What is Pesticides- Global Market?
Pesticides are chemical substances used to eliminate or control pests that can harm crops, animals, and humans. The global market for pesticides is vast and complex, encompassing a wide range of products designed to protect agricultural and non-agricultural environments from pest-related damage. This market is driven by the need to increase agricultural productivity to meet the food demands of a growing global population. Pesticides are categorized into several types, including herbicides, fungicides, insecticides, and others, each serving a specific purpose in pest control. The market is influenced by factors such as technological advancements, regulatory changes, and environmental concerns. As the world becomes more conscious of sustainable practices, the pesticide industry is also evolving, with a focus on developing eco-friendly and bio-based products. The global pesticide market is a critical component of the agricultural sector, playing a vital role in ensuring food security and safety. However, it also faces challenges such as resistance development in pests, health risks to humans and animals, and environmental impact, which necessitate ongoing research and innovation to create safer and more effective solutions.
Herbicide, Fungicide, Insecticide, Others in the Pesticides- Global Market:
Herbicides are a type of pesticide specifically designed to kill or inhibit the growth of unwanted plants, commonly known as weeds. In the global pesticide market, herbicides hold a significant share due to their essential role in agriculture. They help farmers manage weed populations that compete with crops for nutrients, water, and sunlight, ultimately improving crop yields and quality. Herbicides are used in various forms, including liquid sprays, granules, and powders, and can be selective or non-selective. Selective herbicides target specific weed species without harming the desired crops, while non-selective herbicides eliminate all vegetation they come into contact with. The development of herbicide-resistant crops has further boosted the demand for herbicides, as these crops can withstand applications that would otherwise damage them. However, the widespread use of herbicides has raised concerns about environmental pollution, soil health, and the development of herbicide-resistant weed species, prompting the industry to explore more sustainable and integrated weed management practices. Fungicides, another crucial category in the pesticide market, are used to prevent and control fungal diseases that can devastate crops. Fungi can cause significant losses in yield and quality by infecting plants and spreading rapidly under favorable conditions. Fungicides are applied as sprays, dust, or seed treatments and can be either contact or systemic. Contact fungicides remain on the plant's surface and protect it from external fungal spores, while systemic fungicides are absorbed by the plant and provide internal protection. The demand for fungicides is driven by the need to protect high-value crops such as fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants, which are particularly susceptible to fungal infections. However, the overuse of fungicides can lead to resistance development in fungal populations, necessitating the rotation of different fungicide classes and the adoption of integrated disease management strategies. Insecticides are pesticides designed to control insect pests that can cause significant damage to crops, livestock, and human health. They work by targeting the nervous system, growth, or reproductive capabilities of insects, effectively reducing their populations. Insecticides are available in various formulations, including sprays, baits, and granules, and can be classified as contact, systemic, or stomach poisons. The global demand for insecticides is driven by the need to protect crops from insect infestations that can lead to substantial economic losses. However, the use of insecticides raises concerns about non-target effects, such as harm to beneficial insects like pollinators and natural predators, as well as the development of insecticide-resistant pest populations. To address these challenges, the industry is focusing on developing more targeted and environmentally friendly insecticides, as well as promoting integrated pest management practices that combine biological, cultural, and chemical control methods. Other types of pesticides in the global market include rodenticides, nematicides, and molluscicides, each targeting specific pest groups. Rodenticides are used to control rodent populations that can damage crops and spread diseases, while nematicides target nematodes, microscopic worms that attack plant roots. Molluscicides are used to control slugs and snails, which can cause significant damage to crops, particularly in wet and humid conditions. The demand for these specialized pesticides is driven by the need to address specific pest problems in various agricultural and non-agricultural settings. However, like other pesticides, they also face challenges related to environmental impact, resistance development, and regulatory restrictions, prompting the industry to innovate and develop safer and more sustainable solutions.
