What is Global Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) Drug Market?
The Global Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) Drug Market is a specialized segment within the pharmaceutical industry focused on developing and distributing medications to treat Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF), a chronic and progressive lung disease characterized by scarring of lung tissue. This condition leads to a gradual decline in lung function, making it difficult for patients to breathe. The market for IPF drugs is driven by the increasing prevalence of the disease, advancements in medical research, and the growing awareness of IPF among healthcare professionals and patients. The market includes a range of therapeutic options, primarily aimed at slowing disease progression and improving the quality of life for patients. Key players in this market are engaged in extensive research and development activities to introduce innovative treatments and improve existing therapies. The market is also influenced by regulatory approvals, patent expirations, and competitive dynamics among pharmaceutical companies. As the understanding of IPF pathophysiology improves, the market is expected to witness the introduction of more targeted therapies, offering hope for better management of this debilitating disease. The global IPF drug market is a critical component of the broader respiratory drug market, reflecting the urgent need for effective treatments for this challenging condition.
Nintedanib, Pirfenidone in the Global Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) Drug Market:
Nintedanib and Pirfenidone are two cornerstone medications in the Global Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) Drug Market, each playing a significant role in the management of this chronic lung disease. Nintedanib, marketed under the brand name Ofev, is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that targets multiple pathways involved in the fibrotic process. By inhibiting these pathways, Nintedanib helps to slow the progression of lung scarring, thereby preserving lung function over time. Clinical trials have demonstrated its efficacy in reducing the rate of decline in forced vital capacity (FVC), a key measure of lung function in IPF patients. Nintedanib is generally well-tolerated, though it may cause side effects such as diarrhea, nausea, and liver enzyme elevations, which require monitoring and management by healthcare providers. On the other hand, Pirfenidone, sold under the brand name Esbriet, is an antifibrotic agent that also exhibits anti-inflammatory properties. It works by inhibiting the synthesis of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), both of which are involved in the fibrotic process. Pirfenidone has been shown to slow the decline in lung function and improve progression-free survival in IPF patients. Common side effects include gastrointestinal disturbances, skin rash, and photosensitivity, necessitating patient education and monitoring. Both Nintedanib and Pirfenidone have been approved by major regulatory bodies, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), underscoring their importance in the therapeutic landscape of IPF. The availability of these drugs has transformed the management of IPF, offering patients and healthcare providers valuable tools to combat this progressive disease. Despite their benefits, these medications are not curative, and ongoing research is focused on developing combination therapies and novel agents that can further improve patient outcomes. The high cost of these drugs also poses a challenge, highlighting the need for healthcare systems to ensure accessibility and affordability for patients. As research continues to unravel the complexities of IPF, the role of Nintedanib and Pirfenidone in treatment protocols is likely to evolve, potentially in combination with emerging therapies that target different aspects of the disease process. The development of biomarkers to predict treatment response and disease progression is another area of active investigation, which could enhance the precision of IPF management. Overall, Nintedanib and Pirfenidone represent significant advancements in the fight against IPF, providing hope for patients and driving further innovation in the field.
Hospital, Clinics, Others in the Global Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) Drug Market:
The usage of Global Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) drugs extends across various healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, and other medical facilities, each playing a crucial role in the comprehensive management of the disease. In hospitals, IPF drugs are often administered as part of a multidisciplinary approach to patient care. Hospitals provide a setting for initial diagnosis, where patients undergo a series of tests, including high-resolution CT scans and pulmonary function tests, to confirm the presence of IPF. Once diagnosed, patients may receive their first doses of medications like Nintedanib or Pirfenidone in a hospital setting, where healthcare professionals can closely monitor for any adverse reactions and adjust treatment plans as necessary. Hospitals also serve as centers for patient education, where individuals and their families can learn about the disease, treatment options, and lifestyle modifications to manage symptoms effectively. In clinics, the focus shifts to ongoing management and monitoring of IPF patients. Clinics provide a more accessible and less intensive environment for regular follow-up appointments, where healthcare providers assess the effectiveness of prescribed medications and make necessary adjustments. Patients visiting clinics benefit from personalized care plans that address their specific needs, including managing side effects and optimizing medication adherence. Clinics also play a vital role in coordinating care with other specialists, such as pulmonologists and respiratory therapists, to ensure a holistic approach to treatment. Beyond hospitals and clinics, other healthcare settings, such as specialized respiratory centers and home healthcare services, contribute to the management of IPF. Specialized centers offer advanced diagnostic and therapeutic options, including participation in clinical trials for new IPF treatments. These centers often have access to cutting-edge research and technology, providing patients with opportunities to explore innovative therapies. Home healthcare services, on the other hand, offer convenience and comfort for patients who may have difficulty traveling to medical facilities. Home-based care can include medication administration, respiratory therapy, and patient education, all tailored to the individual's needs. This approach not only enhances the quality of life for patients but also reduces the burden on healthcare facilities by minimizing hospital visits. Overall, the usage of IPF drugs across these various settings underscores the importance of a coordinated and patient-centered approach to managing this complex disease. By leveraging the strengths of different healthcare environments, patients with IPF can receive comprehensive care that addresses both their medical and emotional needs, ultimately improving their quality of life.
Global Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) Drug Market Outlook:
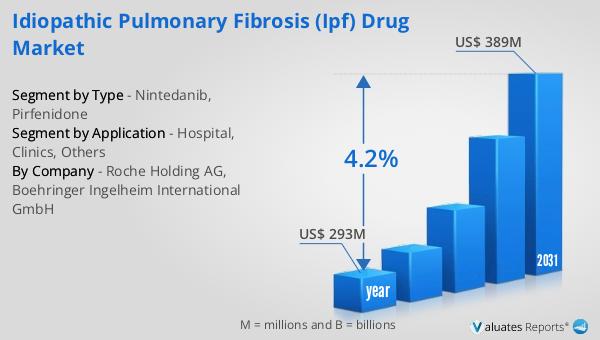
The outlook for the Global Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) Drug Market indicates a promising trajectory, with the market valued at $293 million in 2024 and anticipated to grow to $389 million by 2031, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.2% during the forecast period. This growth is indicative of the increasing demand for effective treatments for IPF, driven by a rising prevalence of the disease and advancements in therapeutic options. In the broader context, the global pharmaceutical market was valued at $1,475 billion in 2022, with an expected CAGR of 5% over the next six years, highlighting the robust expansion of the pharmaceutical industry as a whole. Comparatively, the chemical drug market has shown a steady increase from $1,005 billion in 2018 to $1,094 billion in 2022, underscoring the ongoing demand for chemical-based therapies across various medical conditions. The growth of the IPF drug market is a reflection of the broader trends in the pharmaceutical industry, where innovation and research are driving the development of new and more effective treatments. As the understanding of IPF continues to evolve, the market is poised to benefit from the introduction of novel therapies and improved treatment protocols, offering hope for better patient outcomes. The financial projections for the IPF drug market underscore the importance of continued investment in research and development, as well as the need for healthcare systems to adapt to the growing demand for specialized treatments. Overall, the outlook for the IPF drug market is positive, with significant opportunities for growth and innovation in the coming years.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) Drug Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 293 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 389 million |
| CAGR | 4.2% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Roche Holding AG, Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |