What is Global Dendritic Cell Vaccine Market?
The Global Dendritic Cell Vaccine Market is an emerging segment within the broader field of immunotherapy, focusing on the development and application of vaccines that utilize dendritic cells to stimulate the immune system. Dendritic cells are a type of antigen-presenting cell that play a crucial role in initiating and regulating the body's immune response. By harnessing these cells, dendritic cell vaccines aim to enhance the body's ability to recognize and attack cancer cells or pathogens. This market is driven by the increasing prevalence of cancer and infectious diseases, advancements in biotechnology, and a growing understanding of the immune system's complexities. The development of dendritic cell vaccines involves sophisticated techniques to isolate, modify, and reintroduce these cells into the patient's body, where they can effectively target and destroy harmful cells. As research progresses, the potential applications of dendritic cell vaccines continue to expand, offering hope for more effective treatments for various diseases. The market is characterized by ongoing clinical trials, collaborations between research institutions and pharmaceutical companies, and a focus on personalized medicine approaches. Despite challenges such as high development costs and regulatory hurdles, the Global Dendritic Cell Vaccine Market holds promise for significant advancements in disease treatment and prevention.
Non-Targeted, Target in the Global Dendritic Cell Vaccine Market:
In the Global Dendritic Cell Vaccine Market, the distinction between non-targeted and target-based approaches is crucial for understanding the development and application of these vaccines. Non-targeted dendritic cell vaccines are designed to stimulate a broad immune response without focusing on specific antigens. This approach leverages the natural ability of dendritic cells to present a wide array of antigens to T-cells, thereby activating a generalized immune response. Non-targeted vaccines are often used in early-stage research or when the specific antigens associated with a disease are not well-defined. They offer the advantage of potentially addressing multiple disease pathways simultaneously, but they may also lead to less precise immune activation, which can result in off-target effects or reduced efficacy. On the other hand, target-based dendritic cell vaccines are developed with a specific focus on known antigens associated with a particular disease, such as cancer-specific proteins or viral antigens. This targeted approach involves isolating dendritic cells from the patient, loading them with the specific antigens, and then reintroducing them into the patient's body. The goal is to elicit a strong and precise immune response against the targeted antigens, thereby enhancing the vaccine's effectiveness. Target-based vaccines are often used in cancer treatment, where the identification of tumor-specific antigens allows for a more focused attack on cancer cells. This approach can lead to improved outcomes, as the immune system is directed specifically towards the disease-causing cells, minimizing damage to healthy tissues. The development of target-based dendritic cell vaccines requires a deep understanding of the disease's molecular biology and the identification of suitable antigens. This process involves extensive research and collaboration between scientists, clinicians, and pharmaceutical companies. The precision of target-based vaccines makes them a promising option for personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to the individual characteristics of each patient's disease. However, the complexity of developing these vaccines, along with the need for personalized antigen identification, can lead to higher costs and longer development timelines. Both non-targeted and target-based approaches have their advantages and challenges. Non-targeted vaccines offer a broader application and can be developed more quickly, but they may lack the specificity needed for certain diseases. Target-based vaccines provide a more precise and potentially more effective treatment option, but they require significant research and development efforts. The choice between these approaches depends on various factors, including the nature of the disease, the availability of suitable antigens, and the specific goals of the treatment. In conclusion, the Global Dendritic Cell Vaccine Market encompasses both non-targeted and target-based strategies, each with its own set of benefits and limitations. As research continues to advance, the integration of these approaches may lead to more comprehensive and effective immunotherapy options. The ongoing exploration of dendritic cell vaccines highlights the potential for innovative treatments that harness the power of the immune system to combat complex diseases.