Agricultural, Non-agriculture in the Pesticides- Global Market:
Pesticides play a crucial role in both agricultural and non-agricultural settings, providing essential protection against pests that can cause significant damage and economic losses. In agriculture, pesticides are used to protect crops from a wide range of pests, including weeds, insects, fungi, and rodents. The use of pesticides in agriculture is driven by the need to increase crop yields and quality to meet the growing global demand for food. By controlling pest populations, pesticides help farmers maximize their productivity and profitability, ensuring a stable and reliable food supply. However, the use of pesticides in agriculture also raises concerns about environmental impact, human health risks, and the development of pest resistance. To address these challenges, the industry is increasingly focusing on integrated pest management (IPM) practices that combine chemical, biological, and cultural control methods to achieve sustainable pest control. In non-agricultural settings, pesticides are used to protect public health, infrastructure, and natural resources from pest-related damage. For example, insecticides are used to control mosquito populations that can transmit diseases such as malaria, dengue, and Zika virus. Rodenticides are used to manage rodent populations in urban areas, preventing damage to buildings and infrastructure and reducing the risk of disease transmission. Herbicides are used to control invasive plant species in natural habitats, helping to preserve biodiversity and ecosystem health. The use of pesticides in non-agricultural settings is driven by the need to protect human health and safety, as well as to maintain the integrity of infrastructure and natural resources. However, like in agriculture, the use of pesticides in non-agricultural settings also raises concerns about environmental impact and human health risks. To address these concerns, the industry is focusing on developing more targeted and environmentally friendly pesticide formulations, as well as promoting the use of non-chemical control methods where possible. Overall, the global market for pesticides is a critical component of both agricultural and non-agricultural sectors, providing essential protection against pests that can cause significant damage and economic losses. However, the use of pesticides also raises important environmental and health concerns, necessitating ongoing research and innovation to develop safer and more sustainable pest control solutions.
Pesticides- Global Market Outlook:
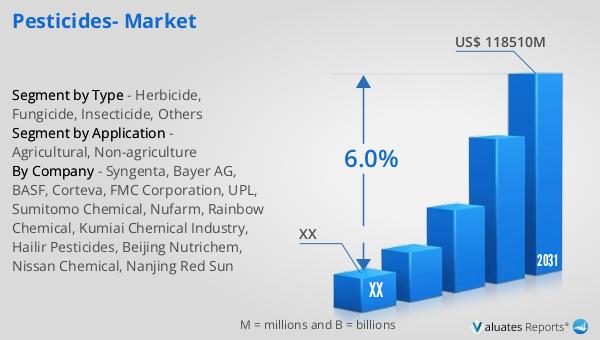
In 2024, the global pesticide market was valued at approximately US$ 79,060 million, with projections indicating a significant increase to around US$ 118,510 million by 2031. This growth is expected to occur at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.0% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2031. In 2023, the market was notably dominated by the top five companies, which collectively held a substantial 57.36% share, highlighting their strong influence and control over the market. This dominance underscores the competitive nature of the pesticide industry, where a few key players have established themselves as leaders through innovation, strategic partnerships, and extensive distribution networks. The market's expansion is driven by the increasing demand for food production, advancements in pesticide technology, and the need for effective pest management solutions in both agricultural and non-agricultural settings. However, the industry also faces challenges such as regulatory pressures, environmental concerns, and the development of pest resistance, which require ongoing adaptation and innovation. As the market continues to evolve, companies are focusing on developing more sustainable and eco-friendly products to meet the changing needs of consumers and regulatory bodies.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Pesticides- Market |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 118510 million |
| CAGR | 6.0% |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| By Company | Syngenta, Bayer AG, BASF, Corteva, FMC Corporation, UPL, Sumitomo Chemical, Nufarm, Rainbow Chemical, Kumiai Chemical Industry, Hailir Pesticides, Beijing Nutrichem, Nissan Chemical, Nanjing Red Sun |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |