acceptance, all of which are necessary to ensure the safe and sustainable use of nuclear energy.
Industrial, Public Utilities in the Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management - Global Market:
The usage of nuclear fuel and waste management in industrial and public utilities sectors is pivotal for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of nuclear power plants and other facilities that utilize radioactive materials. In the industrial sector, nuclear fuel is primarily used in power generation, where it serves as a critical component in the production of electricity. Nuclear power plants rely on a continuous supply of nuclear fuel to maintain operations, and effective fuel management is essential to optimize performance and minimize costs. This involves the careful planning and scheduling of fuel deliveries, as well as the monitoring and maintenance of fuel assemblies to ensure their safe and efficient use. Additionally, the management of spent nuclear fuel and radioactive waste is a key concern for industrial operators, who must adhere to strict regulatory requirements to ensure the safe storage and disposal of these materials. In the public utilities sector, nuclear fuel and waste management play a crucial role in ensuring the reliable and sustainable supply of electricity to consumers. Public utilities are responsible for the operation and maintenance of nuclear power plants, as well as the management of nuclear waste generated by these facilities. This involves the implementation of comprehensive waste management strategies, including the storage, transportation, and disposal of radioactive materials. Public utilities must also engage with stakeholders, including government agencies, environmental organizations, and local communities, to ensure the safe and responsible management of nuclear waste. The development of advanced technologies and best practices is essential to enhance the efficiency and safety of nuclear fuel and waste management in both industrial and public utilities sectors. This includes the use of innovative storage solutions, such as dry cask storage systems, which provide a secure and cost-effective method for storing spent nuclear fuel. Additionally, the implementation of robust regulatory frameworks and international cooperation is crucial to address the challenges associated with nuclear waste management and ensure the long-term sustainability of nuclear energy. As the global demand for clean and reliable energy continues to grow, the effective management of nuclear fuel and waste will play a vital role in meeting these needs while minimizing environmental impacts.
Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management - Global Market Outlook:
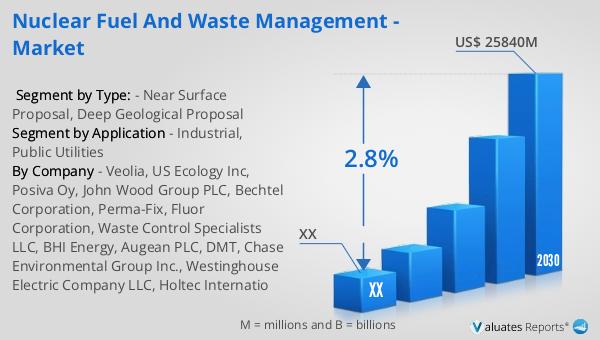
The global market for nuclear fuel and waste management was valued at approximately $21.3 billion in 2023. This market is projected to experience growth, reaching an estimated size of $25.84 billion by the year 2030. This growth trajectory reflects a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.8% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2030. This market outlook underscores the increasing importance of nuclear fuel and waste management as countries around the world seek to balance their energy needs with environmental and safety concerns. The projected growth in this market is driven by several factors, including the ongoing demand for nuclear energy as a low-carbon power source, advancements in waste management technologies, and the implementation of stringent regulatory frameworks. As the global community continues to prioritize sustainable energy solutions, the nuclear fuel and waste management market is expected to play a critical role in supporting the transition to a cleaner energy future. This market outlook highlights the need for continued investment in research and development, as well as collaboration between governments, industry stakeholders, and environmental organizations to address the challenges associated with nuclear fuel and waste management. The anticipated growth in this market presents opportunities for innovation and the development of new technologies that can enhance the safety and efficiency of nuclear energy systems.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management - Market |
| Forecasted market size in 2030 | US$ 25840 million |
| CAGR | 2.8% |
| Forecasted years | 2024 - 2030 |
| Segment by Type: |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| By Company | Veolia, US Ecology Inc, Posiva Oy, John Wood Group PLC, Bechtel Corporation, Perma-Fix, Fluor Corporation, Waste Control Specialists LLC, BHI Energy, Augean PLC, DMT, Chase Environmental Group Inc., Westinghouse Electric Company LLC, Holtec Internatio |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
