What is Global Anti-inflammatory Therapeutics Market?
The Global Anti-inflammatory Therapeutics Market refers to the worldwide industry focused on the development, production, and distribution of medications designed to reduce inflammation. Inflammation is a biological response to harmful stimuli such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and it plays a crucial role in the body's immune response. However, chronic inflammation can lead to various diseases and conditions, necessitating effective therapeutic interventions. The market encompasses a wide range of products, including biologics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and other anti-inflammatory agents. These medications are used to treat a variety of conditions, including arthritis, respiratory diseases, dermatological issues, and gastrointestinal disorders. The market is driven by factors such as the increasing prevalence of chronic inflammatory diseases, advancements in drug development, and a growing aging population. Additionally, ongoing research and development activities aimed at discovering new and more effective anti-inflammatory therapies contribute to the market's growth. The global anti-inflammatory therapeutics market is a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector, with significant potential for innovation and expansion in the coming years.
Anti-inflammatory Biologics, Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs), Corticosteroids, Others in the Global Anti-inflammatory Therapeutics Market:
Anti-inflammatory biologics are a class of drugs derived from living organisms that target specific components of the immune system to reduce inflammation. These biologics include monoclonal antibodies and fusion proteins that inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines or their receptors. For example, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors like adalimumab and infliximab are widely used to treat autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn's disease. Biologics offer the advantage of high specificity and efficacy, but they are often expensive and require administration via injection or infusion. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a more traditional class of anti-inflammatory medications that work by inhibiting the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, which play a key role in the production of pro-inflammatory prostaglandins. Common NSAIDs include ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin. These drugs are widely used for their analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties, making them a popular choice for managing pain and inflammation associated with conditions like arthritis, menstrual cramps, and minor injuries. However, long-term use of NSAIDs can lead to gastrointestinal issues, cardiovascular risks, and renal impairment. Corticosteroids are synthetic drugs that mimic the effects of hormones produced by the adrenal glands. They are potent anti-inflammatory agents that work by suppressing the immune system and reducing the production of inflammatory mediators. Corticosteroids like prednisone and dexamethasone are used to treat a wide range of inflammatory conditions, including asthma, allergic reactions, and autoimmune diseases. While highly effective, corticosteroids can cause significant side effects, especially with long-term use, such as weight gain, osteoporosis, and increased susceptibility to infections. Other anti-inflammatory agents include disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and immunosuppressants, which are used to manage chronic inflammatory diseases by modulating the immune response. DMARDs like methotrexate and sulfasalazine are commonly used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune conditions. Immunosuppressants like cyclosporine and tacrolimus are used to prevent organ rejection in transplant patients and to treat severe autoimmune diseases. These drugs can be highly effective but require careful monitoring due to their potential for serious side effects, including increased risk of infections and malignancies. The global anti-inflammatory therapeutics market is characterized by a diverse range of treatment options, each with its own set of benefits and limitations. The choice of therapy depends on various factors, including the specific condition being treated, the severity of the disease, and the patient's overall health and medical history. Ongoing research and development efforts continue to explore new targets and mechanisms of action, aiming to develop more effective and safer anti-inflammatory therapies.
Arthritis, Respiratory Diseases, Dermatology, Gastroenterology, Others in the Global Anti-inflammatory Therapeutics Market:
The global anti-inflammatory therapeutics market plays a crucial role in the management of various inflammatory conditions, including arthritis, respiratory diseases, dermatological issues, and gastrointestinal disorders. In the case of arthritis, anti-inflammatory medications are essential for reducing pain, swelling, and stiffness associated with the disease. Rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and psoriatic arthritis are among the most common types of arthritis that benefit from anti-inflammatory therapies. Biologics, NSAIDs, and corticosteroids are commonly used to manage these conditions, improving the quality of life for millions of patients worldwide. In respiratory diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), anti-inflammatory drugs help to reduce airway inflammation, improve lung function, and prevent exacerbations. Corticosteroids, both inhaled and systemic, are a mainstay of treatment for these conditions, often used in combination with bronchodilators to achieve optimal control of symptoms. Biologics targeting specific inflammatory pathways, such as interleukin-5 (IL-5) inhibitors, have also shown promise in managing severe asthma. Dermatological conditions like psoriasis, eczema, and dermatitis are characterized by chronic inflammation of the skin. Anti-inflammatory therapies, including topical corticosteroids, systemic biologics, and immunosuppressants, are used to manage these conditions and reduce symptoms such as itching, redness, and scaling. Biologics targeting specific inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-17 (IL-17) inhibitors, have revolutionized the treatment of moderate to severe psoriasis, offering significant improvements in skin clearance and quality of life. In gastroenterology, inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are major areas of focus for anti-inflammatory therapeutics. These chronic conditions involve inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, leading to symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and weight loss. Biologics, including TNF inhibitors and integrin inhibitors, have become standard treatments for moderate to severe IBD, helping to induce and maintain remission. Corticosteroids and immunosuppressants are also used to manage acute flares and maintain long-term control of the disease. Beyond these specific areas, the global anti-inflammatory therapeutics market also addresses other inflammatory conditions, including autoimmune diseases like lupus and multiple sclerosis, as well as acute inflammatory responses to infections and injuries. The versatility and effectiveness of anti-inflammatory therapies make them indispensable tools in the management of a wide range of medical conditions. As research continues to uncover new insights into the mechanisms of inflammation, the development of novel anti-inflammatory agents holds the promise of even more targeted and effective treatments in the future.
Global Anti-inflammatory Therapeutics Market Outlook:
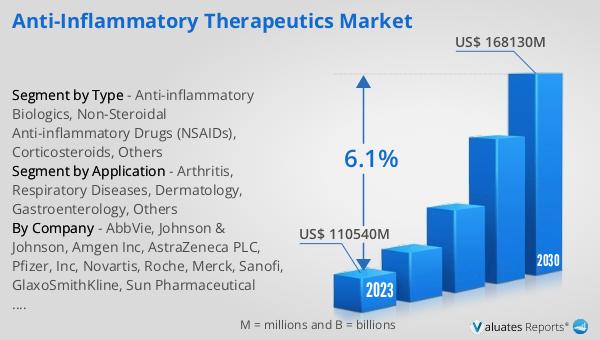
The global market for anti-inflammatory therapeutics was valued at approximately US$ 110.54 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach around US$ 168.13 billion by 2030, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.1% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2030. In 2019, AbbVie held the leading position in the market, accounting for 21.59% of the market share. Other significant players in the market included Johnson & Johnson, Amgen Inc., and AstraZeneca PLC, which held market shares of 14.20%, 5.43%, and 5.32%, respectively. The market's growth is driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic inflammatory diseases, advancements in drug development, and a growing aging population. The competitive landscape of the market is characterized by the presence of several key players, each contributing to the development and distribution of innovative anti-inflammatory therapies. As the demand for effective and safe anti-inflammatory treatments continues to rise, the market is expected to witness significant growth and expansion in the coming years.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Anti-inflammatory Therapeutics Market |
| Forecasted market size in 2030 | US$ 168130 million |
| CAGR | 6.1% |
| Forecasted years | 2024 - 2030 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| By Company | AbbVie, Johnson & Johnson, Amgen Inc, AstraZeneca PLC, Pfizer, Inc, Novartis, Roche, Merck, Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline, Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd, TEVA |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
