What is Global Companion Animal Anti Infective Medicine Market?
The Global Companion Animal Anti-Infective Medicine Market is a specialized segment within the broader veterinary pharmaceutical industry, focusing on medications designed to treat infections in pets such as dogs, cats, and other companion animals. These medicines are crucial for maintaining the health and well-being of pets, as they help combat bacterial, viral, and fungal infections that can otherwise lead to severe health issues or even be life-threatening. The market encompasses a wide range of products, including antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, and other related medications. With the increasing trend of pet ownership worldwide, there is a growing demand for effective and safe anti-infective treatments. This market is driven by factors such as the rising awareness of pet health, advancements in veterinary medicine, and the increasing willingness of pet owners to invest in healthcare for their animals. Additionally, the market is influenced by regulatory frameworks and the development of new and innovative products that cater to the specific needs of different animal species. Overall, the Global Companion Animal Anti-Infective Medicine Market plays a vital role in ensuring the health and longevity of pets, thereby enhancing the quality of life for both animals and their owners.
External Use, Internal Use in the Global Companion Animal Anti Infective Medicine Market:
In the Global Companion Animal Anti-Infective Medicine Market, the application of these medicines can be broadly categorized into external and internal use, each serving distinct purposes in the treatment and prevention of infections in companion animals. External use refers to medications applied directly to the skin or external body parts of animals. These include topical antibiotics, antifungal creams, and antiseptic solutions that are used to treat skin infections, wounds, and other surface-level conditions. External anti-infective medicines are particularly important for addressing issues such as dermatitis, hot spots, and minor cuts or abrasions that are prone to infection. They are designed to provide localized treatment, minimizing systemic exposure and potential side effects. On the other hand, internal use involves medications that are administered orally or through injection to treat systemic infections. These include oral antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and injectable medications that target infections affecting internal organs or systems. Internal anti-infective medicines are crucial for treating more severe or widespread infections that cannot be effectively managed with topical treatments alone. They work by circulating through the animal's body, reaching the site of infection and eliminating the causative pathogens. The choice between external and internal use depends on various factors, including the type and severity of the infection, the specific needs of the animal, and the veterinarian's assessment. In many cases, a combination of both external and internal treatments may be necessary to achieve optimal results. For instance, a dog with a skin infection might require a topical antibiotic to address the surface issue, along with an oral antibiotic to tackle any underlying systemic infection. The development and availability of a wide range of external and internal anti-infective medicines have significantly improved the ability of veterinarians to effectively manage infections in companion animals. This has led to better health outcomes and improved quality of life for pets, as well as increased satisfaction and peace of mind for pet owners. As the market continues to evolve, there is ongoing research and innovation aimed at developing new and improved formulations that offer enhanced efficacy, safety, and convenience for both animals and their caregivers. This includes the development of long-acting injectables, palatable oral formulations, and advanced topical treatments that provide sustained release of active ingredients. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on the responsible use of anti-infective medicines to prevent the development of antimicrobial resistance, which is a significant concern in both human and veterinary medicine. This involves educating pet owners about the importance of adhering to prescribed treatment regimens, avoiding unnecessary use of antibiotics, and seeking veterinary advice for proper diagnosis and treatment. Overall, the Global Companion Animal Anti-Infective Medicine Market plays a critical role in safeguarding the health of pets by providing effective solutions for the prevention and treatment of infections. The distinction between external and internal use highlights the diverse range of options available to veterinarians and pet owners, enabling them to tailor treatment plans to the specific needs of each animal. As the market continues to grow and evolve, it is expected to contribute to further advancements in veterinary medicine and improved health outcomes for companion animals worldwide.
Dogs, Cats, Other in the Global Companion Animal Anti Infective Medicine Market:
The usage of Global Companion Animal Anti-Infective Medicine Market products varies significantly across different types of pets, including dogs, cats, and other animals, each with unique health needs and susceptibilities to infections. Dogs, being one of the most common companion animals, are frequently treated with anti-infective medicines for a variety of conditions. These can range from skin infections caused by bacteria or fungi to more serious systemic infections affecting the respiratory, urinary, or gastrointestinal systems. Dogs are often exposed to environments where they can easily pick up infections, such as parks, grooming facilities, and kennels. As a result, there is a high demand for both external and internal anti-infective treatments to address these issues. Topical treatments are commonly used for skin infections, while oral or injectable antibiotics are prescribed for more severe conditions. Cats, on the other hand, have different health challenges and are often more susceptible to certain viral infections, such as feline herpesvirus and feline calicivirus. Anti-infective medicines for cats often include antiviral drugs, as well as antibiotics for bacterial infections. Cats are also prone to urinary tract infections, which require specific internal treatments. The administration of medicines to cats can be more challenging due to their independent nature and sensitivity to certain drugs, necessitating the development of palatable and easy-to-administer formulations. In addition to dogs and cats, the Global Companion Animal Anti-Infective Medicine Market also caters to other pets, including rabbits, guinea pigs, birds, and reptiles. Each of these animals has unique health requirements and potential infection risks. For example, rabbits are susceptible to respiratory infections and require specific antibiotics that are safe for their delicate digestive systems. Birds may suffer from bacterial or fungal infections affecting their respiratory or digestive tracts, necessitating targeted treatments. Reptiles, such as turtles and lizards, can develop skin and shell infections that require specialized topical or systemic therapies. The diversity of species within the companion animal category highlights the need for a wide range of anti-infective medicines tailored to the specific needs of each type of pet. This includes not only the development of effective treatments but also the consideration of factors such as dosage, administration method, and potential side effects. Veterinarians play a crucial role in diagnosing infections and prescribing appropriate treatments, taking into account the unique characteristics and health status of each animal. Pet owners, in turn, are responsible for ensuring that their pets receive the prescribed treatments and follow-up care to achieve the best possible health outcomes. The Global Companion Animal Anti-Infective Medicine Market continues to evolve to meet the diverse needs of different pets, driven by ongoing research and innovation in veterinary medicine. This includes the development of new drug formulations, improved delivery methods, and a focus on safety and efficacy. As pet ownership continues to rise globally, the demand for effective anti-infective treatments is expected to grow, contributing to the overall health and well-being of companion animals.
Global Companion Animal Anti Infective Medicine Market Outlook:
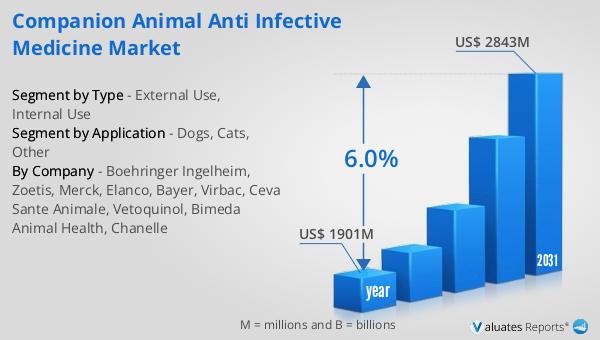
In 2024, the global market for Companion Animal Anti-Infective Medicine was valued at approximately $1,901 million. This market is anticipated to expand significantly, reaching an estimated value of $2,843 million by the year 2031. This growth represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.0% over the forecast period. The increasing valuation of this market underscores the rising demand for effective anti-infective treatments for companion animals, driven by factors such as the growing pet population, heightened awareness of pet health, and advancements in veterinary medicine. As more people around the world adopt pets and consider them integral members of their families, there is a corresponding increase in the willingness to invest in their health and well-being. This trend is reflected in the expanding market for anti-infective medicines, which are essential for treating and preventing infections in pets. The projected growth of the market also highlights the ongoing innovation and development of new products that cater to the specific needs of different animal species. As the market continues to evolve, it is expected to play a crucial role in enhancing the quality of life for pets and their owners, while also contributing to the overall advancement of veterinary medicine.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Companion Animal Anti Infective Medicine Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 1901 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 2843 million |
| CAGR | 6.0% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Boehringer Ingelheim, Zoetis, Merck, Elanco, Bayer, Virbac, Ceva Sante Animale, Vetoquinol, Bimeda Animal Health, Chanelle |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