Covid-19, Cancer, Others in the Global Dendritic Cell Vaccine Market:
The Global Dendritic Cell Vaccine Market has shown promising potential in various areas, including the treatment of COVID-19, cancer, and other diseases. In the context of COVID-19, dendritic cell vaccines are being explored as a novel approach to enhance the immune response against the virus. By presenting viral antigens to the immune system, these vaccines aim to stimulate a robust and long-lasting immune response, potentially offering protection against current and future variants of the virus. The adaptability of dendritic cell vaccines makes them a valuable tool in the fight against pandemics, as they can be quickly modified to address emerging viral threats. In the realm of cancer treatment, dendritic cell vaccines have gained significant attention due to their ability to target tumor-specific antigens. Cancer cells often evade the immune system by downregulating antigen presentation or creating an immunosuppressive environment. Dendritic cell vaccines counteract these mechanisms by enhancing the presentation of tumor antigens and activating cytotoxic T-cells to attack cancer cells. This targeted approach has shown promise in treating various types of cancer, including melanoma, prostate cancer, and glioblastoma. Clinical trials have demonstrated the potential of dendritic cell vaccines to improve patient outcomes, particularly when used in combination with other therapies such as checkpoint inhibitors or chemotherapy. Beyond COVID-19 and cancer, dendritic cell vaccines are being investigated for their potential in treating other diseases, including infectious diseases and autoimmune disorders. In infectious diseases, these vaccines can be designed to present antigens from pathogens such as bacteria or viruses, thereby stimulating an immune response that can prevent or mitigate infection. In autoimmune disorders, dendritic cell vaccines may be used to induce tolerance to specific antigens, potentially reducing the severity of the immune response and alleviating symptoms. The versatility of dendritic cell vaccines lies in their ability to be customized for different diseases and patient populations. This adaptability is particularly important in the era of personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to the unique characteristics of each patient. The ongoing research and development in the Global Dendritic Cell Vaccine Market highlight the potential for these vaccines to revolutionize the treatment landscape for a wide range of diseases. As more clinical trials are conducted and regulatory approvals are obtained, the use of dendritic cell vaccines is expected to expand, offering new hope for patients with challenging medical conditions.
Global Dendritic Cell Vaccine Market Outlook:
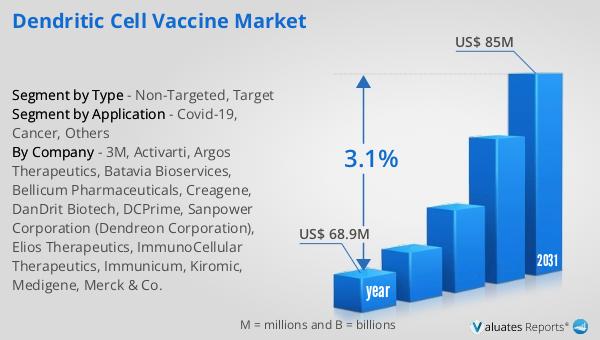
The global market for Dendritic Cell Vaccine was valued at $68.9 million in 2024 and is anticipated to grow to a revised size of $85 million by 2031, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.1% over the forecast period. In comparison, the global pharmaceutical market was valued at $1,475 billion in 2022, with an expected CAGR of 5% over the next six years. Meanwhile, the chemical drug market was projected to grow from $1,005 billion in 2018 to $1,094 billion in 2022. This data highlights the relatively modest size of the dendritic cell vaccine market compared to the broader pharmaceutical and chemical drug markets. However, the steady growth rate of the dendritic cell vaccine market underscores the increasing interest and investment in this innovative area of immunotherapy. As research and development efforts continue to advance, the potential for dendritic cell vaccines to address unmet medical needs and improve patient outcomes is becoming increasingly recognized. The market's growth is driven by factors such as the rising prevalence of cancer and infectious diseases, advancements in biotechnology, and a growing understanding of the immune system's complexities. Despite challenges such as high development costs and regulatory hurdles, the Global Dendritic Cell Vaccine Market holds promise for significant advancements in disease treatment and prevention.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Dendritic Cell Vaccine Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 68.9 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 85 million |
| CAGR | 3.1% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | 3M, Activarti, Argos Therapeutics, Batavia Bioservices, Bellicum Pharmaceuticals, Creagene, DanDrit Biotech, DCPrime, Sanpower Corporation (Dendreon Corporation), Elios Therapeutics, ImmunoCellular Therapeutics, Immunicum, Kiromic, Medigene, Merck & Co. |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |